Hemodynamics
Hemodynamics
ADHF
Pacemakers
A client in cardiogenic shock is receiving norepinephrine via continuous IV infusion. The nurse should titrate the medication based on which hemodynamic parameter?
A) Pulmonary artery pressure (PAP)
B) Mean arterial pressure (MAP)
C) Central venous pressure (CVP)
D) Mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO₂)
B) Mean arterial pressure (MAP)
- Rationale: Norepinephrine is a vasopressor used to maintain MAP ≥65 mmHg in shock. MAP is the most reliable indicator of organ perfusion.
Which of the following laboratory values would be most indicative of acute decompensated heart failure?
A) Serum sodium of 145 mEq/L
B) Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) of 950 pg/mL
C) Hemoglobin of 14 g/dL
D) Serum potassium of 3.9 mEq/L
Answer: B) Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) of 950 pg/mL
- Rationale: BNP is released when the ventricles are stretched due to fluid overload. A BNP level >100 pg/mL suggests heart failure, and levels >500 pg/mL indicate acute decompensation.
A client with symptomatic bradycardia is unresponsive to atropine. Which action should the nurse anticipate next?
A) Prepare for synchronized cardioversion
B) Initiate transcutaneous pacing
C) Administer IV adenosine
D) Increase IV fluid administration
Answer: B) Initiate transcutaneous pacing
- Rationale: If bradycardia is unresponsive to atropine, transcutaneous pacing provides temporary electrical stimulation until a permanent solution is implemented.
Which type of precautions are required for a client diagnosed with Ebola virus disease?
A) Standard precautions
B) Droplet precautions
C) Contact and airborne precautions
D) Only hand hygiene is necessary
Answer: C) Contact and airborne precautions
- Rationale: Ebola is transmitted via direct contact with bodily fluids, and airborne precautions may be needed for aerosol-generating procedures.
A nurse is caring for a patient with a central line catheter. Which action is the most important to prevent a central line-associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI)?
A) Changing the dressing only when visibly soiled
B) Using a sterile technique when changing the dressing
C) Administering antibiotics prophylactically
D) Replacing the catheter every 10 days
Answer: B) Using a sterile technique when changing the dressing
- Rationale: Strict sterile technique and chlorhexidine-based antisepsis reduce CLABSI risk.
Which of the following is a hallmark sign of hypoxemic respiratory failure?
A) PaCO₂ > 50 mmHg
B) PaO₂ < 60 mmHg despite oxygen therapy
C) SpO₂ > 95%
D) Respiratory alkalosis with normal PaO₂
Answer: B) PaO₂ < 60 mmHg despite oxygen therapy
- Rationale: Hypoxemic respiratory failure is defined as PaO₂ < 60 mmHg despite supplemental oxygen, often due to ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch, diffusion impairment, or shunting.
A client with a CVP of 20 mmHg, decreased urine output, and bilateral crackles is most likely experiencing:
A) Hypovolemia
B) Fluid overload
C) Right-sided heart failure
D) Pulmonary embolism
B) Fluid overload
- Rationale: High CVP (normal: 2-8 mmHg) with low urine output and pulmonary congestion indicates fluid overload.
A client with acute decompensated HF has a BP of 190/100 mmHg and severe dyspnea. Which pharmacologic intervention is most appropriate?
A) Administer IV furosemide
B) Give IV norepinephrine
C) Administer IV fluids
D) Start high-dose beta blockers
Answer: A) Administer IV furosemide
- Rationale: Loop diuretics (furosemide) reduce preload and pulmonary congestion by removing excess fluid.
Which of the following symptoms would indicate poor perfusion due to a conduction problem?
A) Increased urine output and hypertension
B) Flushed skin and bounding pulses
C) Confusion, hypotension, and dizziness
D) Bradypnea and hyperactive reflexes
Answer: C) Confusion, hypotension, and dizziness
- Rationale: Decreased perfusion from a conduction problem (e.g., bradycardia, heart block) leads to decreased cardiac output, causing altered mental status, hypotension, dizziness, and syncope.
- What is the primary treatment for botulism?
A) Supportive care only
B) Botulinum antitoxin
C) Broad-spectrum antibiotics
D) Antiviral therapy
Answer: B) Botulinum antitoxin
- Rationale: Botulinum antitoxin neutralizes circulating toxin but does not reverse nerve damage.
Which of the following factors increases the risk of health care-associated infections?
A) Strict adherence to hand hygiene
B) Inappropriate use of antibiotics
C) Use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
D) Routine disinfection of high-touch surfaces
Answer: B) Inappropriate use of antibiotics
- Rationale: Overuse or misuse of antibiotics contributes to antibiotic resistance, increasing the risk of MDRO infections.
A nurse is caring for a mechanically ventilated patient. Which action is most effective in preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)?
A) Keeping the head of the bed at least 30 degrees
B) Administering antibiotics prophylactically
C) Suctioning the patient every hour
D) Increasing sedation to prevent coughing
Answer: A) Keeping the head of the bed at least 30 degrees
- Rationale: Elevating the head of the bed (30-45°) prevents aspiration, reducing VAP risk.
A client’s hemodynamic values are as follows: CVP 2 mmHg, PAWP 5 mmHg, CO 3.5 L/min. What is the most likely clinical condition?
A) Left ventricular failure
B) Fluid overload
C) Hypovolemia
D) Cardiogenic shock
Answer: C) Hypovolemia
- Rationale: A low central venous pressure (CVP) and pulmonary artery wedge pressure (PAWP) indicate decreased preload, often due to fluid loss (hypovolemia). The low cardiac output (CO) suggests inadequate perfusion.
Which compensatory mechanism initially helps maintain cardiac output in heart failure but ultimately worsens the condition?
A) Decreased sympathetic nervous system activation
B) Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
C) Decreased preload due to diuresis
D) Decreased myocardial workload
Answer: B) Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
- Rationale: The RAAS system is activated in response to decreased renal perfusion, causing fluid retention, increased preload, and vasoconstriction, ultimately worsening heart failure.
Which of the following is the primary purpose of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)?
A) To pace the heart at a fixed rate
B) To prevent bradycardia
C) To detect and correct life-threatening dysrhythmias
D) To eliminate the need for anticoagulants
Answer: C) To detect and correct life-threatening dysrhythmias
- Rationale: An ICD monitors heart rhythm and delivers shocks or pacing stimuli for ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF).
- A nurse working in the emergency department notices a sudden increase in clients with unexplained fever, respiratory distress, and shock. What should the nurse suspect?
A) An isolated case of bacterial pneumonia
B) A community-acquired viral infection
C) A potential bioterrorism event
D) Foodborne botulism outbreak
Answer: C) A potential bioterrorism event
- Rationale: A sudden, unexplained outbreak of severe illness should raise suspicion for bioterrorism, especially if symptoms suggest exposure to airborne pathogens.
A patient is admitted with a MRSA bloodstream infection. What type of isolation precautions should the nurse implement?
A) Standard precautions only
B) Contact precautions
C) Droplet precautions
D) Airborne precautions
Answer: B) Contact precautions
- Rationale: MRSA is transmitted through direct/indirect contact, requiring gloves, gowns, and proper hand hygiene.
Which of the following interventions is most effective in improving oxygenation in ARDS?
A) Increasing tidal volume
B) Using low PEEP to prevent lung damage
C) Prone positioning
D) Administering bronchodilators only
Answer: C) Prone positioning
- Rationale: Prone positioning improves oxygenation by redistributing lung perfusion, improving alveolar recruitment, and reducing shunting, which is crucial in ARDS management.
A client with severe sepsis is undergoing hemodynamic monitoring. The nurse notes the following parameters: CO = 3.0 L/min, CVP = 4 mmHg, MAP = 55 mmHg, and SVR = 2,100 dynes/sec/cm⁵. Which intervention should the nurse anticipate?
A) Administer a fluid bolus
B) Initiate a vasodilator infusion
C) Prepare for emergent intubation
D) Increase diuretic therapy
A) Administer a fluid bolus
- Rationale: Septic shock often causes low CO and low CVP due to vasodilation and fluid leakage. Fluids help restore intravascular volume.
A client with decompensated heart failure is exhibiting signs of pulmonary congestion and decreased oxygen saturation. Which pathophysiologic process is responsible for these findings?
A) Increased right ventricular afterload
B) Left ventricular systolic dysfunction
C) Decreased systemic vascular resistance (SVR)
D) Increased cardiac output
Answer: B) Left ventricular systolic dysfunction
- Rationale: Left-sided heart failure results in decreased left ventricular contractility, leading to pulmonary congestion as blood backs up into the lungs, causing dyspnea, crackles, and hypoxia.
Which of the following cardiac dysrhythmias is most likely to require pacemaker therapy?
A) Atrial fibrillation with a ventricular rate of 100 bpm
B) Sinus bradycardia at 50 bpm with no symptoms
C) Third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block
D) Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) occurring twice per minute
Answer: C) Third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block
- Rationale: Third-degree AV block (complete heart block) results in no communication between the atria and ventricles, often requiring a pacemaker to maintain adequate cardiac output and perfusion.
- A client who may have been exposed to inhalational anthrax asks about treatment. What is the best response?
A) “You will receive supportive care only.”
B) “You will be treated with an antitoxin.”
C) “You will receive a 60-day course of ciprofloxacin or doxycycline.”
D) “There is no effective treatment available.”
Answer: C) “You will receive a 60-day course of ciprofloxacin or doxycycline.”
- Rationale: Post-exposure prophylaxis for inhalation anthrax includes a 60-day antibiotic course because spores can remain dormant.
Which infection prevention strategy is most effective in reducing catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTI)?
A) Administering antibiotics with every catheter placement
B) Replacing urinary catheters daily
C) Using indwelling urinary catheters only when necessary and removing them as soon as possible
D) Flushing urinary catheters with sterile saline every 6 hours
Answer: C) Using indwelling urinary catheters only when necessary and removing them as soon as possible
- Rationale: Minimizing catheter use and prompt removal reduces CAUTI risk.
- A client with ARDS is receiving mechanical ventilation. The nurse notes an FiO₂ of 100% and a PaO₂ of 50 mmHg. What should the nurse anticipate?
A) Increasing tidal volume
B) Prone positioning
C) Decreasing positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)
D) Discontinuing sedation
Answer: B) Prone positioning
- Rationale: A PaO₂ of 50 mmHg despite high FiO₂ indicates severe hypoxemia. Prone positioning improves lung recruitment and oxygenation.
A client has a blood pressure of 120/75 mmHg. What is the client’s mean arterial pressure (MAP)? Is this acceptable MAP?
(Formula: MAP = [(SBP + 2 × DBP) ÷ 3])
MAP = [(120 + (2 × 75)) ÷ 3] = [(120 + 150) ÷ 3] = 90 mmHg
- Rationale: MAP is the average pressure in the arteries, critical for organ perfusion (goal: ≥65 mmHg in critically ill clients).
Which of the following conditions increases the risk of compensated heart failure progressing to acute decompensated heart failure?
A) Regular exercise
B) Adherence to a low-sodium diet
C) Uncontrolled hypertension
D) Use of ACE inhibitors
Answer: C) Uncontrolled hypertension
- Rationale: Chronic hypertension increases afterload, forcing the heart to work harder. Over time, this leads to ventricular dysfunction and decompensation.
A nurse is reviewing telemetry for a client with a pacemaker. Which rhythm finding indicates that the pacemaker is failing to capture?
A) Pacing spikes with no associated QRS complexes
B) P waves occurring at a regular interval
C) QRS complexes occurring before pacing spikes
D) Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response
Answer: A) Pacing spikes with no associated QRS complexes
- Rationale: Failure to capture occurs when the pacemaker delivers an impulse (visible pacing spike) but does not generate a QRS complex, meaning the heart is not responding to pacing.
Which of the following is a hallmark clinical sign of botulism?
A) Hemorrhagic fever
B) Flaccid paralysis
C) Painful vesicular rash
D) Severe diarrhea
Answer: B) Flaccid paralysis
- Rationale: Botulism is caused by a neurotoxin that blocks acetylcholine release, leading to descending paralysis.
A patient undergoing weekly hemodialysis is diagnosed with a vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) infection. What is the most important infection prevention strategy in this case?
A) Administering broad-spectrum antibiotics
B) Using proper hand hygiene and contact precautions
C) Isolating the patient in a negative pressure room
D) Using airborne precautions
Answer: B) Using proper hand hygiene and contact precautions
- Rationale: VRE spreads via contact, so strict hand hygiene and contact precautions are required.
A client with acute respiratory failure has an ABG with the following values: pH 7.28, PaCO₂ 58 mmHg, PaO₂ 80 mmHg, and HCO₃ 26 mEq/L. What type of respiratory failure is present?
A) Hypoxemic respiratory failure
B) Hypercapnic respiratory failure
C) Mixed respiratory failure
D) Metabolic acidosis
Answer: B) Hypercapnic respiratory failure
- Rationale: Hypercapnic respiratory failure is defined as PaCO₂ > 50 mmHg with acidemia (pH < 7.35). This condition is caused by hypoventilation (e.g., COPD, neuromuscular disorders).
A client with decompensated heart failure has a cardiac output (CO) of 2.5 L/min. Which compensatory mechanism is most likely to occur?
A) Decreased heart rate
B) Increased urine output
C) Activation of the sympathetic nervous system
D) Decreased systemic vascular resistance (SVR)
C) Activation of the sympathetic nervous system
- Rationale: A low CO (normal: 4-8 L/min) triggers sympathetic activation, increasing heart rate and contractility to maintain perfusion. The body also retains fluid, leading to decreased urine output.
A nurse is caring for a client with decompensated right-sided heart failure. Which clinical finding is most consistent with this condition?
A) Pulmonary crackles and dyspnea
B) Jugular vein distention and peripheral edema
C) Frothy pink-tinged sputum
D) Orthopnea and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
Answer: B) Jugular vein distention and peripheral edema
- Rationale: Right-sided heart failure results in systemic venous congestion, leading to JVD, hepatomegaly, ascites, and peripheral edema.
A client with a new permanent pacemaker reports dizziness and feeling lightheaded. The nurse checks the telemetry monitor and notes a heart rate of 40 bpm despite the pacemaker being set at 70 bpm. What is the nurse’s priority action?
A) Administer oxygen at 2 L/min
B) Assess pacemaker function and notify the provider
C) Encourage the client to ambulate
D) Increase the client’s fluid intake
Answer: B) Assess pacemaker function and notify the provider
- Rationale: A pacemaker set at 70 bpm should prevent bradycardia. A heart rate of 40 bpm indicates pacemaker failure, requiring immediate evaluation.
A bioterrorism event involving smallpox would be identified by which characteristic symptom?
A) Sudden onset of sepsis
B) Widespread vesicular rash in the same stage of development
C) Bloody diarrhea and dehydration
D) Muscle rigidity and spasms
Answer: B) Widespread vesicular rash in the same stage of development
- Rationale: Smallpox causes a vesicular rash that progresses uniformly, unlike chickenpox, which has lesions in different stages.
- A nurse is collecting a wound culture for suspected MRSA. Which action is most important?
A) Swabbing the outer edge of the wound
B) Using sterile technique to collect a sample from deep within the wound
C) Collecting the specimen after starting antibiotics
D) Transporting the specimen at room temperature
Answer: B) Using sterile technique to collect a sample from deep within the wound
- Rationale: Sterile technique ensures an accurate culture without contamination.
Which noninvasive ventilation method is commonly used in hypercapnic respiratory failure?
A) High-flow nasal cannula
B) BiPAP
C) CPAP
D) Simple face mask
Answer: B) BiPAP
- Rationale: BiPAP provides inspiratory and expiratory pressure support, improving ventilation and CO₂ removal.
- A client with acute heart failure has a PAWP of 20 mmHg, CO of 3.0 L/min, and SVR of 1600 dynes/sec/cm⁵. Which medication would be most beneficial?
A) Dobutamine
B) Norepinephrine
C) Furosemide
D) Normal saline bolus
Answer: C) Furosemide
- Rationale: Elevated PAWP indicates fluid overload. Furosemide (a diuretic) reduces preload and pulmonary congestion.
A client with heart failure is prescribed digoxin. Which assessment is most critical before administering the medication?
A) Respiratory rate
B) Blood glucose level
C) Serum potassium level
D) Urine output
Answer: C) Serum potassium level
- Rationale: Low potassium (<3.5 mEq/L) increases the risk of digoxin toxicity, leading to arrhythmias, nausea, and vision changes.
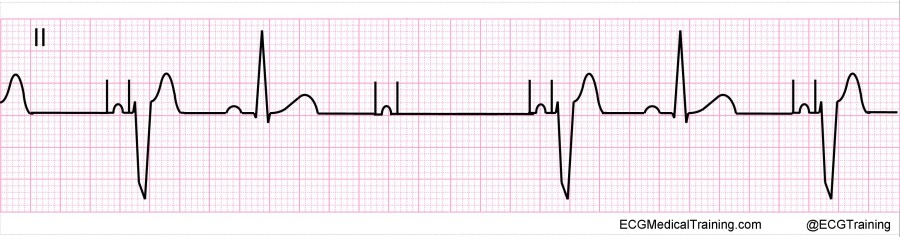 Interpret this EKG
Interpret this EKG
AV paced with loss of ventricular capture
- What is the first step in decontaminating a patient exposed to a chemical attack?
A) Administering IV fluids
B) Removing contaminated clothing
C) Applying topical antibiotics
D) Placing the patient in isolation
Answer: B) Removing contaminated clothing
- Rationale: Clothing removal eliminates 80-90% of contamination and prevents further exposure.
Which of the following is a goal of The Joint Commission’s National Patient Safety Goals regarding infection prevention?
A) To eliminate the need for antibiotic therapy
B) To reduce health care-associated infections through hand hygiene and evidence-based guidelines
C) To reduce hospital costs by limiting isolation precautions
D) To require all patients to receive prophylactic antibiotics upon admission
Answer: B) To reduce health care-associated infections through hand hygiene and evidence-based guidelines
- Rationale: The Joint Commission's National Patient Safety Goal #5 focuses on hand hygiene, infection control, and HAI prevention.
A client with COPD and chronic hypercapnia presents with increased confusion and PaCO₂ of 65 mmHg. What intervention is most appropriate?
A) Start noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (BiPAP)
B) Administer high-flow oxygen at 10 L/min
C) Restrict fluid intake
D) Give a bronchodilator only
Answer: A) Start noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (BiPAP)
- Rationale: BiPAP supports ventilation, reducing PaCO₂ and preventing intubation in hypercapnic respiratory failure.