What is the mechanism of Noncompetitive Enzyme inhibition?
a. The inhibitor binds to the allosteric site
b. The inhibitor competes with substrates for active site.
c. Inhibitor binds only to enzyme-substrate complex
d. The Inhibitors have high affinity and causes permanent enzyme inactivation
a. The inhibitor binds to the allosteric site
How long do Erythrocytes normally survive in circulation?
120 days
innervation of the anterior compartment of the arm?
innervation of the posterior compartment?
Musculocutaneous nerve; radial nerve
Maxillary 1st premolar calcification timeline?
1.5-2 years
Two proteins associated with lipid bilayer?
transmembrane and peripheral
What is a characteristic feature of Eosinophils? are they granular or agranular?
they have a Bilobed nucleus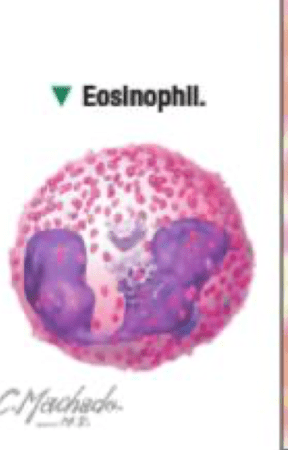
What nerve inervates the Serratus Anterior Muscle?
a. Dorsal Scapular Nerve
b. Thoracodorsal N.
c. Long Thoracic N.
d. Musculocutaneous N.
C. Long thoracic nerve
Mandibular 2nd premolar calcification timeline?
2-2.5 years
what is the black arrow pointing to? what is the RO section surrounding it?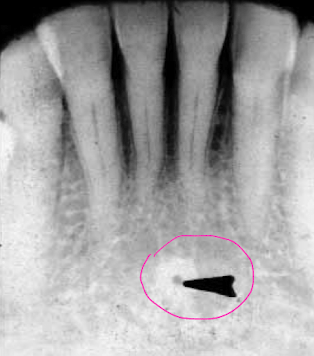
Lingual Foramen; genial tubercle
Which type of transport requires ATP hydrolysis?
A. Simple diffusion
B. Facilitated diffusion
C.Primary active transport
D. Osmosis
C: Primary active transport
Which formed element of the blood arises from megakaryocytes?
platelets
Three major components of the cubital fossa?
TAN- Tendon of biceps brachii, Brachial Artery, Median Nerve
Compared to maxillary canines, mandibular canines have:
A) A more developed lingual surface
B) A sharper cusp
C) Less convex labial surface
D) Longer roots
Identify each structure associated with each color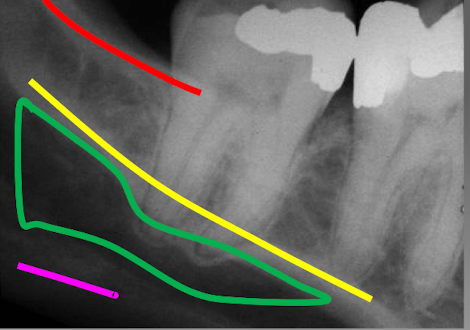
red: external oblique ridge
yellow: Mylohyoid (internal oblique) ridge
Green: submandibular fossa
Pink: Inferior border of mandible
The energy that must be supplied for molecules to react with one another is called the ___?
activation energy
Lymphoid Structures derive embryonically from?
Mesoderm
What nerve inervates the Pectoralis Major Muscle?
a. Medial Pectoral Nerve
b. Medial Brachial Cutaneous Nerve
c. Lateral Pectoral Nerve
d. Medial and Lateral Pectoral Nerve
D. Medial and Lateral Pectoral nerve
The mandibular canine usually erupts at:
A) 6–7 years
B) 9–10 years
C) 11–12 years
D) 12–14 years
B) 9-10 years
Identify this structure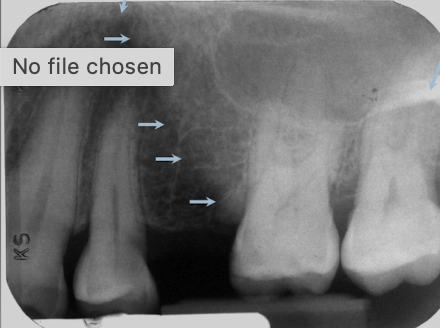
Naso-labial fold
What disease is related to the Post-Traslation Modification: Hydroxylation and is characterized by “elastic skin”
a. Marfan’s Syndrome
b. Williams Syndrome
c. Ehler’s Danlos Syndrome
d. Hurler Syndrome
Ehler's Danlos Syndrome
What type of epithelium makes up the endothelium (internally lines the system) of the cardiovascular system?
Which roots of the brachial plexus contribute to the long thoracic nerve?
C5, C6, C7
The mandibular canine usually erupts at:
A) 6–7 years
B) 9–10 years
C) 11–12 years
D) 12–14 years
Identify each structure with their assigned pictures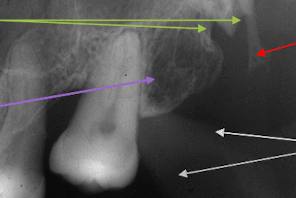
Green: lateral pterygoid plate
Purple: Tuberosity of maxillla
Red: Hamular process
Gray: Coronoid process
Which Enzyme catalyzes lysis of a substrate by breaking bonds or generating double bonds between the products?
a. Oxidoreductases b. Translocases c. Lyases d. Ligases
C. Lyases
what is the structure that joins myocardial cells end to end and side to side?
Intercalated discs
What nerve innervates the Teres Major Muscle?
a. Lower subscapular N.
b. Upper Subscapular N.
c. Radial N.
d. Median N.
A. Lower subscapular nerve
Which characteristic best distinguishes mandibular from maxillary canines?
A) Mandibular crown is wider mesiodistally
B) Mandibular lingual surface is less developed
C) Mandibular root is always longer
D) Mandibular cingulum is more prominent
B) Mandibular lingual surface is less developed – Key difference.
what is the definition of "quality" when discussing an x-ray beam? How about quantity?
the energy of the beam; # of x-rays produced
An increased enzyme concentration (increase/decreases) the rate of a reaction?
Increases
Which granulocyte on a slide has 'Mickey mouse ear' shaped nuclei
neutrophils
What is the motor innervation of the Median Nerve?
LOAF Muscles of the hand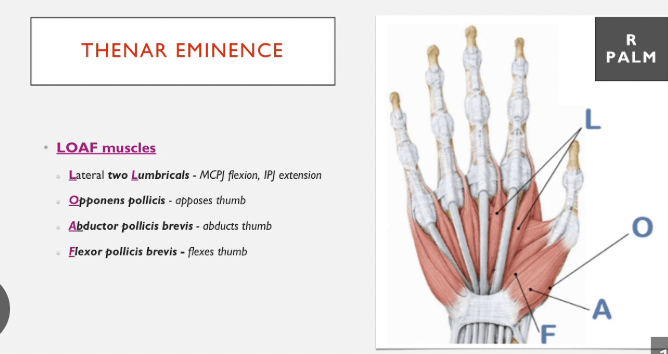
Which cusps are generally equal in size on mandibular molars?
A. Mesiobuccal and distobuccal
B. Lingual cusps
C. Buccal cusps
D. Distal cusps
B) Lingual Cusps
Describe the Inverse Square Law
intensity of radiation is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of radiation.
What happens to the Km and Vmax during Competitive inhibition?
Km Increases, Vmax remains unchanged
Which part in the lymphatic system reaches its maximum size during puberty and contains Lamellar centers known as Hassall corpuscles
Thymus
Origins and insertion of the Biceps brachii
Long head: Supraglenoid tubercle on superior border of scapula
Short head: Coracoid process of scapular
Insertion: both converge at the radial tuberosity of the radius
. A patient presents with pain in an impacted mandibular molar. Which tooth is most likely involved?
A. Mandibular first molar
B. Mandibular second molar
C. Mandibular third molar
D. Mandibular premolar
C mandibular third molar
What are the two factors that influence quality of the x-ray beam?
kVp: increases or decreases mean energy
Filtration: takes out low energy bean and makes beam higher energy
What are Microvilli composed of? Cilia?
Microvilli: actin filaments
Cilia: microtubules
What kind of tissues lines the pharyngeal tonsils?
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Where is the humerus most commonly fractured? What can often be damaged by these types of fractures?
Surgical neck is common site of fractures; axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery wrap around site
Which constant feature is observed in mandibular third molars?
A. BL dimension is greater than MD dimension
B. MD dimension is greater than BL dimension
C. Roots are always separate and divergent
D. Occlusal design is symmetrical
B.
MD dimension is greater than BL dimension
mA --> more x-rays
kVp --> higher energy x-rays
time --> more x-rays
Which vesicular coat assists in transport from the plasma membrane to golgi apparatus
Clathrin coat
Which capillary has a wide and irregular lumen, highly specialized and, there lacks a basement membrane?
Sinusoidal capillary
Draw the brachial plexus from memory!
Person who draws it the closest gets the point.
Which statement is TRUE about mandibular third molars?
A. They are the largest of mandibular molars
B. They are frequently impacted
C. They always have 5 cusps
D. They usually erupt before premolars
B. they are frequently impacted
What are x-ray beams composed of? What is their mass and charge?
they are made up photons, and have no mass and no charge
What is the function of SarI?
responsible for assembly the COPII coat
Which valve connects the right atrium to the right ventricle?
Tricuspid Valve
Which nerve innervates the triceps brachii?
radial nerve
Typical eruption age of mandibular third molars is:
A. 6–7 years
B. 11–13 years
C. 17–21 years
D. 25–30 years
C. Mandibular 3rd molars
When the high-speed electrons hit the anode/target, they create photons by two types of radiation. What are those two types?
Characteristic and Braking/Bremsstrahlung