Hermione is trying to teach Ron how to cast a spell, the “Wingardium Leviosa”. When Hermione is saying it with him, he nails the pronunciation. But when she’s not leading him, he pronounces it wrong and isn’t able to cast the spell. What concept does Ron’s level of ability illustrate, and what action is Hermione engaging in when she helps Ron cast the spell?
a) scaffolding and zone of proximal development
b)zone of proximal development and scaffolding
c)theory of cognitive development and scaffolding
d)scaffolding and theory of cognitive development
Julia Baima, 2025
 b)
b)
Regina’s mom, Mrs. George wants to be the “cool mom”. She never says no to Regina and praises all of her actions, even if they are morally questionable.
According to Baumrind’s parenting styles, Mrs. George is:
a)authoritarian
b)uninvolved
c)permissive
d)authoritative
Julia Baima, 2025
c)
During a foggy night, a lifeguard at the beach is scanning for distress signals. Suddenly, he thinks he sees someone waving for help, but when he investigates, no one is there. This is an example of:
Miss
Hit
False Alarm
Correct rejection
Janvi Mehta (2025)
Explanation!
- Option C is the right answer as a false alarm occurs when a signal is detected even though it is not actually present.
- Option A happens when a real signal is present, but it is not detected. In this case, there was no real signal.
- Option B happens when a real signal is present and is correctly detected.
- Option D happens when there is no signal, and the person correctly recognizes that no signal is present.
In Pavlov's experiments, the tone/bell is the:
- conditioned response
- conditioned stimulus
- unconditioned response
- unconditioned stimulus
Claude AI, 2025
2.
A student studies late at night under bright artificial light and then struggles to fall asleep.Which brain region is sensitive to light?
Hippocampus
Frontal lobe
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
Basal ganglia
Janvi Mehta, 2025
Explanation:
c)
Suprachiasmatic nucleus, present in the hypothalamus, which is sensitive to light directs the pineal gland to release melatonin.
Hippocampus helps with memory formation, so not relevant here.
Frontal lobe is responsible for planning, thinking, intelligence. So it is not relevant here.
Basal ganglia is also not relevant here since it is involved in motor control.
According to Harlow, what is most important factor for infant attachment?
a. Food
b. Soft contact
c. Cloth
d. Genetics
Credit:Jun Gesteland (2025)
According to Harlow, what is most important
factor for infant attachment?
a. Food
In Harlow’s study, the monkeys went to the soft-cloth mother (no food)
instead of the food-providing wire mother.
b. Soft contact
In Harlow’s study, the monkeys went to the soft-cloth mother (no food)
instead of the food-providing wire mother.
c. Cloth
This is specific to the monkey study. Soft contact (i.e. skin) is more applicable to humans.
d. Genetics
This is irrelevant to Harlow’s study.
A child is told that there are pennies inside a box with a “green crayons” label. If they have not developed the theory of mind, how would they answer the question,
“What would another child think is inside the box?”
a. Green crayons
b. Nothing
c. Band-Aids
d. Cat
e. Pennies
Jun Gesteland (2025)
Green crayons
The theory of mind is understanding others’ perspectives. Another child who does not know about the pennies would assume there are green crayons inside the box because of the label.
b. Nothing
The box is labeled “green crayons,” so a child would naturally think there are green crayons inside.
c. Band-Aids
Band-Aids are not mentioned.
d. Cat
=^..^=
e. Pennies
A child who cannot understand others perspectives would assume everyone sees the world the same way as they do.
A doctor reviews a patient’s bloodwork and notices an unusual result but decides it’s probably not serious and sends the patient home. Months later, the patient is hospitalized with a serious illness, and the doctor deeply regrets their decision.
What type of error did the doctor make, and what is the doctor most likely to do in the future?
He displayed a ____. In the future, the doctor is most likely to display___.. Fill in the blanks:
Miss; false alarm
Miss; correct rejection
False alarm; miss
Correct rejection; false alarm
Julia Baima (2025)
a) Key word: Overcompensate
Overcompensation -> Response bias
Every time you visit your grandmother, she bakes cookies, and the smell makes you feel happy. Now, just arriving at her house makes you feel happy. The unconditioned response in this scenario is:
- arriving at grandmother's house
- feeling happy to the smell of cookies
- the smell of cookies
- feeling happy when arriving at the house
Claude AI, 2025
1.
Austin is sleeping but is awakened by a sudden involuntary jerk. Which stage of the sleep cycle is he in?
N3
N2
N1
REM
Janvi Mehta, 2025
c)
Explanation:
In N1 stage of sleep cycle, the person is in light sleep and this stage is often characterised by hypnic jerks or hypnagogic hallucinations. (Key word: sudden and involuntary jerk)
In N2 stage of the sleep cycle, the brain activity slows down along with reductions in heart rate and muscle tension
In N3 stage of the sleep cycle, the brain activity further slows down, it is difficult to wake a person up and growth hormones are released
REM ( rapid eye movement) is the stage where the brain waves would resemble wakefulness know as paradoxical sleep. In this stage you would experience dreams or sometimes sleep paralysis.
Anna, a 19-year-old who is popular and has many friends, believes she will always have a large social circle because it's part of her personality. However, her mother tells her that as she gets older, she won't have as many friends and should focus on her closest ones.
What is the most likely reason for her mother’s advice?
a) As people get older, the zones of proximal development get smaller.
b) As people get older, they tend to have more surface-level relationships.
c) As people get older, they usually have a smaller group of close friends with strong bonds.
d) As people get older, their social skills tend to decline.
Julia Baima (2025)
c) Socioemotinal selectivity theory
Sarah is a child with a secure attachment style, what characteristic will she show?
Avoid their caregiver upon return after separation
Be distressed when their caregiver leaves but comforted upon return
Be indifferent to their caregiver’s departure and return
Show intense distress even after the caregiver returns
Janvi Mehta (2025)
B is the right answer as it is the characteristic of secure attachment.
- Option A describes an Insecure avoidant attachment style as the child does not react to the arrival of the caregiver.
- Option c describes an avoidant attachment style
- Option D describes an insecure-anxious/ambivalent attachment style
The tendency to see the circles forming a diamond shape is an example of what grouping principle?
a. Proximity
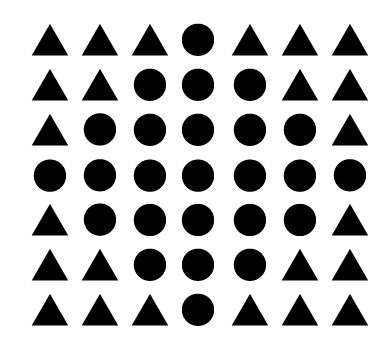
b. Similarity
c. Continuity
d. Closure
Jun Gesteland (2025)
The tendency to see the circles forming a diamond shape
is an example of what grouping principle?
a. Proximity
Incorrect because all shapes are spread out evenly.
b. Similarity
The circles, which are exact replicas of each other, create the illusion
of the diamond because of the contrast with the triangles.
c. Continuity
Nothing in the image suggests the presence of a continuous line/shape.
d. Closure
Closure is seeing an incomplete figure as complete, which
is not applicable here. This would be an example of closure:
In Pavlov's experiment, the dogs' salivation following the tone is_
and the dogs' salivation follwoing the the food is _
conditioned response, unconditioned response
Sakamoto-san dreams of discovering an infinite fish glitch. According to the activation synthesis theory, his dream stems from what?
a need for brain stimulation
random brain activity
his unconscious desire for fish
his dinner from last night, which consisted of fish
Jun Gesteland, 2025
a)This is the preserving neural pathways theory of dreams
b)random brain activity during sleep -cprrect
c) his unconscious desire for fish
This is Freudian theory of dreams
d) his dinner from last night, which consisted of fish
This is the information processing theory of dreams, which states that dreams form from memories of events
Lily is 2 years old, and she loves horses. One day, she sees a unicorn on a kids TV program. She identifies the horse-like features, points and says “pretty horse”. Her mom says she’s wrong, and that is a unicorn, horses don’t have horns. Now, whenever she sees a picture of a unicorn, she can differentiate it from a horse.
What were the two processes that occurred in the little girl’s mind, according to Piaget?
a)assimilation, then accommodation
b)accomodation, then assimilation
Julia Baima (2025)
Jade believes her dolls need to eat with her to stay healthy. Which characteristic and stage of Piaget’s Cognitive Theory does this represent?
Egocentric, Preoperational
Object Permanence, Sensorimotor
Animistic Thinking, Preoperational
Conservation, Concrete Operational
Janvi Mehta (2025)
Explanation!
-Option C is right as Animistic thinking is when children believe inanimate objects, like dolls, have thoughts and emotions. This is a characteristic of the preoperational stage.
- Option A refers to the inability to take another person's perspective
- Option B is the understanding that objects continue to exist even when out of sight, which is not relevant in this case.
- Option D Conservation is the understanding that quantity remains the same despite changes in shape or appearance, which occurs in the concrete operational stage, not preoperational.
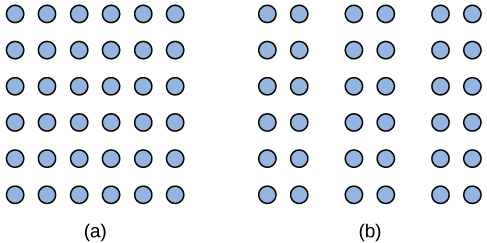 Mio sees one block of circles in image 1 and three columns of circles in image 2 because of what grouping principle?
Mio sees one block of circles in image 1 and three columns of circles in image 2 because of what grouping principle?
Continuity
Similarity
Proximity
Closure
Jun Gesteland, 2025
Continuity
There is no continuous line/shape that is cut off.
Similarity
All of the stimuli (circles)are the same, so similarity is not why your brain groups the dots into 3 columns in image 2
3. Proximity
The gaps make your brain separate the dots into columns.
4. Closure
Closure is when we perceive incomplete figures as complete. There is no incomplete figure in image 1 or 2.
When Ethan’s mom asks him to wash his plate, he does so to avoid losing TV time at the end of the day. When his oldest sibling, Layla, is asked to wash her plate, she does so because she believes it’s important to help her family with chores. When his brother George is asked to wash his plate, he does so because he believes following his parents' rules is the right thing to do.
According to Kohlberg’s theory of moral development, what stage is each child in, respectively?
a) preconventional, conventional, postconventional
b) conventional, preconventional, postconventional
c) preconventional, postconventional, conventional
d) postconventional, preconventional, conventional
Julia Baima (2025)
c)
Set of principles and personal beliefs -> postconventional
Punishment -> preconventional
Law and order -> conventional
Ask yourself: they’re making this moral decision mainly based on what?
Reed lacks purpose and feels like life is meaningless. They are experiencing the ___ aspect of the _______ stage.
generativity; generativity vs. stagnation
stagnation; generativity vs. stagnation
ego integrity; integrity vs. despair
4. despair; integrity vs. despair
Jun Gesteland, 2025
generativity; generativity vs. stagnation
Midlife; Generativity is generating things to contribute to future generations.
stagnation; generativity vs. stagnation- correct
Midlife; Stagnation is lacking purpose and seeing life as meaningless. Think, “stagnant,” which means, “no activity.”
ego integrity; integrity vs. despair
Late life; ego integrity is, upon reflection, feeling like one’s life had coherence & purpose.
despair; integrity vs. despair
Late life; despair in this context means regret. Reed is not regretting anything.