3,000 CA growers produce what percent of raisins?
what is 100%?
What is a Poaceae seed called? And what nutrients are its endosperm and SINGLE cotyledon rich in?
What is a Caryopsis?
What is the endosperm stores the complex carbohydrate – starch and some protein?
What is the single cotyledon stores oils and proteins?
Define Glucosinolates.
Define a gamete.
What is a reproductive cell of an animal or plant? female gametes are called ova or egg cells, and male gametes are called sperm.
what type of fruit do asparagus form?
What is a berry?
What is ethanolic fermentation?
what is a reaction done by yeast/fungi that convert starch to glucose to ethanol?
Describe Domestication Syndrome?
What is a suite of behavioral and morphological characteristics consistently observed in domesticated populations?
Explain how plants are not affected by the toxin nature of glucosinolate break-down molecules.
What is the production/biosynthesis of glucosinolates and the enzyme that breaks it down are cell-type specific?
Explain the difference between haploid and diploid.
What is haploid refers to the presence of a single set of chromosomes such as in gametes? Fertilized eggs and somatic cells are diploid (having two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent).
Which part of the asparagus plant are modified stems? the shoots or the crown?
What is both?
What feedstock compounds were used in 1st generation biofuels and 2nd generation feedstocks?
What is starch and cellulose to ethanol, respectively?
Describe nixtamalization's importance?
What is nixtamalization releases essential Vit.B3, niacin, from starch making it biological available.
What type of receptor, touch or taste, perceive capsaicin?
What is a touch receptor?
Define breeding true.
What is progeny look like their parents?
How many copies of every gene does a diploid organisms have?
What is 2 copies of every gene?
Name the three classes of angiosperms.
What is Magnoliids, Eudicots, and Monocots?
Define the Columbian exchange.
What is the exchang of plants/animals/diseaese to and from the Old World to the New World?
Define a phenotypic trait and give one example.
What is an obvious and observable trait?
What is the central dogma?
What is DNA to RNA to proteins?
Which phenotypic trait segregates as a Mendelian trait? the production of asparagus odor or the ability to smell the asparagus odor?
What is the ability to smell asparagus odor?
Why did we move away from 1st generation biofuel crops?
What is diversion of food crops lead to food insecurity?
Define Center of Origin and how it relates to Center of Diversity.
What is Centers of Crop Origin are where
domestication events occurred?
What is Centers of diversity are where wild relatives of a crop grow? Sometimes were are the same place, but sometimes the wild progenitor moves and then becomes domesticated.
Define a genetic bottleneck.
What is an event in which there is a major loss in biodiversity of a population? After these events, there is less trait/gene diversity.
define a dominant allele.
What is an allele that produces a dominant phenotype in a heterozygote (F1 generation = the offspring of an outcross from two different true breeding/homozygous plants)?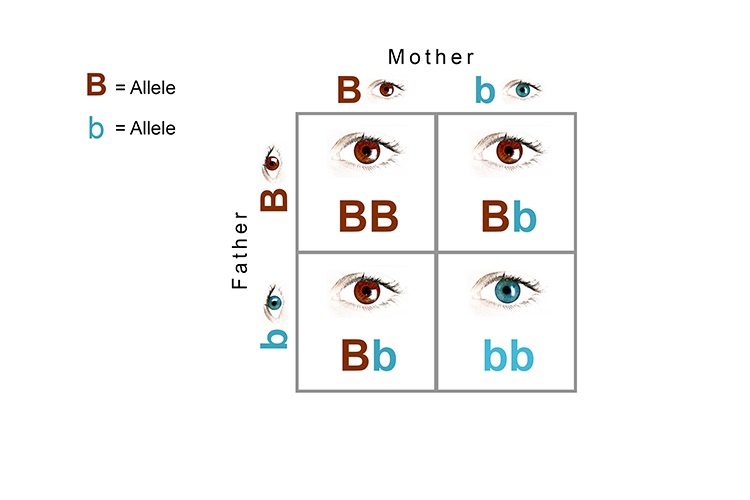
What made Mendel's experiments successful?
What is:
He picked peas as his model system: peas are annuals so many experiments could be done throughout the year
He developed true breeding lines used a large number of plants and stats?