The largest muscle in the body.
What is the gluteus maximus?

What is the humerus?
The most superficial layer of the skin. (Don't overcomplicate it)
What is the epidermis?
The lowest part of the brain, made up of the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain.
What is the brain stem?
What is a mixed nerve?
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Subscapularis, and ...
What is the teres minor?
The part of the bone that you can palpate on your hip.
What is the greater trochanter of the femur?
The layer of the epidermis only present in thick skin.
What is the stratum lucidum?
Functions in the coordination of skeletal muscle contractions, and maintenance of normal muscle tone, posture, and balance. :background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14006/gb3g875wc16BYZDIAP6c7g_Cerebellum_1.png)
Innervates the pectoral girdle and upper limb, with contributions from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-T1.
What is the brachial plexus?
The muscle that functions in elevating your upper lip.
What is the levator labii superioris?
The structure that sticks out of the back of the vertebrae. You can palpate this on your own back.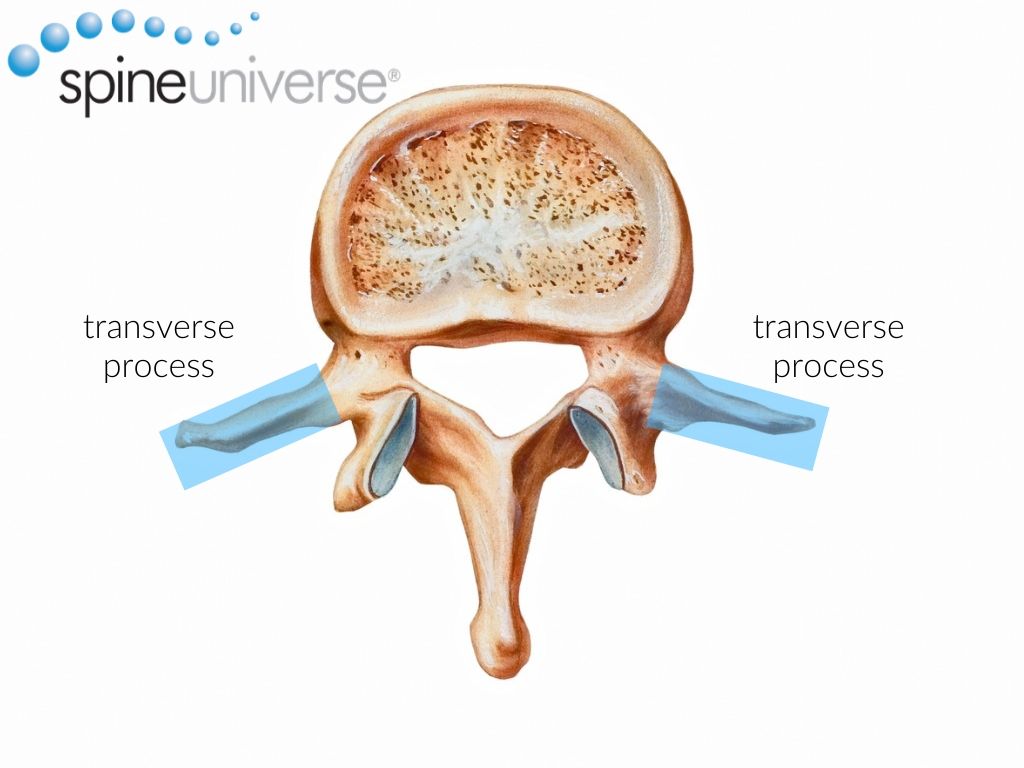
The deepest layer of the dermis, composed of collagen and course elastic fibers, adipose cells, hair follicles, nerves, and sebaceous and sudoriferous glands.
What is the reticular layer?
Connects the lateral ventricles to the 3rd ventricle.
What is the interventricular foramen?
Origin is C5-T1, and arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.
What is the radial nerve?
The second F in PFPF of the superficial flexor muscles of the forearm.
What is the Flexor Carpi Ulnaris?
Articulates with the head of the humerus and forms the shoulder joint.
What is the glenoid cavity?
The type of sweat gland that empties into a hair follicle.
What is an apocrine gland?
The cranial nerve responsible for the muscles of mastication and touch and pain in the skin of face, in nose, sinuses, mouth, and anterior tongue.
What is the trigeminal cranial nerve?
The nerve that descends in the posterior compartment of the leg and passes posterior to the medial malleolus.
What is the tibial nerve?
The ischial tuberosity function.
What is the origin for all three hamstring muscles? (Accept Biceps Femoris, Semimembranosis, Semitendinosis)
The bone that is "Home" in the mnemonic for the carpal bones, it articulates with the 4th and 5th metacarpals.
What is the hamate?
The type of receptor that is located in the papillary dermis, and detects touch.
What is a Meissner's Corpuscle?
Testing gag reflex, ability to swallow, and touch/pain of the posterior tongue and pharynx.
What is the test for the glossopharyngeal nerve?
This nerve passes superficial to the neck of the fibula, where it is subcutaneous and vulnerable to injury.