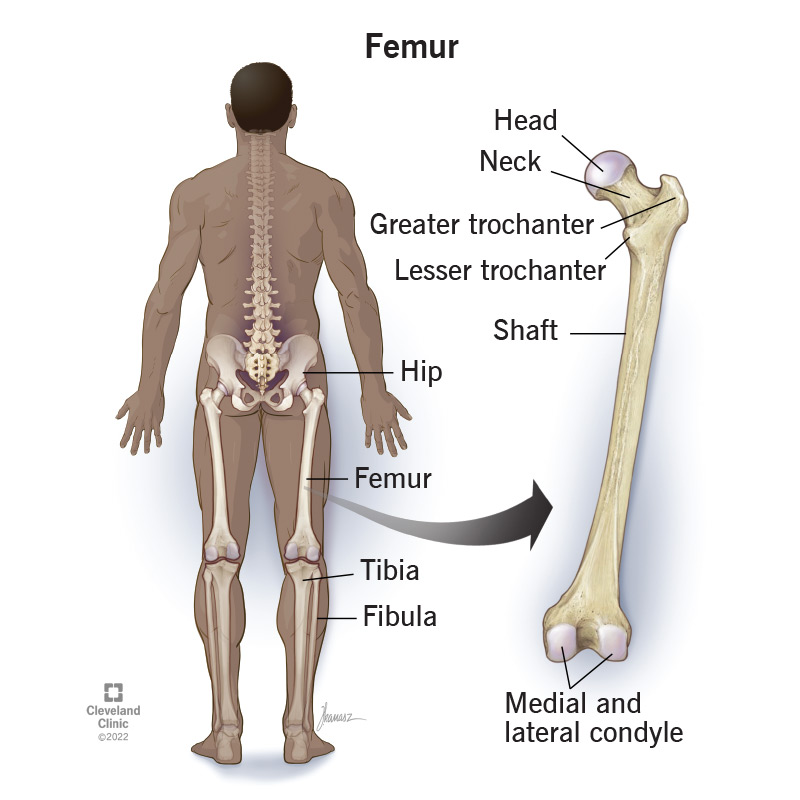
What is the longest bone in the body?
The femur
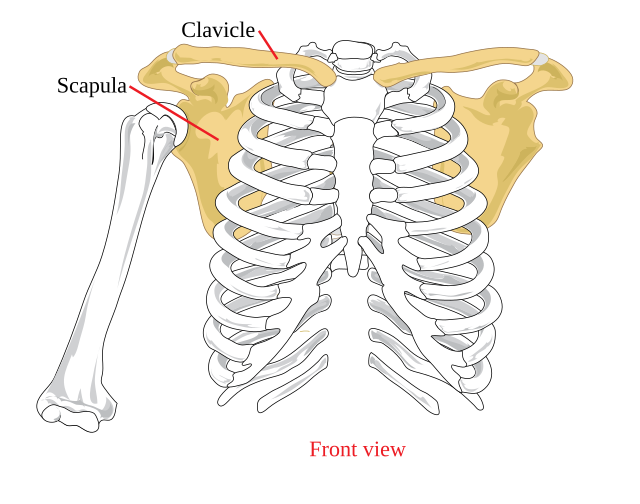
The Pectoral Girdle consists of these 2 bones
Scapula and Clavicle
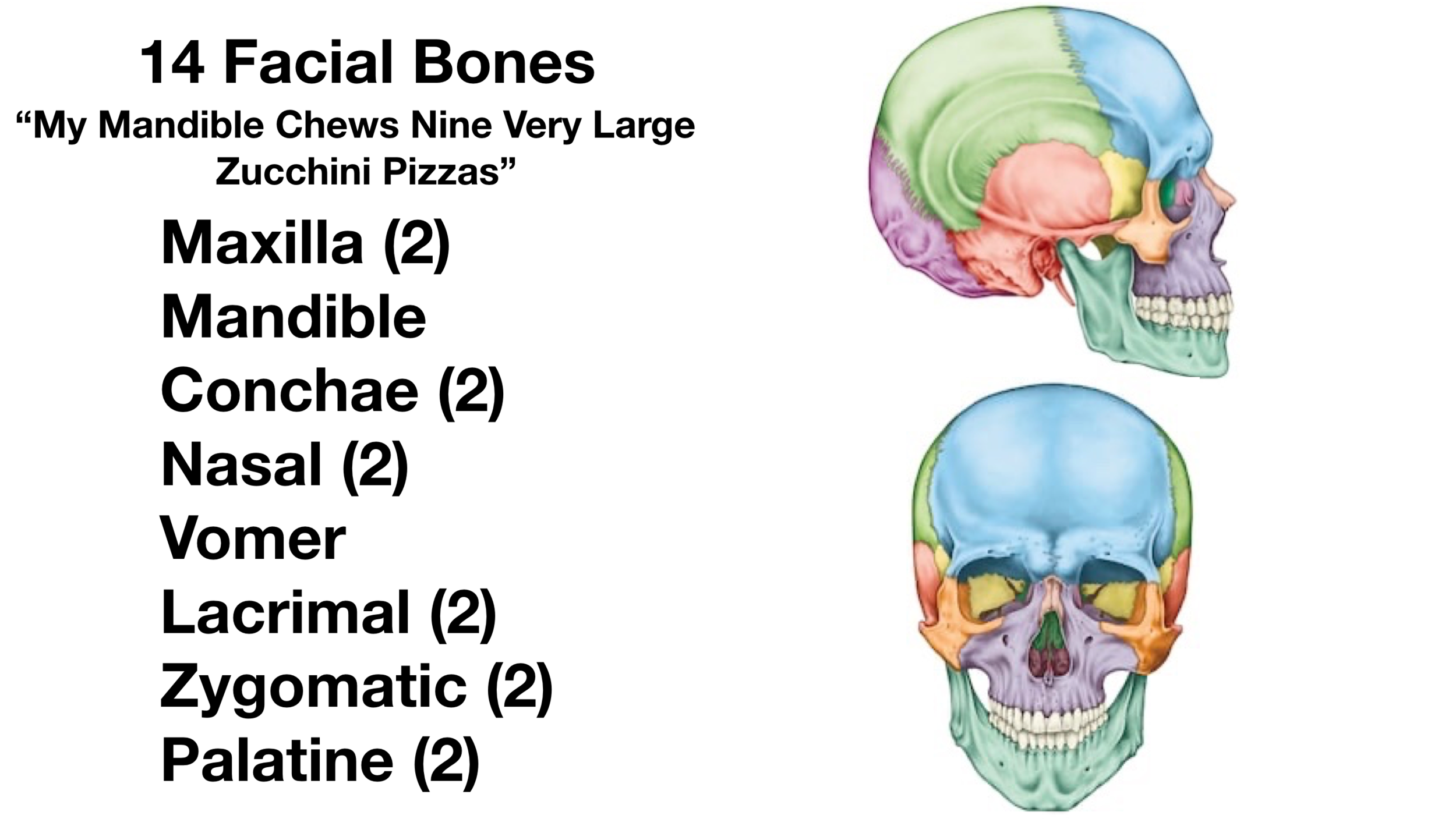
How many facial bones are there
14
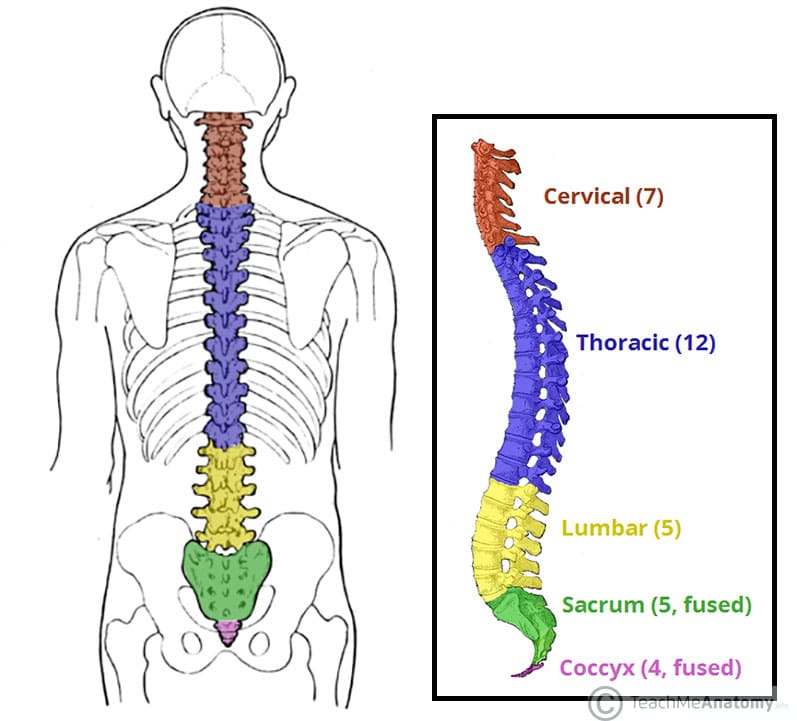
How many cervical, how many thoracic, and how many lumbar vertebrae are there?
7, 12, and 5
Another name for the heel
Calcaneus

ABduction = Away from the body

This condyle of the humerus articulates with the ulna.
Trochlea

What is the only point of connection between the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton?
The clavicle
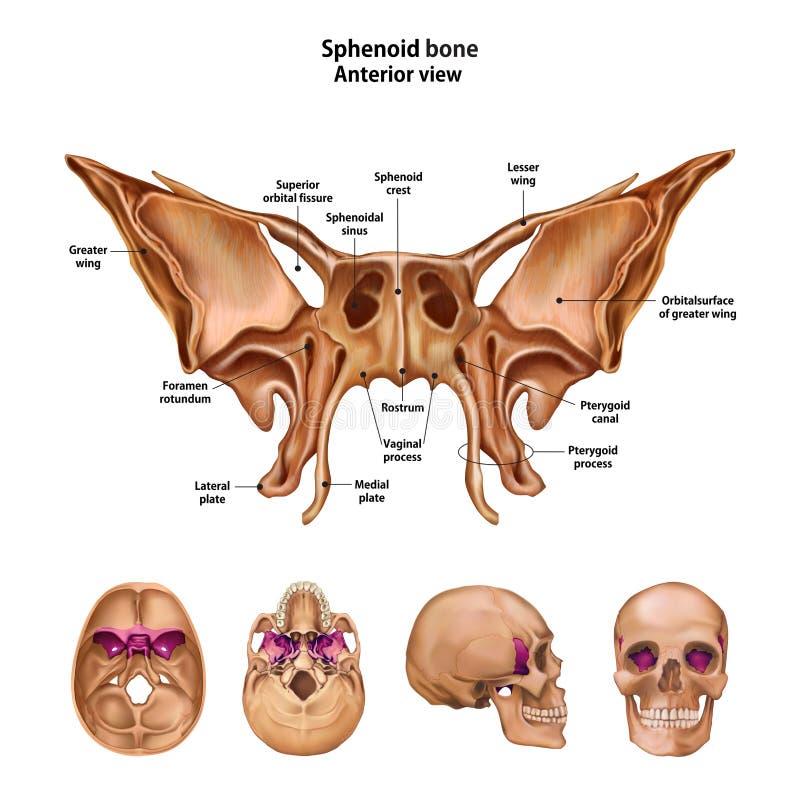
This cranial bone looks similar to a bat with open wings
Sphenoid Bone
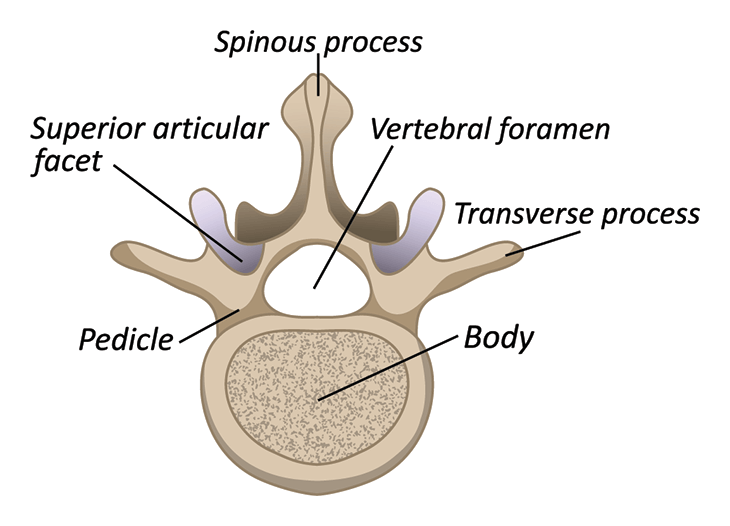
When you feel your spine on your back, what you're really feeling are the _______ ________ of your vertebrae.
Spinous Processes
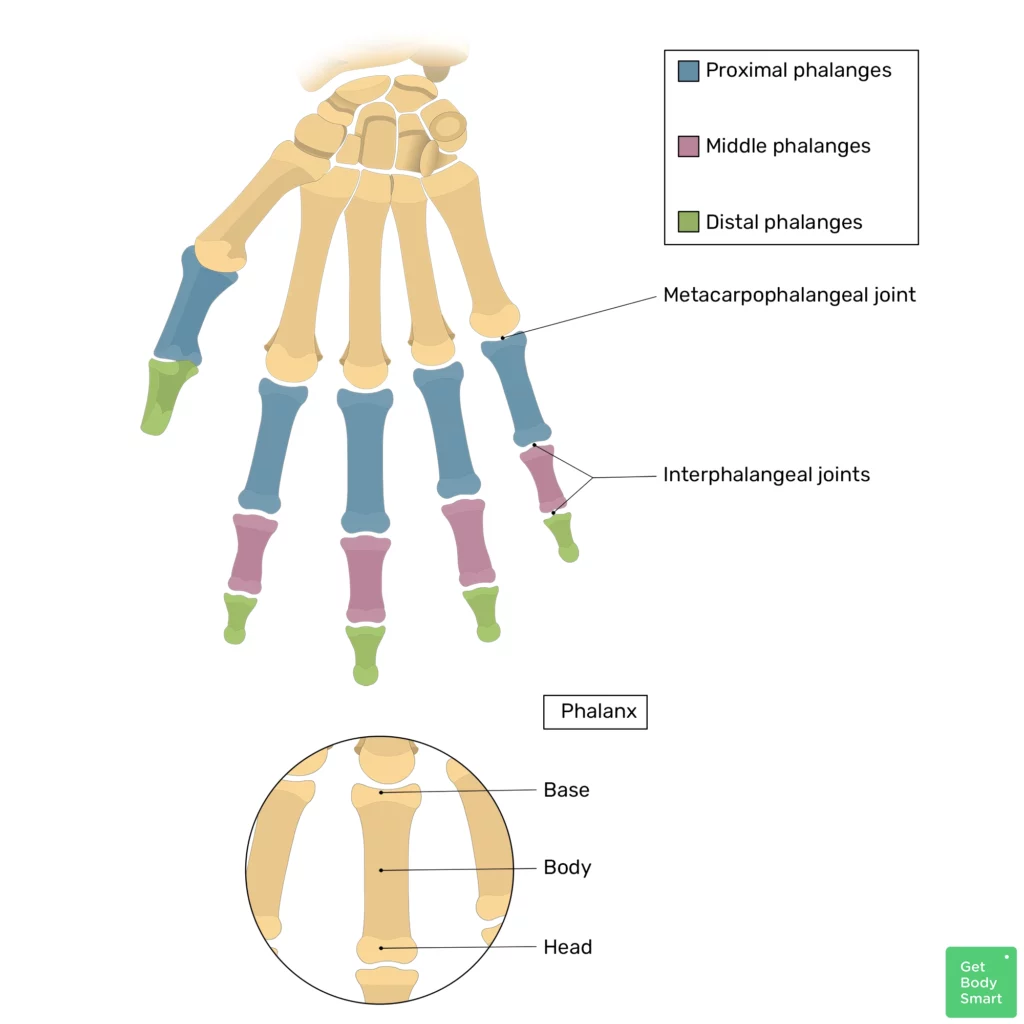
How many phalanges are in each hand or foot?
14
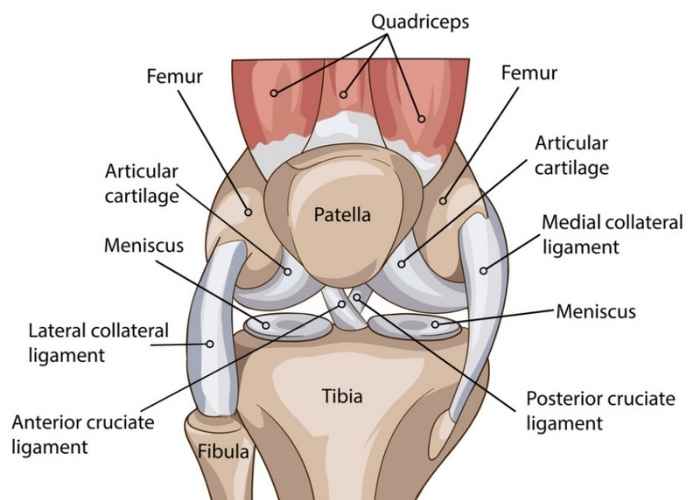
The fibular collateral ligament (FCL) is (medial/lateral)
Lateral
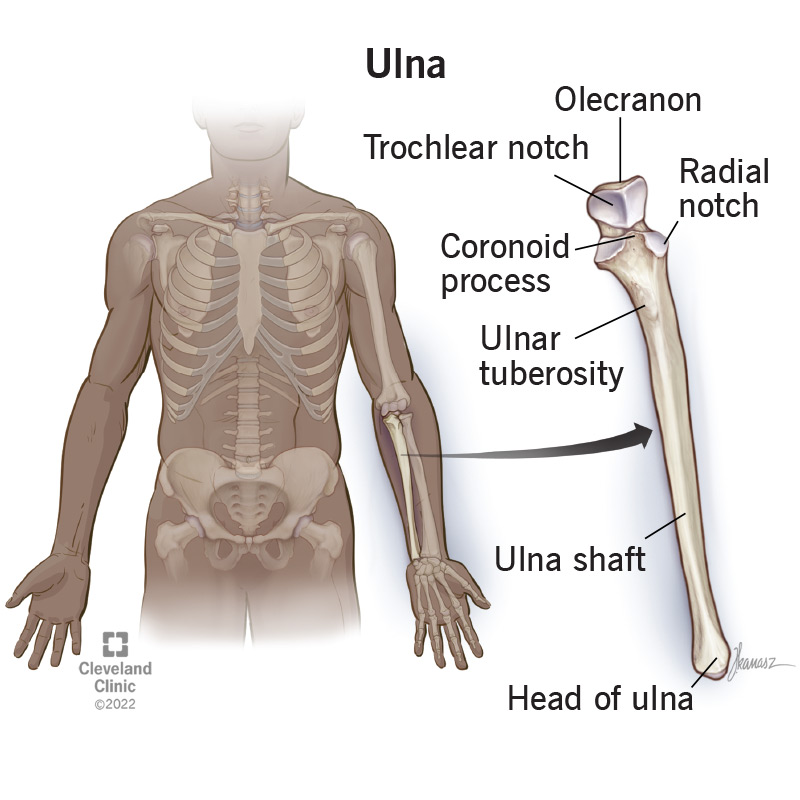
Where would you find the head of your ulna?
Near your wrist, more distal
This surface that's shaped like an ear is the point of attachment of the sacrum
The auricular surface

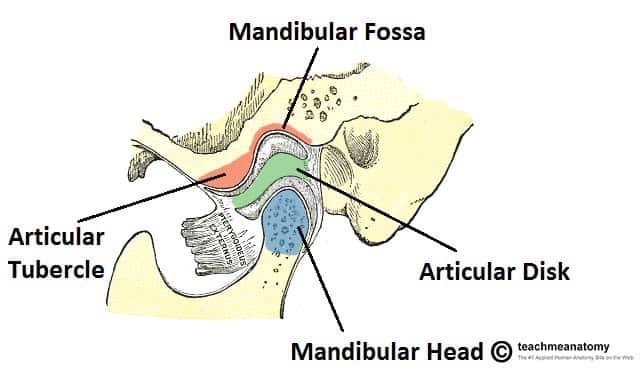
What is the name of the fossa where the mandible articulates?
mandibular fossa (temporomandibular joint - TMJ)
You can feel this vertebrae's spinous process at the base of your neck posteriorly (name and number)
C7 - Vertebral prominens (prominence)
When numbering metacarpals or metatarsals, number 1 would be the _______
Thumb or big toe

Synarthrotic: non-movable
Amphiarthrotic: slightly movable
Diarthrotic: freely movable
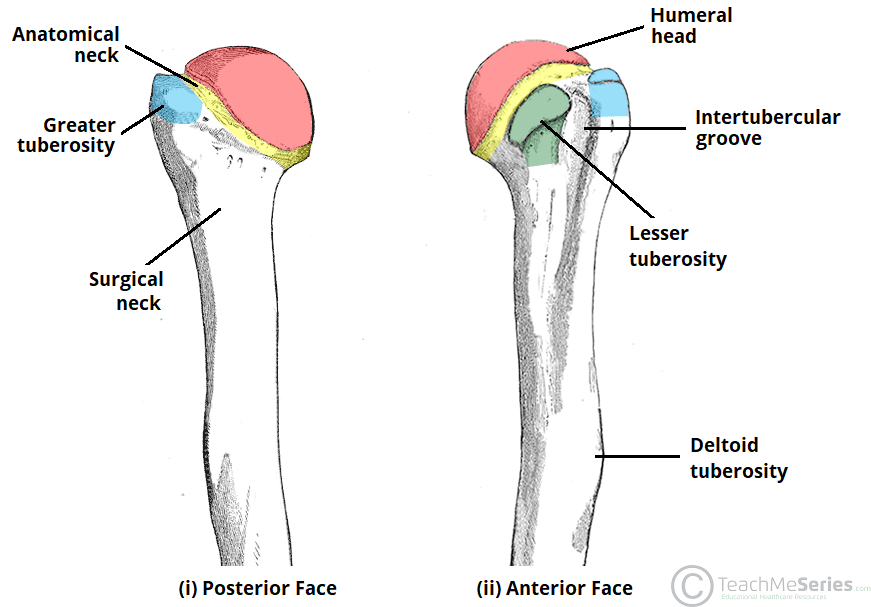
What are the 2 necks of the humerus called?
Anatomical and Surgical necks
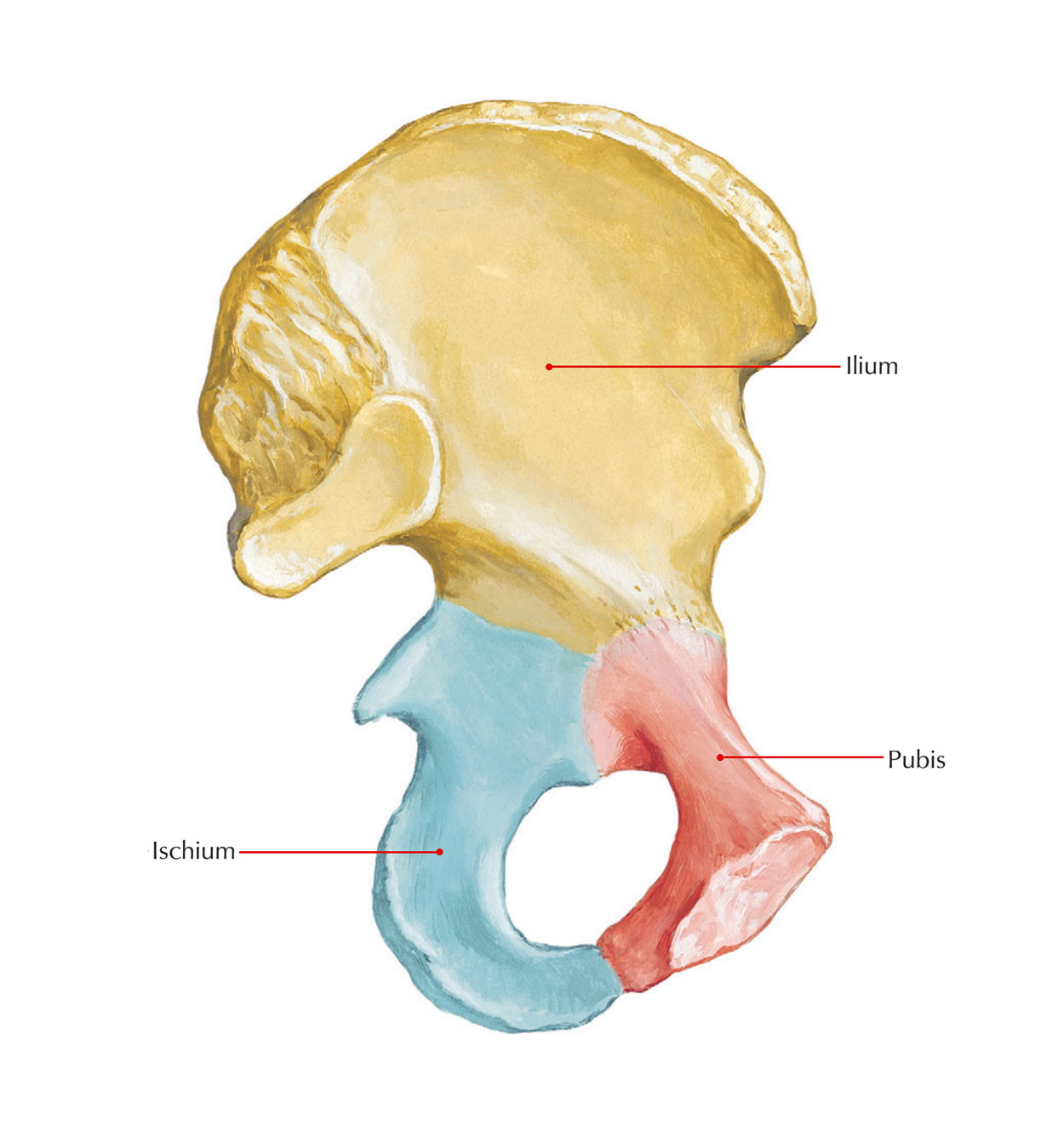
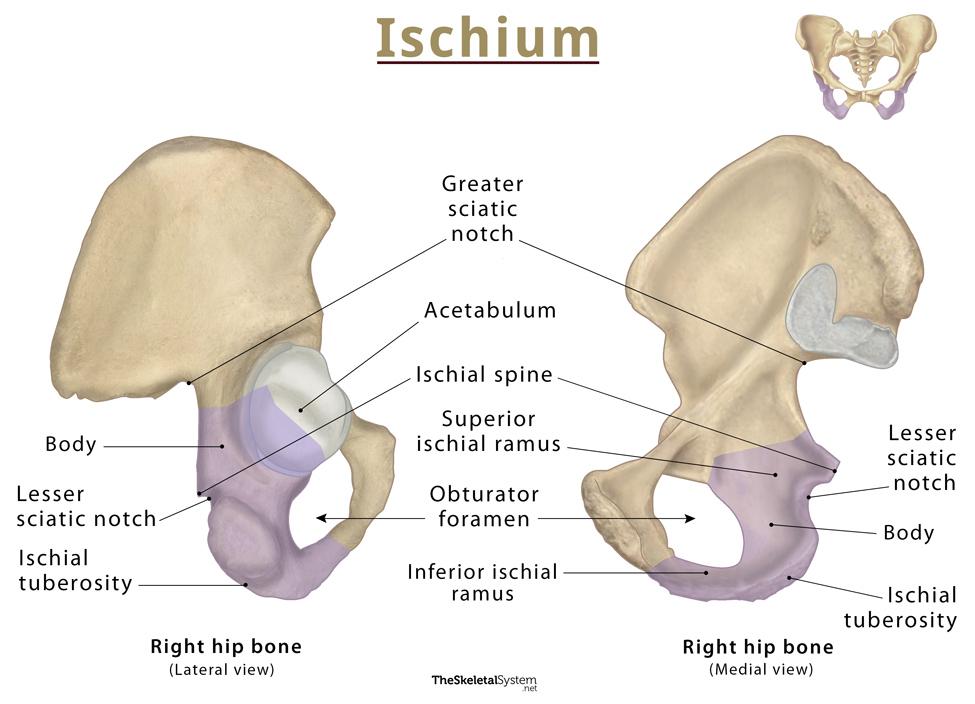
You sit on your _____. (part of the os coxae)
Ischium (more specifically ischial tuberosity)

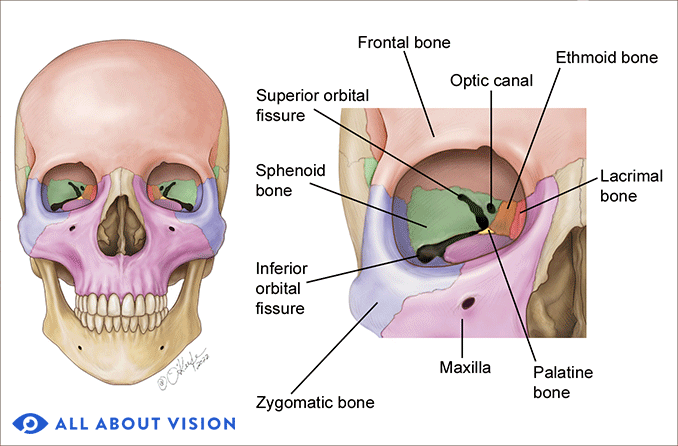
Name the 7 bones that make up the eye orbit
Ethmoid, sphenoid, lacrimal, zygomatic, frontal, maxilla, and palatine.
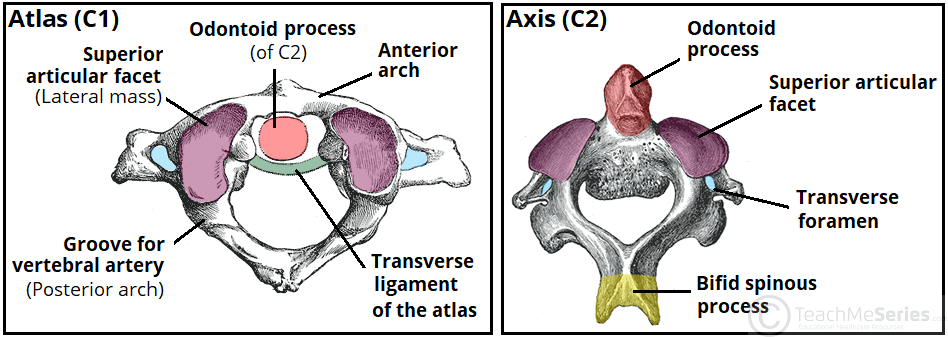
____ is the axis and ____ is the atlas.
C2 - Axis
C1 - Atlas
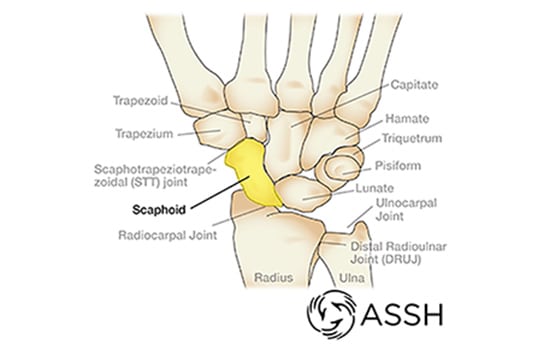
These 2 carpals articulate with the radius
Scaphoid and Lunate
The movement classification given to synovial joints
Diarthrotic - Freely Movable
Ex: Knees, elbows, shoulders, hips, etc.
This part of the humerus articulates with the head of the radius.
Capitulum

The os coxae are divided into 3 parts, what are the 3 parts
Ilium, Ischium, and Pubis
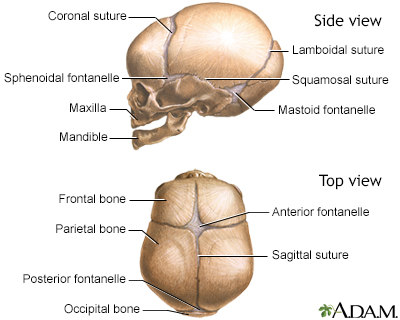
Name the 4 sutures between the skull plates
Coronal: Between frontal and parietal
Sagittal: Between parietals
Lambdoid: Between occipital and parietal
Squamous: Between parietals and temporals
Which direction does the vertebral foramen run?
up and down (to hold the spinal cord)

What carpal makes up the bony, ball part of your wrist on your ulnar side
Pisiform
An example of a synarthrotic synostosis
The frontal/metopic suture
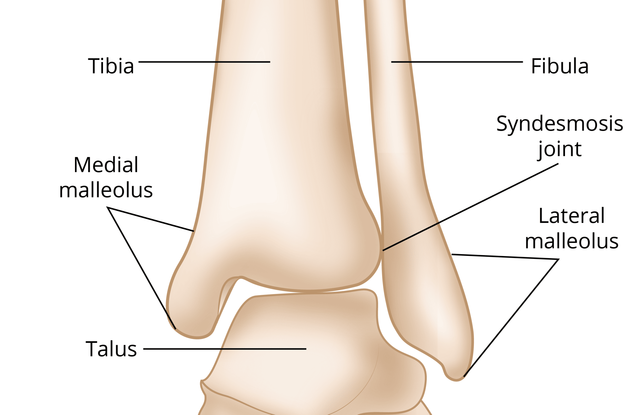
The lateral bony protuberances on your ankle, made from the tibia and fibula.
Malleoli
The head of the femur articulates here.
Acetabulum
The name of the bony ridge, directly posterior and superior to the foramen magnum
External Occipital Protuberance

Which way do the intervertebral foramen run?
Side to side (for nerves and blood vessels)

The largest bone in the ankle that articulates with the tibia and fibula
Talus
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/talus/BoXL5kFPpz75zsfup6Ov7A_talus_large_6jpJTI0t5h7TCcAE3bzg.png)
These synarthrotic fibrous joints insert in the alveolar processes of the skull
Gomphoses

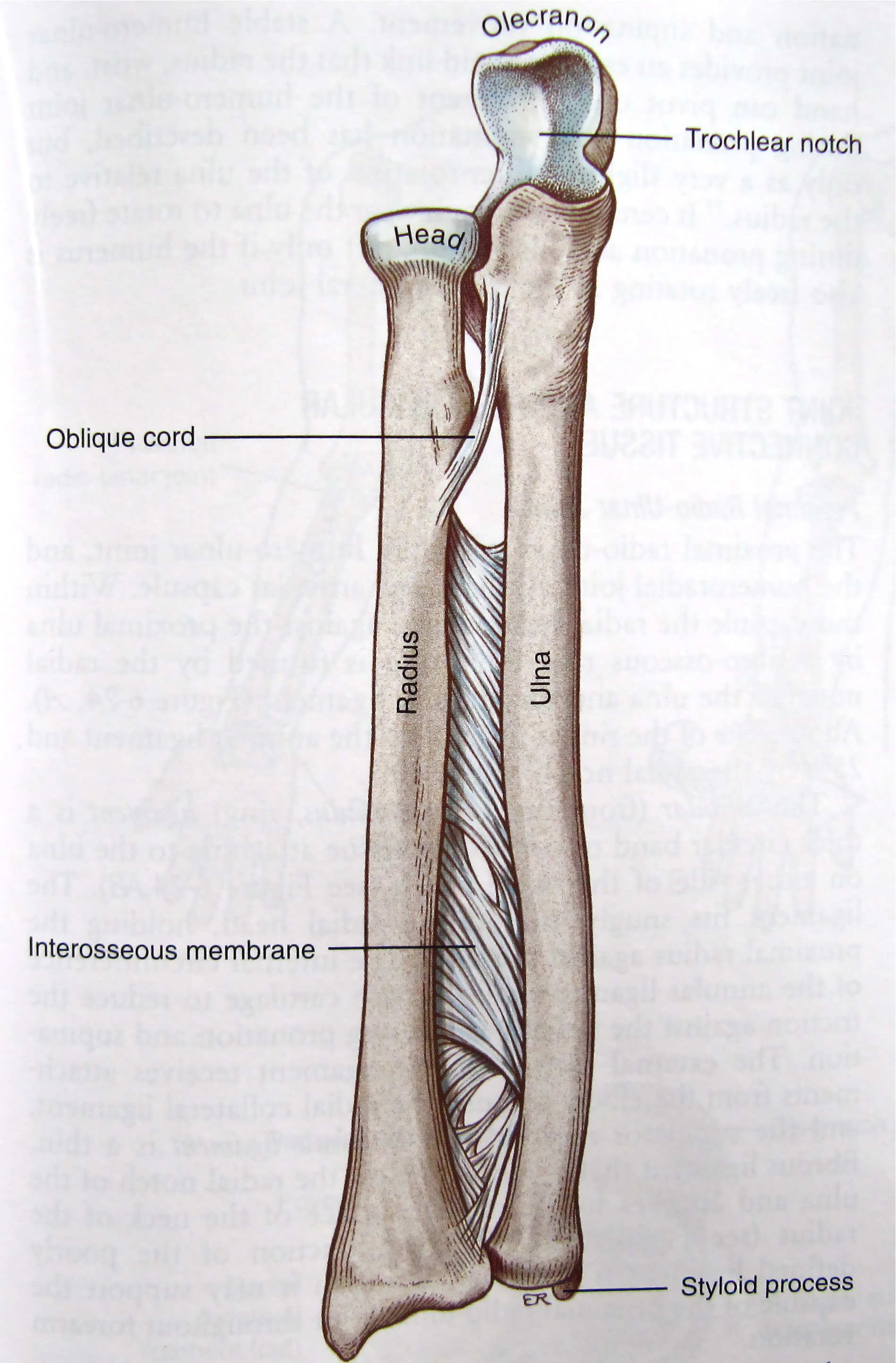
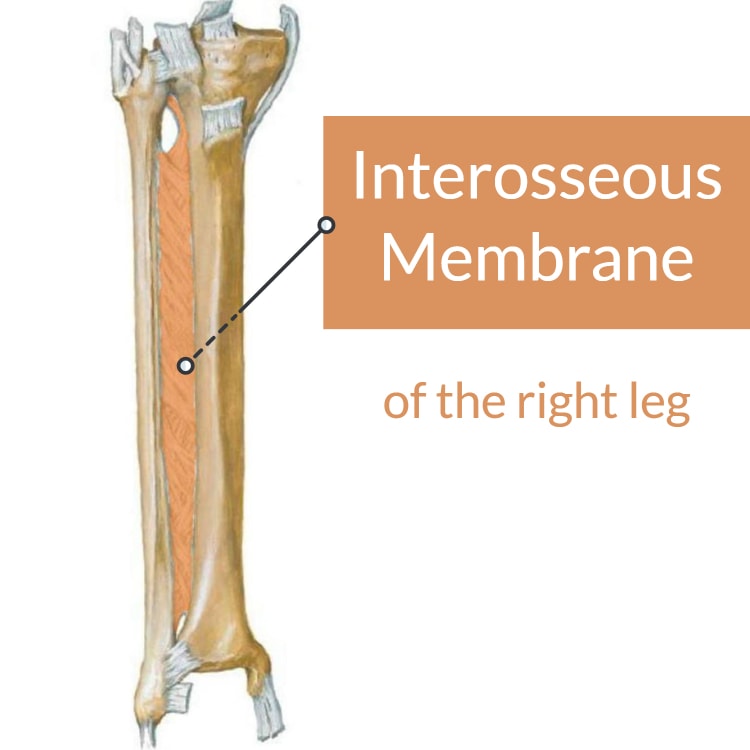
This amphiarthrotic syndesmosis or fibrous joint membrane allows for the pronation and supination of the forearm. Also found in the leg.
Interosseous membrane
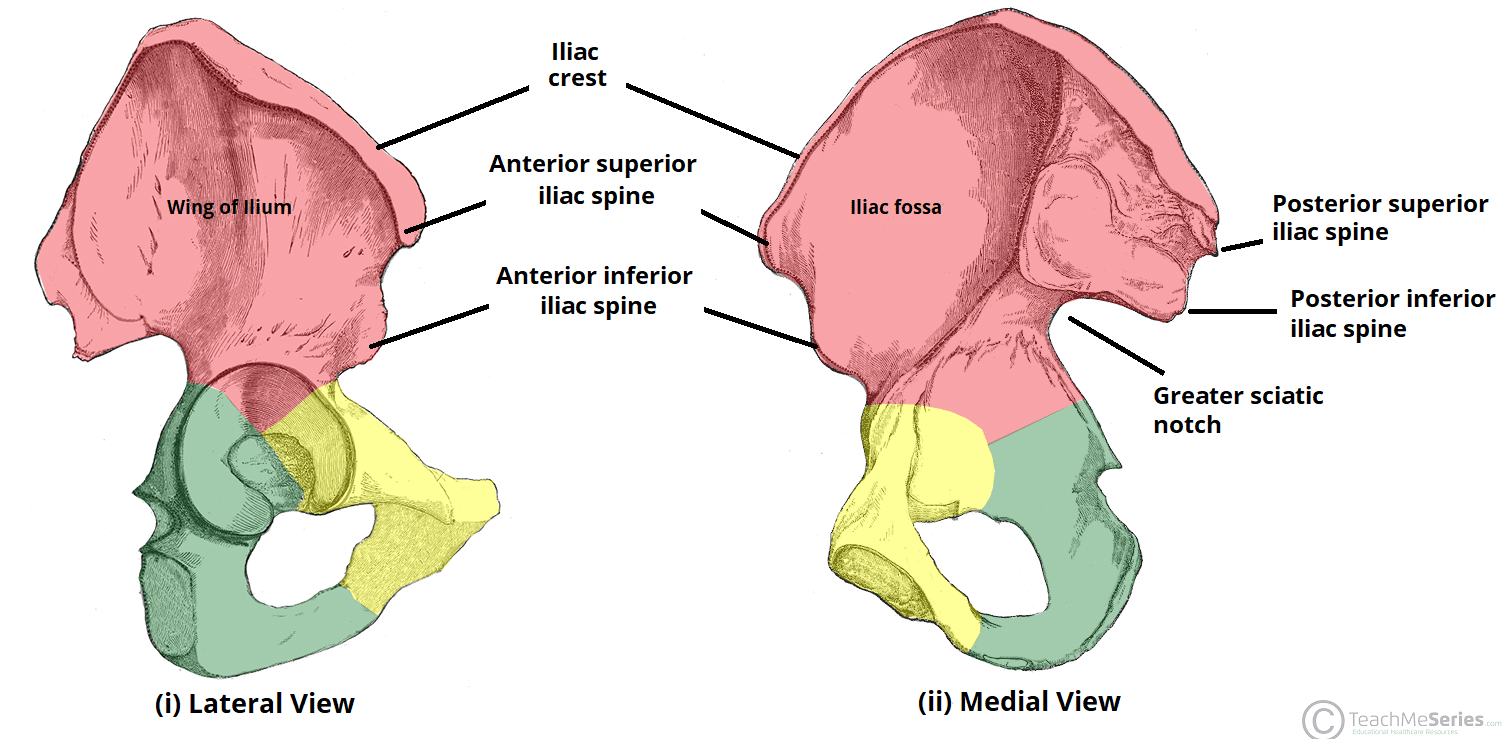
What are the names of the 4 iliac spines?
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine
Posterior Superior Iliac Spine
Posterior Inferior Iliac Spine
The name of the process directly anterior to the condylar process
Coronoid Process

The thoracic and sacral curves are anteriorly (concave/convex) and the cervical and lumbar are anteriorly (concave/convex)
Thoracic & Sacral (primary) - Concave
Cervical & Lumbar (secondary)- Convex

This tarsal is directly distal to the talus
Navicular bone
3 functions of synovial fluid
1: Lubrication of the articulating cartilage
2: Nourishment of the chondrocytes in the cartilage
3: Shock absorption

The name of the space found between the medial and lateral condyles of the femur
Intercondylar fossa

The coracoid process is on the (anterior/posterior) side
Anterior

The mastoid and styloid processes are part of which cranial bone
Temporal bone
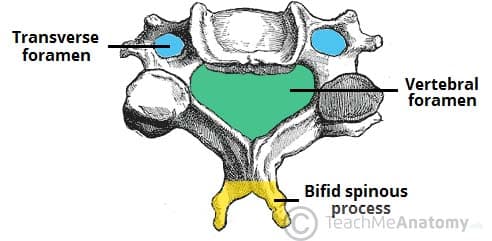
What is special about the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae?
They are usually bifid (2-pronged)
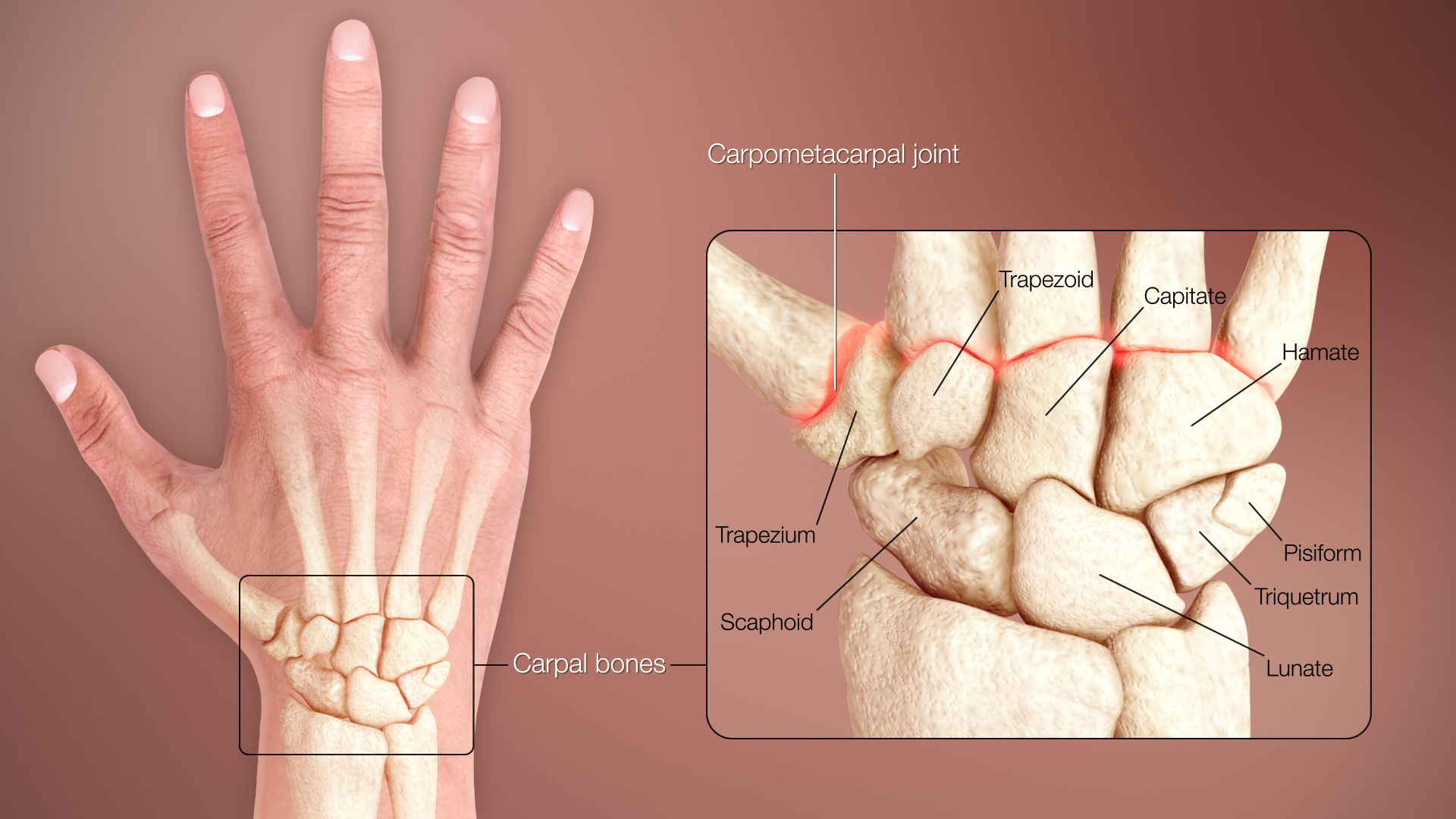
The trapezium and trapezoid carpals are on the (radial/ulnar) side, while the triquetrum and hamate are on the (radial/ulnar) side
Trapezium & trapezoid = radial side
Triquetrum & hamate = ulnar side
This ligament attaches to the medial epicondyle of the femur and the medial condyle of the tibia
The TCL/MCL (tibial collateral ligament/medial collateral ligament)
This ridge runs down the posterior side of the femur and is the point of attachment for many thigh muscles
Linea Aspera

The ______ end of the ______ articulates with the manubrium of the sternum
The sternal end of the clavicle
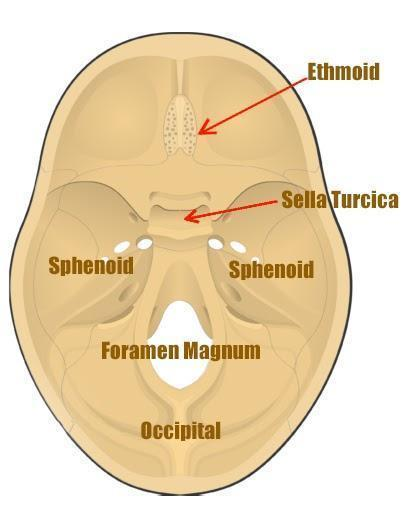
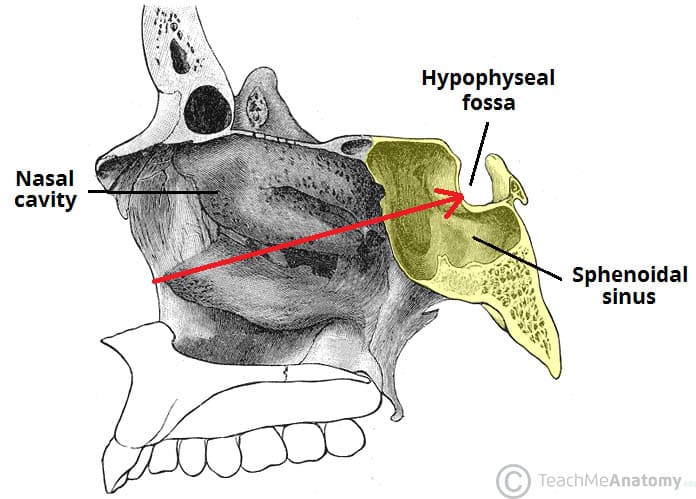
What is the name of the space where the pituitary sits and what bone can you find it in
Sella Turcica in the Sphenoid Bone
This carpal is directly deep to the pisiform bone
Triquetrum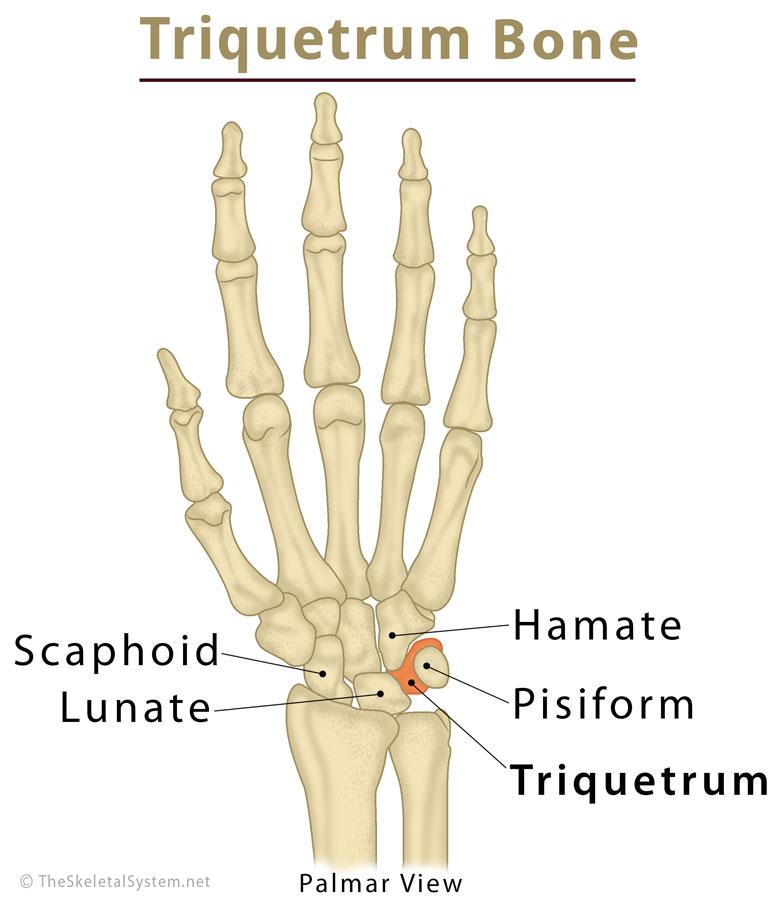
The only fibrous amphiarthrotic joint type
Syndesmoses
Ex: Interosseous membranes in forearms and legs that help pronate and supinate
The greater and lesser sciatic notches are separated by this
Ischial Spine
The process of the zygomatic arch that's part of the temporal bone is called the _____
Zygomatic process of the temporal bone

C1 and C2 are different from the other cervical vertebrae for what reason?
They are fused so they have no intervertebral disc
C1 has no body and no spinous process

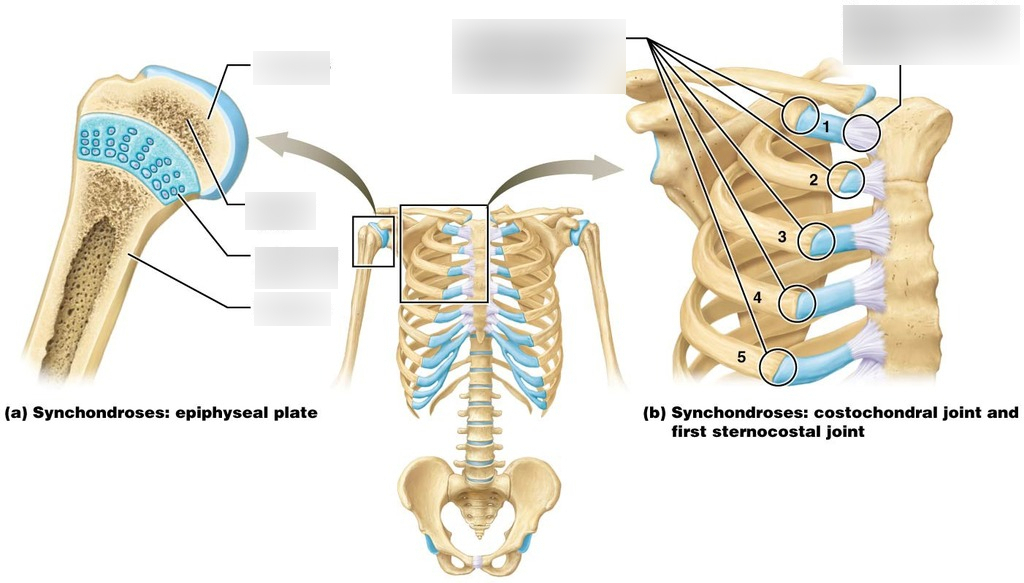
The only synarthrotic joint type that is cartilagenous
Synchondroses
Ex: Between ribs and sternum, epiphyseal plates of long bones