Any condition that decreases the kidney’s ability to function normally
Renal Failure
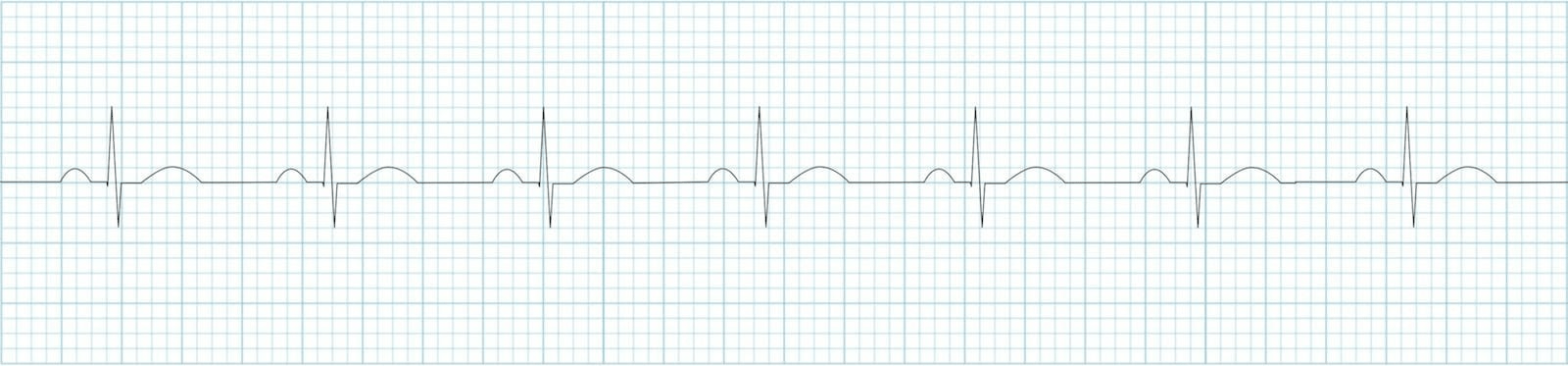
NSR
The inability of the heart to meet the metabolic demands of the body because the pumping ability of the heart is ineffective
Heart failure
Widening pulse pressure
Bradycardia
Irregular respirations
Cushing's triad
Treatment for Sickle Cell Crisis
HOP to it!
Hydration, oxygen, pain control
Progressive destruction of the nephrons of both kidneys
Chronic Renal Failure
This new growth of blood vessels allow perfusion to to continue around arterial blockages
Collateral Circulation
Secreted by ventricles with increased volume seen in heart failure
Higher the levels the more severe the heart failure
BNP (Beta-type natriuretic peptide)
Your Neuro patient has: HR 40, BP 180/42, Resp 8 and irregular. This diagnostic test is contraindicated
Lumbar puncture
a genetic disease in which the affected person lacks some of the blood-clotting factors normally found in plasma
Hemophilia
Pain in the epigastric region or around the umbilicus – will shift to the right lower quadrant
May show signs and symptoms of peritonitis
Appendicitis
Abrupt blockage of blood flow resulting in irreversible necrosis in the heart muscle beyond the blockage
MI
Symptoms characteristically include weakness, a sore tongue, and numbness of the hands or feet. If severe, the patient may have jaundice, ataxia, and cognitive impairment
pernicious anemia
Name one seizure trigger:
Trauma
Reduced cerebral perfusion
Infection
Electrolyte disturbances
Tumors
Genetic tendency
Epilepsy
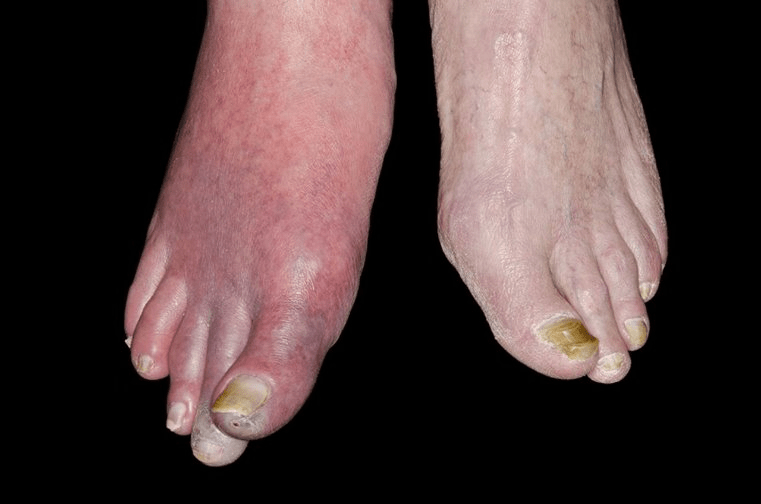
Peripheral Artery Disease
This complication of hemodialysis has S/S of:
Hypotension
Muscle cramps
Irregular heart rhythms
Headache
Nausea and vomiting
disequilibrium syndrome
What type of heart failure will have SOB, cyanosis, and cough?
Left
Name a trigger of Sickle Cell crisis
They include dehydration, infection, overexertion, cold weather changes, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking
At 0730 your patient’s blood sugar is 242. How much insulin will you administer
Patient Order:
Insulin aspart sliding scale AC & HS
< 200 – no coverage
201-250 – 4 units
251-300 – 8 units
301-350 – 12 units
351-400 – 15 units
> 400 – give 15 units and call the physician
4 units
Clinical manifestation
Severe, acute pain
Pain aggravated by movement or pressure
Absent distal pulses
Sharp line of color and temperature demarcation
Arterial embolism
A client has undergone esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD). This is what the nurse is most concerned about after the procedure:
Return of the gag reflex
What is MONA?
Treatment for chest pain
Morphine, oxygen, nitroglycerine, aspirin.
This potentially fatal clotting disorder is always secondary to another pathologic process, such as overwhelming sepsis, shock, major trauma, crush injuries, burns, cancer, acute tumor lysis syndrome, or obstetric complications such as abruptio placentae or fetal demise
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
A group of metabolic risk factors that occur together and increases the risk for diseases such as stroke, coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus
Metabolic Syndrome
Classic symptoms
Dyspnea
Chest pain
Hemoptysis
Orthopnea
Cough
Pulmonary Embolism