True or False. Rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes attached to it.
True
Smooth ER (smooth endoplasmic reticulum) performs functions including:
A) Protein synthesis
B) Lipid synthesis and detoxification
C) Packaging and shipping proteins
D) Breaking down worn-out cell parts
B) Lipid synthesis and detoxification
The majority of the cell membrane is composed of what type of lipids?
A) Steroids
B) Phospholipids
C) Fats
D) Collagen
B) Phospholipids
A molecule broke down into monomers by adding water. What process is this?
A) Dehydration synthesis
B) Hydrolysis
C) Denaturation
D) Phosphodiester linkage
B) Hydrolysis
Which organelle both gives a plant cell its rigid structure and controls the movement of materials like food and waste into and out of the cell?
A) Mitochondrion
B) Cell wall
C) Cell membrane
D) Nucleus
B) Cell wall
Phospholipids forms a bilayer in water but not in oil. Why does this occur, and how does it relate to their cellular role?
A) Hydrophilic heads repel oil; they form energy storage molecules
B) Hydrophobic tails avoid water; they create a barrier in cell membranes
C) Hydrophobic heads attract oil; they stabilize cell walls
D) Hydrophilic tails face water; they allow nutrient transport
B) Hydrophobic tails avoid water; they create a barrier in cell membranes
Which of the following structures stores waste produced by cell processes, as well as food for later use?
A) Nucleus
B) Ribosome
C) Vacuole
D) Mitochondrion
C) Vacuole
The _____ is most closely linked with the destruction of worn out cells.
A) Ribosome
B) Lysosome
C) Vacuole
D) Mitochondrion
B) Lysosome
What distinguishes DNA from RNA in terms of structure?
A) DNA is single-stranded; RNA is double-stranded
B) DNA contains thymine; RNA contains uracil
C) DNA has ribose sugar; RNA has deoxyribose
D) DNA forms a single helix; RNA forms a double helix
B) DNA contains thymine; RNA contains uracil
In sickle-cell disease, one amino acid change in hemoglobin makes red blood cells sickle-shaped. What protein structure is first affected, and how does it cause problems?
A) Secondary; it breaks coils, stopping oxygen transport
B) Primary; a wrong amino acid messes up the protein’s shape
C) Tertiary; it adds extra chains, blocking blood flow
D) Quaternary; it removes oxygen, causing cell damage
B) Primary; a wrong amino acid messes up the protein’s shape
What structure, found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, is a double layer of phospholipids that controls what enters and exits the cell?
A) Cell wall
B) Nucleus
C) Plasma membrane
D) Cytoskeleton
C) Plasma membrane
In animal cells, which type of junction forms cytoplasmic channels for communication between adjacent cells?
A) Tight junctions
B) Desmosomes
C) Gap junctions
D) Plasmodesmata
C) Gap junctions
The _____ endoplasmic reticulum has a role in transporting proteins to different compartments in the cell.
rough
Compare the structures of mitochondria and chloroplasts: both have double membranes, but chloroplasts have what additional feature for photosynthesis?
A) Cristae and matrix
B) Thylakoids stacked into granam
C) Nuclear envelope
D) Bound ribosomes
B) Thylakoids stacked into granam
Overcooking an egg white and egg yolk changes their proteins, turning them from clear to white and rubbery. What process causes this color and texture change, and how does it affect the proteins?
A) Splitting; it breaks proteins into bits, changing their color
B) Denaturation; it unfolds proteins, stopping their normal job
C) Adding water; it makes proteins hard and white
D) Stretching; it pulls proteins to work better
B) Denaturation; it unfolds proteins, stopping their normal job
Why are lipids like fats not considered polymers, unlike carbohydrates?
A) They lack a repeating monomer structure
B) They are hydrophilic and form micelles
C) They contain glycosidic linkages
D) They are synthesized by hydrolysis
A) They lack a repeating monomer structure
A hiker stores energy in their body for a long journey. Which molecule is primarily used?
A) Glycogen
B) Triacylglycerol
C) Phospholipids
D) Cellulose.
B) Triacylglycerol
A bacterial cell like Bacillus coagulans lacks which feature that distinguishes it from a eukaryotic cell like an onion root cell?
A) Plasma membrane
B) Ribosomes
C) Membrane-bound nucleus
D) Cytosol
C) Membrane-bound nucleus
Which organelle’s cristae provide a large surface area for enzymes involved in ATP synthesis?
A) Chloroplast
B) Peroxisome
C) Mitochondria
D) Lysosome
C) Mitochondria
Proteins are moved from rough endoplasmic reticulum to _____ for modification.
Golgi apparatus
Which of the following is not a function of proteins in cells?
A) Speeding up chemical reactions in digestion
B) Storing genetic instructions for building molecules
C) Moving muscles for body motion
D) Protecting against viruses and bacteria
B) Storing genetic instructions for building molecules
A student eats a starchy potato, which is broken down into glucose in the stomach. What process allows this breakdown, and why is starch easier to digest than cellulose?
A) Dehydration; starch has β-linkages, which are weaker than cellulose’s α-linkages
B) Hydrolysis; starch has α-linkages, which human enzymes can break, unlike cellulose’s β-linkages
C) Denaturation; starch lacks double bonds, unlike cellulose
D) Phosphorylation; starch is hydrophilic, unlike cellulose
B) Hydrolysis; starch has α-linkages, which human enzymes can break, unlike cellulose’s β-linkages
Draw a general structure of an amino acid
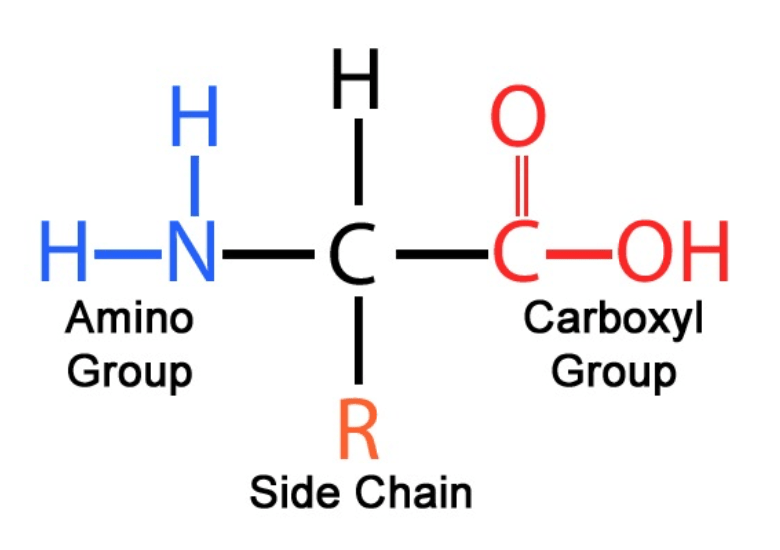
A protein stops working when its side chains can’t form water-loving bonds. What structure is affected, and why does this matter?
A) Primary; it changes the amino acid order
B) Tertiary; it messes up the protein’s folded shape
C) Secondary; it breaks protein coils
D) Quaternary; it splits multiple protein chains
B) Tertiary; it messes up the protein’s folded shape
A eukaryotic cell’s plasma membrane is damaged, reducing its selective permeability. What is the most likely impact on the cell’s function?
A) Uncontrolled influx of nutrients and ions, disrupting homeostasis
B) Immediate cessation of protein synthesis
C) Loss of mitochondrial ATP production
D) Breakdown of the nuclear envelope
A) Uncontrolled influx of nutrients and ions, disrupting homeostasis
Name all components of the endomembrane system.
Nuclear envelope
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Vacuoles
Plasma membrane
Match each macromolecule to the small building blocks that make it up.
A) Carbohydrates 1. Amino acids
B) Fats 2. Fatty acids and glycerol
C) Phospholipids 3. Nucleotides
D) Proteins 4. Glycerol+ fatty acids +phosphate
E) Nucleic acids 5. Monosaccharides
6.
7.
A-5 (Wagyu beef?🤔🤤)
B-2
C-4
D-1
E-3
Does this amino acid like water and why?
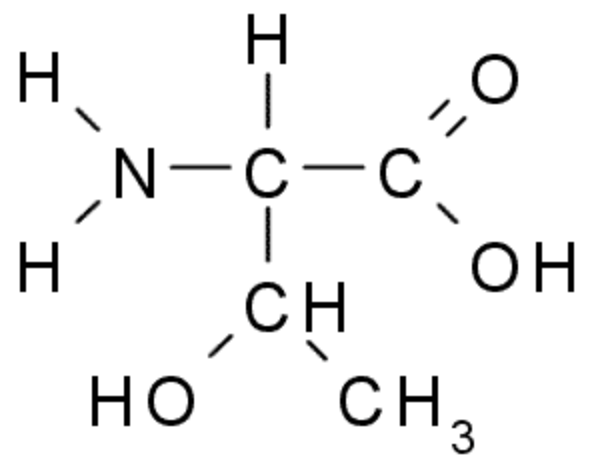
Yes because it is polar. (HO! HO! HO!)
Match each type of bond to the macromolecule.
A) Glycosidic bond 1. Proteins
B) Ester bond 2. Nucleic acids
C) Peptide bond 3. Lipids
D) Phosphodiester bond 4. Carbohydrates
A-4
B-3
C-1
D-2
What molecule is shown in the diagram, and in which types of macromolecules is it a key component? 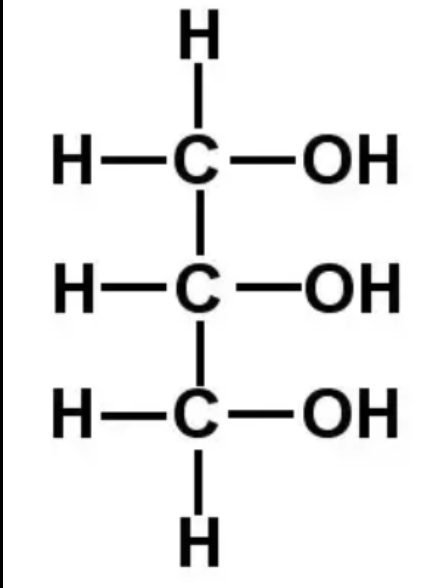
Glycerol – fats (triacylglycerols) and phospholipids