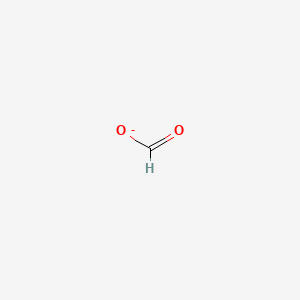
What hybridization is most stable? Why?
sp. More s character. 50% s orbital 50% p orbital. More s character has more characteristics of a sigma bond which are stronger and harder to break than pi bonds. sp orbitals have lower energies than sp2 or sp3.
What do resonance contributors represent?
Electron distribution within a molecule. Electrons are shared between more than one atom at a time, so each resonance contributor shows a possible location of the electrons. All resonance contributors are averaged together to represent one single molecule.
eclipsed is when the groups on the back carbon are in line with the groups attached to the front carbon
Staggered is when the groups attached to the back carbon are not in line with the groups on the front carbon. Groups on the back carbon can be seen when looking down the bond from the front carbon.
What position do bulkier groups prefer? (Where are they most stable?)
equatorial
What is constructive formation of hybrid orbitals? deconstructive?
constructive has a lower energy and forms the bonding orbital. Constructive is more favorable.
Deconstructive has a higher energy, since the p orbitals do not overlap. This forms the anti bonding orbital.
How can 13C NMR provide evidence of resonance?
Check for number of signals to determine single or double bond property (ex: amide bond)
Resonance shifts chemical signal
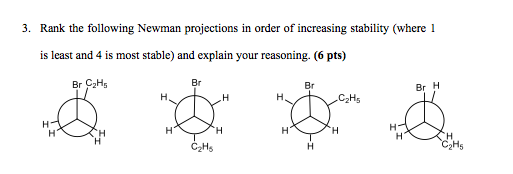
1. A
2. D
3. C
4. B
What is meant when a molecule is said to be cis or trans?
cis- substituent groups are on the same side, or in the same plane (both wedge or both dash). Both groups are in an up position or both are in a down position.
trans- substituent groups are on the opposite sides, or not in the same plane (one wedge, one dash). One group is in an up position, while the other is in a down position.
Rotation clockwise about a pi bond starting in the nonbonding orbitals will result in what orbital at 90 degrees? 180 degrees? 270 degrees? 360 degrees?
0= nonbonding
90= bonding= most stable
180= nonbonding
270= antibonding= least stable
360= nonbonding
Draw the resonance contributors of the molecule below.

Convert the following into a line bond structure.

Is the following molecule cis or trans?
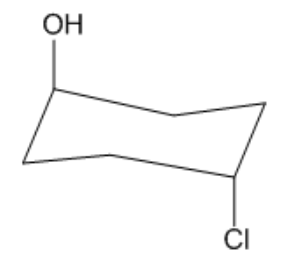
Trans. Although they are both axial groups, one is pointing up and one is pointing down.
What is the hybridization of the indicated atoms?

B
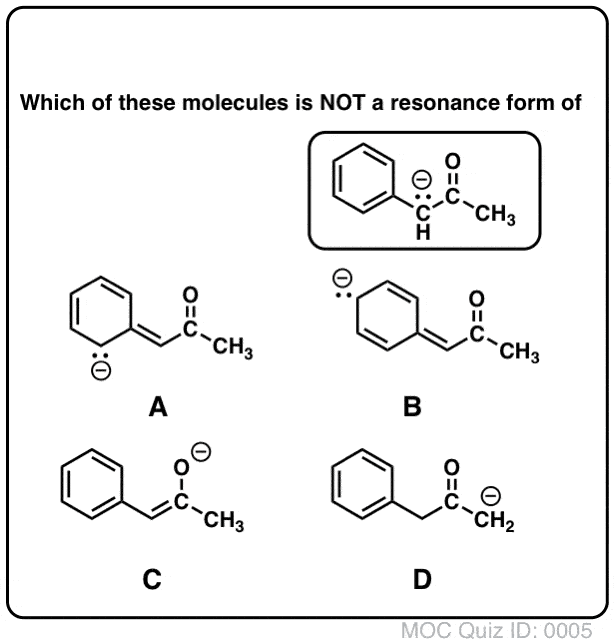
D- The C with the negative was sp3
Draw the Newman projections down C2 and C3 of the following molecule.
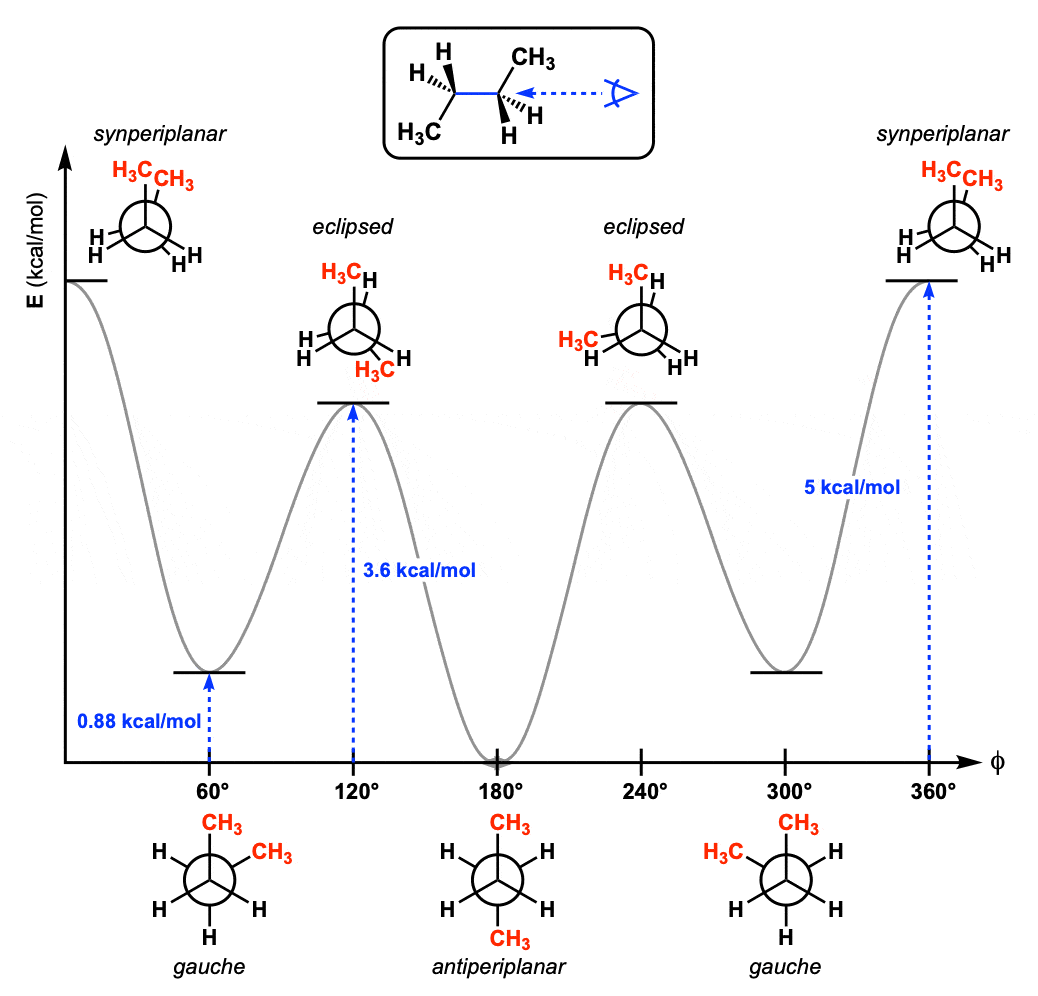
Which of the following is most stable? 
B- both bulkier substituent groups are equatorial
What is the hybridization of the atoms 9, 12, and 13? What are their bond angles and electron geometry?

9: sp2, 120, trigonal planar
12: sp3, 109.5, tetrahedral
13: sp2, 120, trigonal planar
Draw the resonance contributors of the flowing molecule.

Draw the Newman projections and corresponding energy diagram of propane.

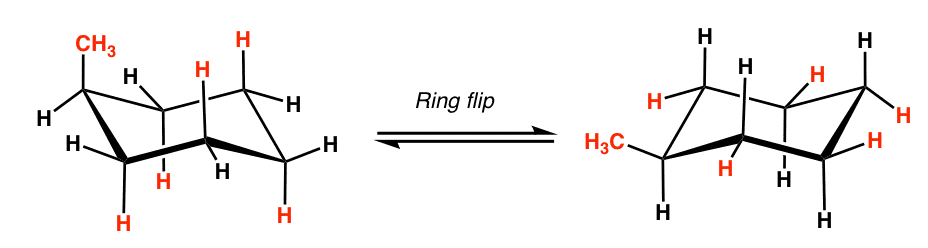
What happens when you conduct a ring flip?
Draw the ring flip of the molecule below. State which one is more stable. Why? (Ignore the blue arrows. That was the only picture I could find)
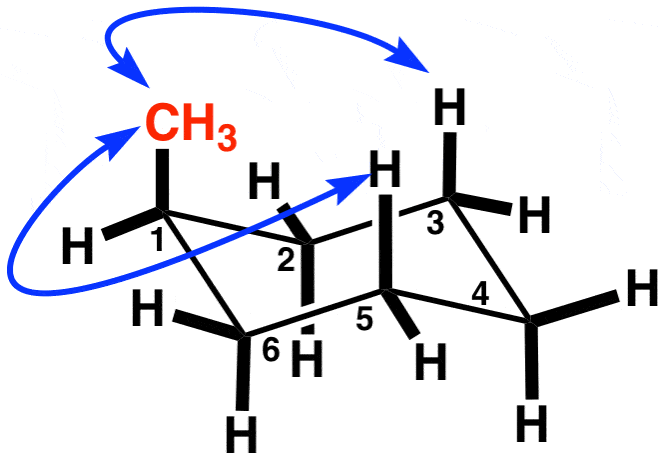
Everything that is equatorial becomes axial and vice versa.
The one on the right is more stable, since the methyl group is equatorial.