What are 5 common forces on bodily tissues?
1. Traction (Distraction/Stretch)
2. Compression (Squash)
3. Shear (Friction)
4. Twist (Rotation)
5. Bending
Using the mnemonic device FRE 123, answer the following questions:
What is in the middle of the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd class levers?
1st Class Lever: _______ is in the middle
2nd Class Lever: _______ is in the middle
3rd Class Lever: ________ is in the middle
1st Class Lever: Fulcrum is in the middle
2nd Class Lever: Resistance is in the middle
3rd Class Lever: Effort (Force) is in the middle
Where is the center of gravity in a person who is standing with good posture?
Around the 2nd Sacral Vertebrae (S2)
Tenodesis grasp is critical for patients at which spinal motor levels?
C5, C6, & C7
What is the difference between an isolation exercise & compound exercise?
Isolation exercise: A single joint in motion under resistance with the purpose of targeting a specific muscle or muscle group.
Compound Exercise: More than one joint in motion under resistance with the purpose of targeting a certain number of muscles or muscle groups.
True or False:
All muscle grades from 3- to 5 are performed against gravity.True
The Biomechanic Feedback Loop helps to explain the interdependent relationship of each part. Fill in the blanks:
Anatomy determines __________.
Physiology and biomechanics determine _____________.
Efficiency determines __________.
Performance is the __________.
Anatomy determines what’s possible.
Physiology and biomechanics determine how it’s done.
Efficiency determines how well it’s done.
Performance is the result.
A _____ class lever can occur at the Atlanto-Occipital Joint.
A _____ class lever can occur at the Humeroulnar Joint.
A _____ class lever can occur at the metatarsal phalangeal joints of the foot.
A 1st class lever can occur at the Atlanto-Occipital Joint.
A 3rd class lever can occur at the Humeroulnar Joint.
A 2nd class lever can occur at the metatarsal phalangeal joints of the foot.
If the center of gravity moves outside your base of support, you may lose your balance & fall. A patient that has poor posture or cannot bear weight through one of their legs as they walk, may have a center of gravity that has shifted outside of their base of support. What assistive devices may help broaden their base of support?
Crutches, Canes, and Walkers
This type of stretch is the most common method of force application and doesn't require another person.
Static Stretch
Most common method of force application; Sustained, controlled stretch that is done slowly; Doesn’t require another person; Usually more tolerable for the patient.
The Superman Exercise is an example of which type of exercise?
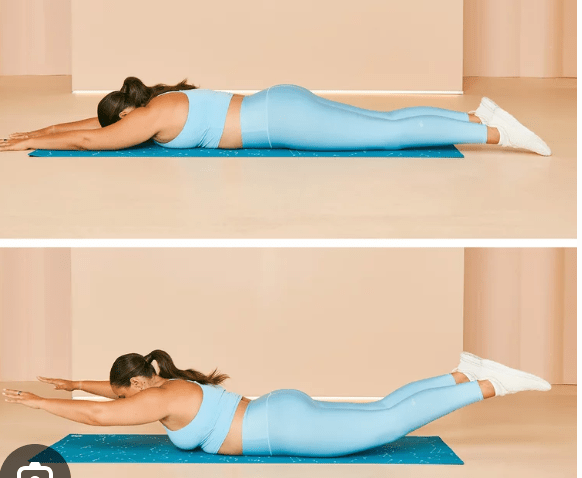
Stabilization Exercise
Isometric exercises that strengthens the muscles, tendons, and ligaments that support your joints, improving your body's balance and ability to control movement.
Which muscle grades are performed in a gravity-eliminated plane? (3 options)
2+ (Poor Plus)
2 (Poor)
2- (Poor Minus)
*Zero (0) and Trace (1) can be assessed in both gravity-eliminated and against gravity positions.
External forces are acting on our bodies at all times. They affect our posture, balance, and movement efficiency.
What are at least 3 examples of External Forces?
1. Bodyweight
2. Gravity
3. Resistance (from tools/equipment)
4. Manual contact (from another person)
5. Friction
________ levers help reduce required effort by increasing mechanical advantage, which is common in ergonomic tools and modifications.
2nd class levers help reduce required effort by increasing mechanical advantage, which is common in ergonomic tools and modifications.
The foundation of proper posture, balance, and functional movement is __________.
Pelvic Positioning
The pelvis acts as the base of support for the entire trunk and upper body.
You observe Olympic athletes performing torso twists and high knees before their High Jump. What type of stretching did you observe?
Dynamic Stretching
Muscle stretched by muscular contraction; Usually, a warm-up to prep for a particular sport or activity
True or False:
Closed Kinetic Chain Exercises are considered more functional & stability-focused than Open Kinetic Chain Exercises.
True
CKCE: The body moves while the hand or foot is fixed in a stationary position, such as a wall or the floor.
Your patient cannot perform shoulder flexion against gravity. You decide to assess their shoulder flexion in a gravity-eliminated position.
You observe that they can perform full shoulder flexion in a gravity-eliminated position.
Do you apply resistance when performing MMT in a gravity-eliminated position?
No.
We never apply resistance in a gravity-eliminated position.
If the patient performed full shoulder flexion in a gravity-eliminated position, then we would score a 2+ and move on.
Internal forces counteract or control external forces to allow for controlled movement and joint protection.
What is 1 Active Internal Force and 1 Passive Internal Force?
Active: Muscle tension
Passive: Ligament stretch
_______ levers focus on speed and range, but OTs teach ways to reduce torque and strain within these systems.
3rd class levers focus on speed and range, but OTs teach ways to reduce torque and strain within these systems.
In an anterior pelvic tilt, the tailbone _________.
In a posterior pelvic tilt, the tailbone _________.
In an anterior pelvic tilt, the tailbone lifts up.
In a posterior pelvic tilt, the tailbone tucks down.
You're having trouble stretching your own quadricep and ask a classmate for help. The classmate is able to bring your quadricep into a maximal stretch and holds it in position for about 30 seconds. What type of stretching is this?
Manual Passive Stretching
Short-term duration (15 sec to 60 sec) where the tissue is elongated beyond resting length against an external force; Usually done to the point of maximal stretch or a few degrees past the point of discomfort.
Name at least 3 examples of external resistance.
1. Water
2. Air
3. Weights (dumbbells, barbells, and dowel bars)
You observe your patient independently don a shirt over their head, reach behind their back to tuck in a shirt, and stretch out their arms to don a jacket.
Based on this observation, you could state the patient's shoulder & rotator cuff muscles are grossly at which muscle grade?
3+ (Fair Plus): Complete ROM, against gravity, no resistance.
"Grossly" is required in the documentation because isolated MMT was not performed.
The picture depicts an example of which force?
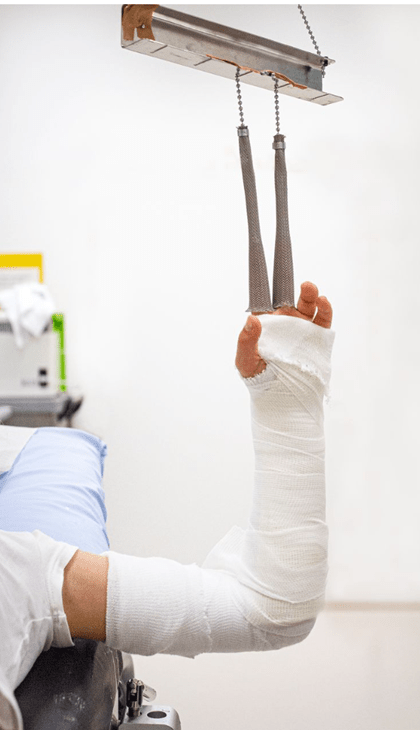
Traction: Can be used to treat and reduce any joint dislocation or bone fracture
Name at least 3 examples of adaptive equipment acting as 2nd class levers.
1. Jar openers
2. Key Turners
3. Door lever handles
True or False:
A non-reducible posture means the posture is flexible and can be corrected to neutral with proper intervention.
False
Explanation:
A non-reducible posture cannot be corrected. Providing equipment that supports the posture and redistributes pressure, will help prevent further progression.
Reducible posture is flexible and can be changed. This does not mean the posture can be corrected into neutral. Providing equipment that supports corrected posture will help prevent reducible posture from becoming non-reducible.
Serial Casting is an example of what type of stretch?
Mechanical Stretching
Low-intensity external load that is donned for a prolonged period of time by means of positioning, Braces, Splints, or Serial Casting.
Name at least 3 things that would be considered pertinent information under the patient's response or tolerance to a home exercise program.
1. Activity tolerance (ex: rest breaks)
2. If pain was reported
3. Just right challenge (ex: too easy or too hard)
4. Hindered by cognition (ex: distracted, unable to follow commands)
5. Sensory deficits (ex: required tactile, verbal, or visual prompts)
Your patient is able to hold complete ROM, against gravity, for 1 second.
Which muscle grade would this indicate?
4- (Good Minus): Complete ROM, against gravity, minimum resistance
Your patient has poor eccentric control of their hamstrings when performing stand to sit transfers. You observed that they "plop" into their chair. You provide the verbal prompt, "reach back for the armrests and lower yourself with your arms." Which law of motion is involved with this scenario?
Law of Inertia: An object continues in its state of rest or of uniform speed in a straight line unless it is compelled to change that state by forces acting on it. When sitting, the body remains in motion toward the chair until it’s stopped by the seat (external force).
Name at least 3 examples of adaptive equipment acting as 3rd class levers.
1. Reachers
2. Long-handled Shoehorns
3. Long-Handled tools for IADLs (cleaning, gardening)
Name at least 3 things an OTR can do to help address posture & alignment issues for someone in a wheelchair.
1. Seat & Cushion Adjustments (Contoured or pressure-relieving cushions)
2. Back Support Modifications (Reclined backs, lateral supports)
3. Pelvic Positioning (Pelvic belts, wedges)
4. Lower Extremity Supports (Footrests, heel loops)
5. Upper Body & Head Supports (headrests, armrests)
Your patient does not want you to touch their leg due to sensitive skin. They're willing to perform a few leg stretches, but only if they control it. They kick out their leg and hold it in the air for a few seconds and then lower it back down to the ground. What type of stretch is this?
Active Stretch
A contraindication to exercise means do not proceed if these conditions are present.
A precaution to exercise means consider the situation, proceed with caution, and make adjustments as needed to maintain safety of the patient.
If a patient reports dizziness while standing, an appropriate response would be to allow the patient to sit, monitor their vitals, and determine if it's safe to continue or to terminate the session.
Dizziness is considered a ____________.
Precaution
Your new patient came in with stroke symptoms. You note that the left arm is flaccid. You instruct the patient through wrist extension, but they are unable to perform the motion. You feel for the wrist extensors, but there is no muscle contraction seen or palpated. This would indicate which muscle grade?
0 (Zero)