What is strabismus? Will people with strabismus ever perceive binocular, 3d percepts?
One eye looks directly at the object you are viewing, while the other is misaligned inward (Cross-eyed)
What is akinetopsia?
Issues perceiving motion in the visual field
Name the five basic tastes. What is the fifth taste and how does it differ from the other four?
-Sweet
-Sour
-Bitter
-Salty
-Umami
Not a hardwired effect
What is the purpose of pain?
Bodies alarm system. Helps avoid detrimental damage
What sense does your instructor primarily research?
Audition
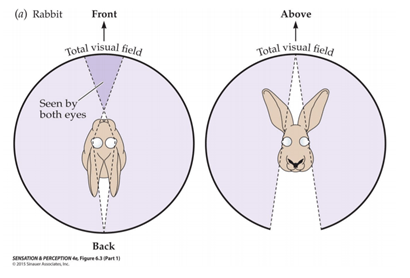
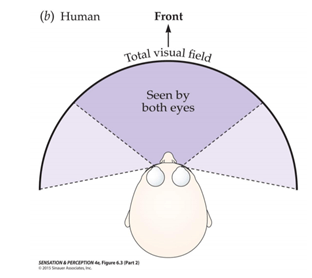
Name one advantage and one disadvantage of side-facing eyes.
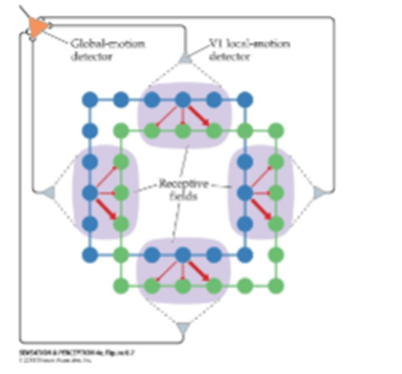
What is second-order motion?

If you were to destroy a single brain area to knock out your sense of taste, which area would you choose?
Insular (gustatory) cortex
What are the two spinal pathways that are important to touch perception? How do they differ?
Spinothalamic Pathway (temperature and pain) and DCML Pathway (mechanoreceptors, muscles, tendons, and joints)
Name and define two naturally occurring Illusions.
-Depth Illusion
-Forced Perception
-Moon Illusion
-Mirage
What are three spatial cues in monocular vision? Describe them.
-Relative size
-Familiar size
-Interposition
-Linear Perspective
-Aerial Perspective
-Texture Gradient
-Motion Parallax

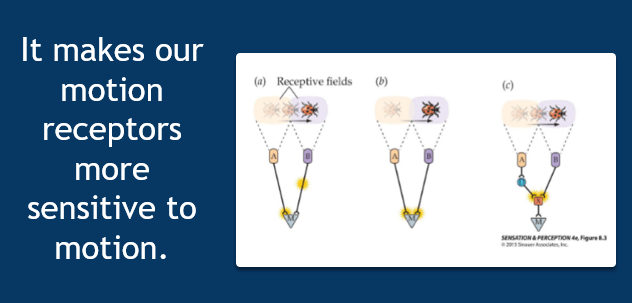
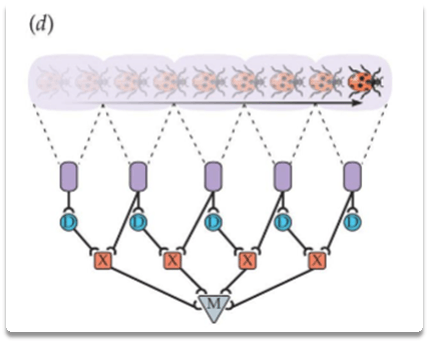
Why do we need the delay in our motion detectors?
What does the chroda tympani do?
Helps carry taste information from the anterior, mobile tongue to the brain
What are the three receptors that are related to touch and what are they for?
Thermoreceptors: Sensation of temperature
Mechanoreceptors: General sensation of contact from the skin
Nociceptors: Sensation of pain
Proprioceptors are located in the ______ and ______.
Muscles;Joints
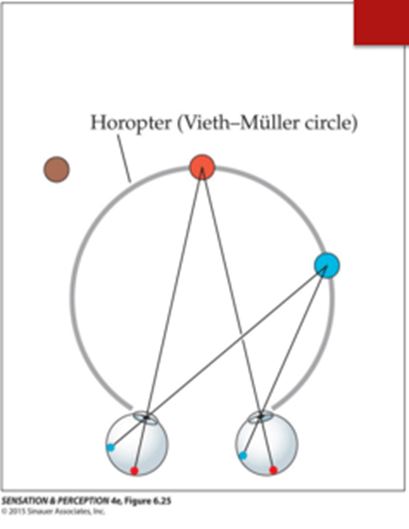
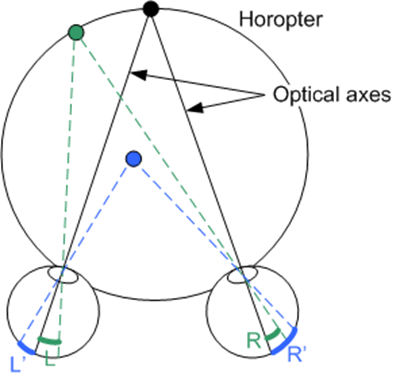
What is the horopter? (definition only)
What is the motion correspondence problem? How does our perceptual system deal with it?

Sour objects are produced by ______ ions, and salty tastes are produced by _______.
Hydrogen Ions, Sodium chloride
Define and relate the following terms: Somatosensation, Proprioception, and Kinesthesia
Somatosensation: Sensory signals from skin, muscles, tendons, joints, and internal receptors
Proprioception: Perception mediated by kinesthetic and internal receptors
Kinesthesia: Perception of the position and movement of our limbs in space
Why is proprioception important for our movement?
Movement in space.
What is binocular disparity? How is it used to distinguish objects in relation to the horopter?
Why does the motion detector in this image only detect motion in one direction and at certain speeds?
Lots to explain.
Name the four types of papillae and define them.
Filiform: Bumpy appearance. No taste
Fungiform: Mushroom shaped, edge of the tongue. Six taste buds per papillae
Foliate: Fold found in rear of tongue, where tongue attaches to mouth.
Circumvallate: Mound like structures. Larger than fungiform.
Name the two types of slow-acting mechanoreceptors. Name the two types of mechanoreceptors with large receptive fields.
Slow: Merkel (SA-I) and Ruffini (SA-II)
Large receptive field: Ruffini (SA-II) and Pacinian (FA-II)
Give an example of an illusion for 3 senses that doesn’t include vision.
Lots of answers.