Explain what is happening inside an atom to produce unique atomic absorption spectra and atomic emission spectra.
In atomic absorption spectra, the dark lines indicate the energy of the photon being absorbed by the electron moving to an excited state.
In atomic emission spectra, the colored lines indicate the photon emitted by the electron as it falls from the excited state to a lower energy level.
Which atom has the largest atomic radius:
O, Ne, S, Cl
S
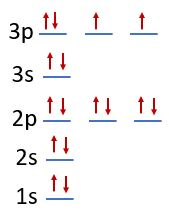
Draw the atomic orbital diagram for sulfur.
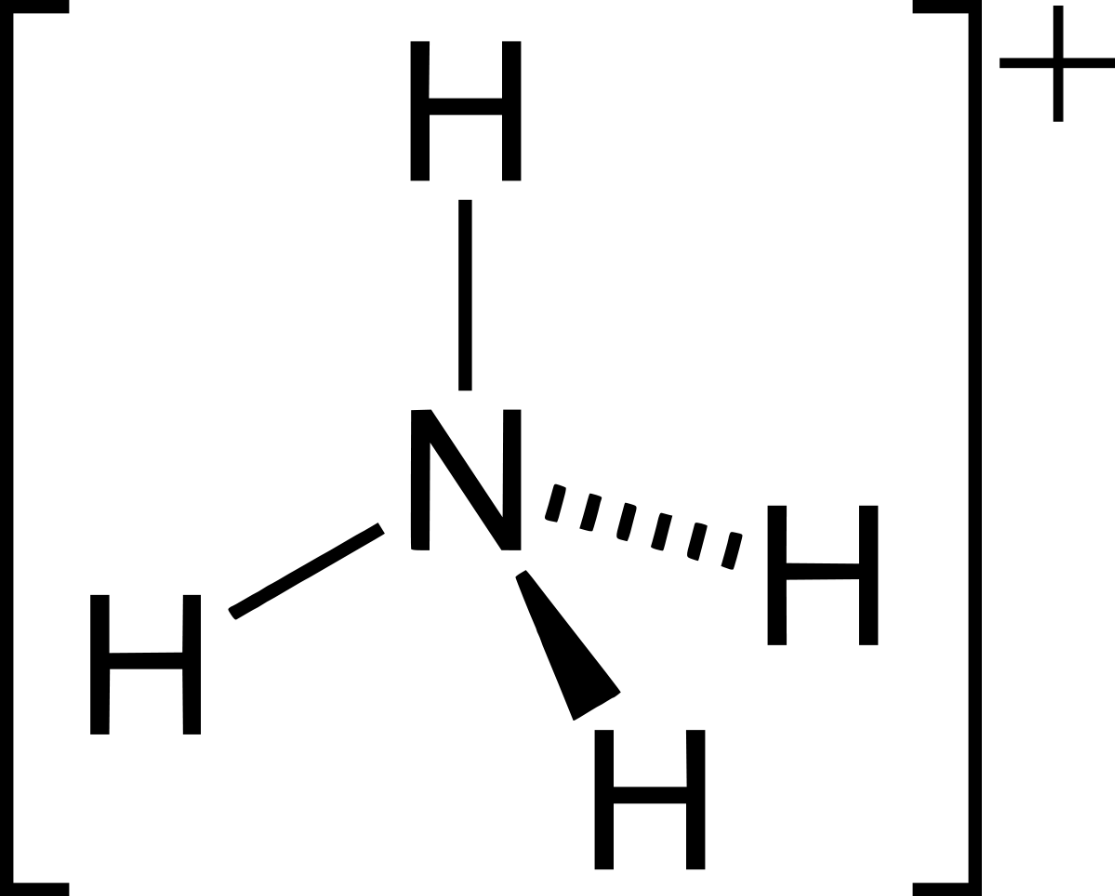
Draw the Lewis structure for NH4+.
Explain how sigma and pi bonds are formed from atomic orbitals.
Sigma bonds are formed from direct overlap of s or p orbitals. Pi bonds are formed from side by side overlap of p orbitals.
The threshold frequency of tin is 1.2x1015 Hz. What is the first ionization energy (J) of this atom? What is the wavelength of this light in nm?
8.0x10-19 J, 250 nm
Which atom has the highest ionization energy:
K, V, Al, P
P
What are the possible quantum numbers for a valence electron of Indium?
Indium has 3 valence electrons 5s2 and 5p1
n = 5; l = 0, 1; ml = -1, 0, 1; ms = +/- 1/2
Identify the electron domain and molecular geometry of XeF4.
Electron domain: Octahedral
Molecular: Square Planar
How many sigma and pi bonds are in a HCCH molecule?
3 sigma (2xHC and 1xCC) and 2 pi (2xCC)
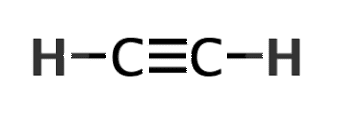
In a hydrogen atom, an excited electron falls from n=3 to n=2. What color photon is emitted? (You will be given electromagnetic spectrum on exam, but for now you can look it up)
Frequency = 4.57x1014 Hz
Wavelength = 657 nm
Color = Red
Which atom do you expect to have an exothermic electron affinity:
Na, Mg, Zn, Kr
Na
de Broglie argued that an electron acted as circular standing wave. Explain how this theory fits with Bohr's ideas of quantized orbitals.
In the standing wave, only an integer number of wavelengths could fit exactly within the orbit (2πr=n wavelengths).
Order the following molecules by increasing bond angle and explain why the angles change:
H2O, CH4, SO2, NH3
H2O < NH3 < CH4 < SO2
SO2 is the largest because it has 3 electron domains as opposed to 4. Of the tetrahedral molecules, lone pairs have a stronger repulsion force for the more lone pairs the smaller the bond angles gets, making NH3 smaller than CH4 and H2O smaller than NH3.
Explain how we know that molecular orbitals are hybridized.
Because of measuring bond energy and bond angles. Example: CH4 has 4 equal energy bonds which means they must be hybridized between s and p atomic orbitals; H2O has a bond angle of <109 instead of the expected 90 from the orientation of the atomic p orbitals.
Many scientists used the Bohr model to explore electronic transitions of the hydrogen atom. The Lyman series categorized transitions from n=7 to n=1, the Balmer series categorized transitions from n=7 to n=2, the Paschen series categorized transitions from n=7 to n=3, and the Brackett series categorized transitions from n=7 to n=4. Which series would have the largest average energy change in the transitions? Which series would have the longest average wavelength of light released by the transitions?
The largest gap in energy is n=7 to n=1 so Lyman series would have the largest average energy change.
Longest wavelength is lowest energy, and lowest energy gap is Brackett series from n=7 to n=4.
Write the electron configuration for calcium and identify the number of valence and core electrons.
[Ar] 4s2
Core electrons = 18Valence electrons = 2
Describe the two unexpected findings from photoelectric effect experiments.
1) That electrons were only emitted from the metal after a certain threshold frequency was met.
2) That the kinetic energy of the electrons was independent of the amplitude of the light and was related only to the frequency.
Draw the Lewis structure for sulfate and any resonance structures. Determine the electron domain geometry, molecular geometry, and bond angle.
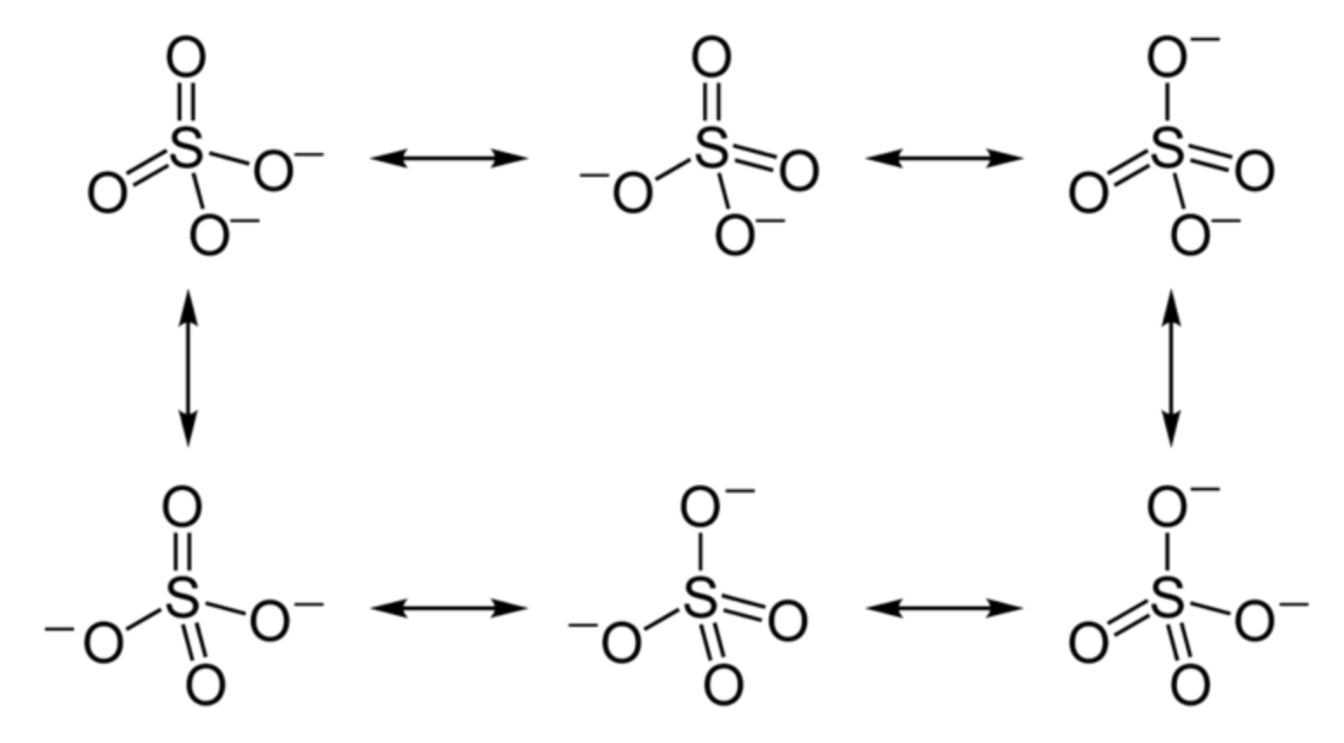
Electron Domain & Molecular: Tetrahedral
Bond angle: 109.5
What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms in this molecule:
sp2
The Bohr equations only work for hydrogen-like atoms. Why do you think these calculations are effected when there is more than one electron?
Multiple correct answers:
Multiple electronic transitions release different waves that can cause constructive or destructive interference.
Bohr equations do not account for electronic repulsion of multiple electrons.
The electron configuration of Mo+ is [Kr] 4d5. Explain why this is the case.
In order to half-fill the d orbital, one electron from the 5s orbital moves to the 4d, giving Mo an electron configuration of 5s1 4d5. Since 4d is half-filled it is lower in energy than the 5s, so the first electron removed for Mo+ is from the 5s orbital.
The Schrödinger equation is 𝐻𝜓=𝐸𝜓. Describe what H represents and what 𝜓 represents.
H is the hamiltonian operator; a set of mathematical operations representing the total energy of the quantum particle (such as an electron in an atom)
ψ is the wavefunction which describes electrons as three-dimensional stationary waves that can be used to find the special distribution of the probability of finding the particle
Finish the Lewis structure below and determine the molecular geometry of the carbon atoms. Label any bond dipoles with vector arrows.
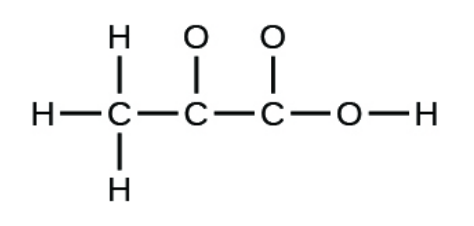
Tetrahedral (CH3) and trigonal planar (C=O). Bond dipoles from C to O and H to O.
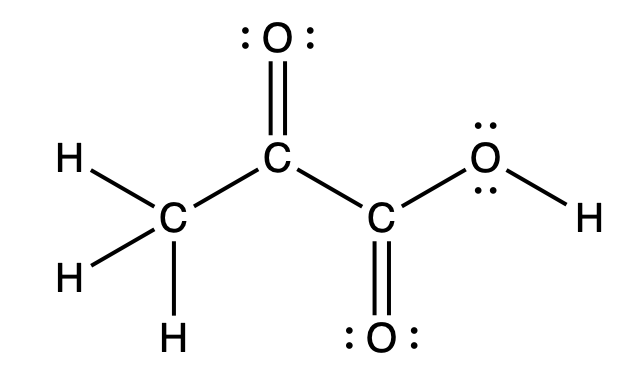
Estimate the bond angles of each numbered region and identify the hybridization of the central atom.
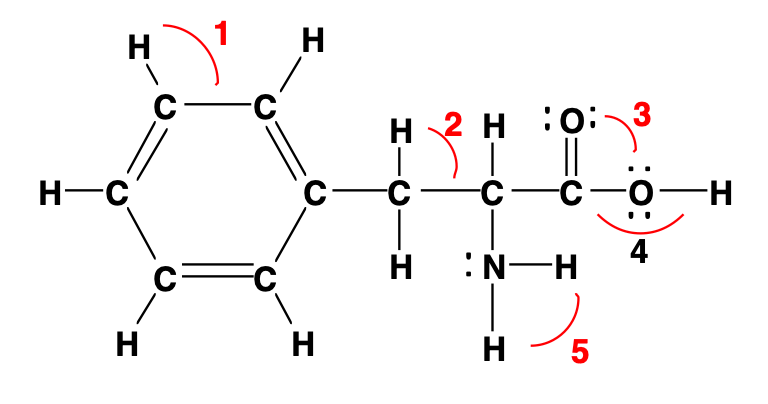
1 = 120, sp2
2 = 109.5, sp3
3 = 120, sp2
4 = <109.5, sp3
5 = <109.5, sp3