What body plane divides the body into left and right portions?
midsagittal plane

What body plane is this?
Sagittal/midsagittal
Healthcare workers (MAs, doctors, etc.) are mandated reporters of __________.
abuse
Give an example of an intentional tort.
- Assault someone (punch them in the face)
- Defamation (talk badly about someone)
- False imprisonment (lock someone in a room)
Harm caused by action or inaction is also known as...
tort
What body plane divides the body into top and bottom sections?
transverse
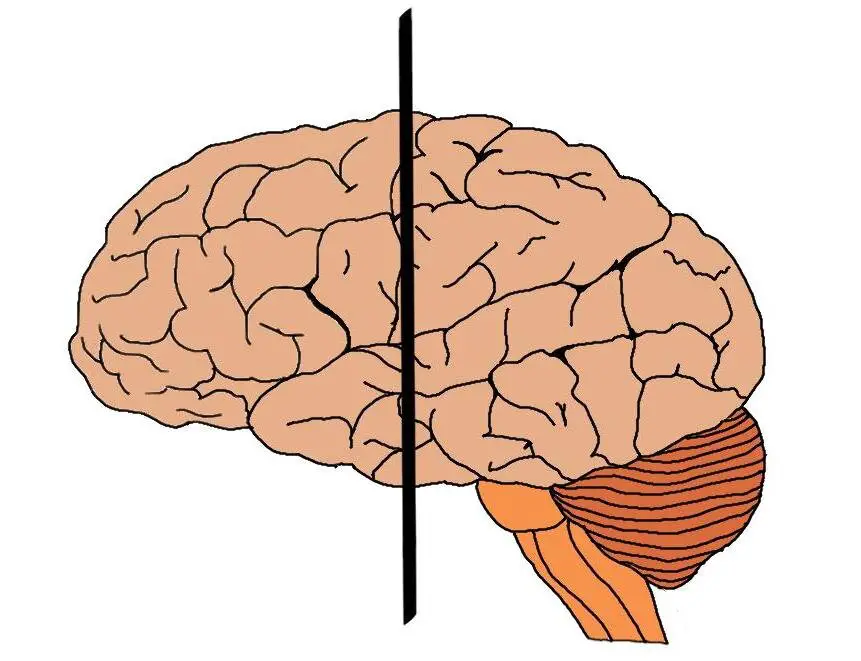
This plane divides the brain into front and back sections, what plane is it?
Frontal
HIPAA stands for...
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
Give an example of a negligent tort.
Any harm caused because you didn't do something correctly.
- Didn't update allergy list and the pt has a bad reaction
- Didn't pay attention while driving and cause an accident
- Didn't watch a child and they fall and get hurt
Gossiping or speaking badly about someone is also known as...
slander/defamation
Define BOTH of the following directional terms:
Posterior and Inferior
posterior: toward the back
inferior: below or under

What cavity is yellow?
What cavity is green?
Yellow: ventral cavity
Green: dorsal cavity
Type of defamation where someone posts something false/damaging on the internet.
Libel
Give an example of a subjective finding.
Give an example of an objective finding.
Subjective: symptoms experienced by the patient (nausea, headache, pain, dizziness, fatigue)
Objective: anything measured (pulse, temp, height, weight, bloodwork, imaging)
Things you're allowed to do based on training, education, and experience is also known as...
scope of practice
Name a body part that is both lateral to and inferior to the umbilical region.
Any body part that is more away from the midline and below the belly button.
Hips, knees, feet, ankles, etc.
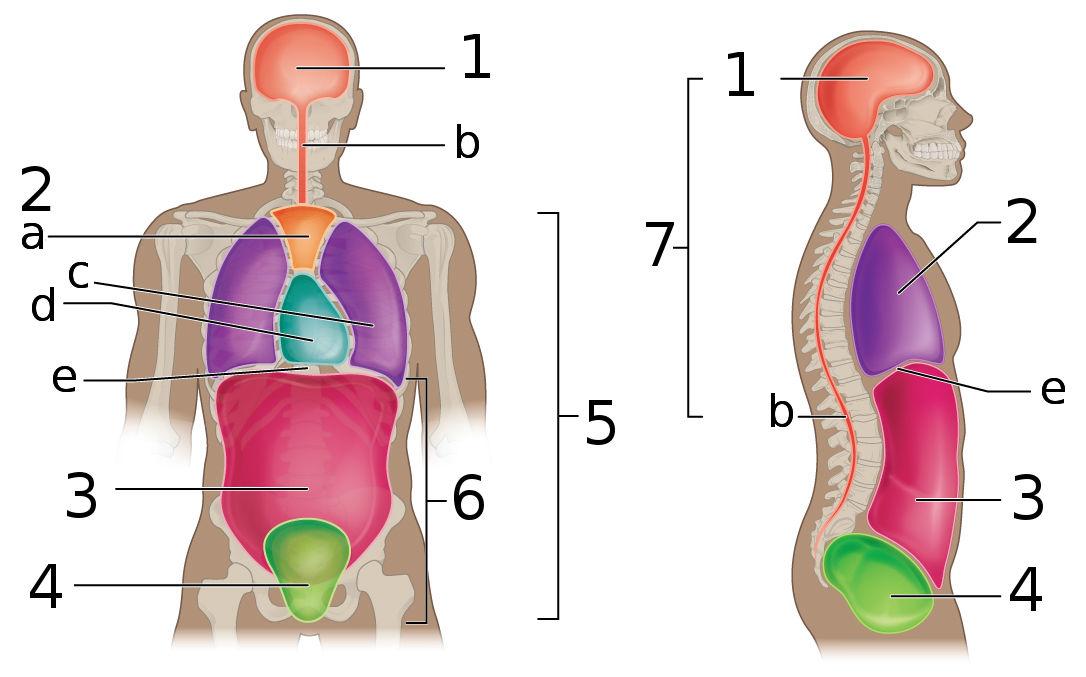
Fill in the blank using medical terminology:
The body area labeled 1 is __________ to the body area labeled 4.
superior
Lifting your shirt for an abdominal exam, holding your arm out for a BP, etc.
Give an example of civil rights and an example of human rights.
Civil rights: things that the government protects you from or gives you the right to do (the right to vote, the right to not be discriminated against in public places, the right to a fair trial)
Human rights: things you get just for being a human (the right to life, right to food and water)
A person appointed to make decisions for a patient if the patient can't make decisions for themselves is also known as...
durable power of attorney
Name 2 organs in the thoracic cavity.
Name 2 organs in the dorsal cavity.
Thoracic: (chest) heart, lungs, esophagus
Dorsal: (back) brain and spinal cord
Name the three midline abdominal regions from top to bottom.
epigastric
umbilical
hypogastric (-ium)
protected patient-physician relationship, anything discussed during a physician appointment is confidential and covered by law
Give three examples of legal disability.
Anyone who can't legally give consent
(minors, someone who is unconscious, someone who is under the influence of alcohol, someone who is not of sound mind, etc.)
Patient centered, relaxed communication that helps the MA gather information from the patient is also known as...
therapeutic communication