An unknown solution is determined to have a pH of 13.2. Is it acidic, basic or neutral?
basic
pH > 7 means a basic solution
Which solution is most concentrated?
5.0 M NaOH
0.25 M NaOH
15.0 M NaOH
15.0 M NaOH
because it has 15 moles of NaOH dissolved in a liter of solution.
VSEPR Theory is based on the idea that same charges repel and opposite charges attract. The attraction and repulsion affects the geometry of the molecule.
When thinking about a water molecule, describe VSEPR's affect on the molecular geometry.
While the electron geometry of water is tetrahedral, the presence of 2 sets of lone pairs on water forces the hydrogens to get closer to each other forcing the molecule into a bent molecular geometry.
The purpose of Lewis Structures is to help determine locations where bonding will occur. When drawing a Lewis structure, what is the maximum number of electrons that can be placed on each side of the symbol?
2
What is the psychoactive ingredient found in all alcoholic beverages?
ethyl alcohol or ethanol or CH3CH2OH
Is zinc hydroxide (ZnOH) soluble in water?
No.
Rule: Hydroxide salts of transition metals are insoluble.
Would you expect the pH of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in an aqueous solution to be <7, >7 or 7?
<7
Which of the following compounds are electrolytes?
NaOH
HCl
C3H5O3
KBr
A central atom has 2 atoms bonded to it and 2 sets of lone pairs. What is the molecular geometry?
bent
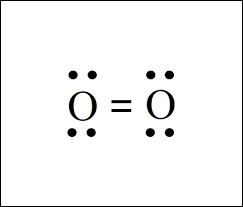
Does this Lewis structure of oxygen satisfy the octet rule for each oxygen?
Yes, each oxygen has a total of 8 electrons.
4 lone pairs + 4 electrons in the double bonds
If a substance is 80 proof, what is the percent alcohol by volume?
40%
Is potassium nitrate (KNO3) soluble in water?
Yes.
Rule: Salts containing nitrate ion (NO3-) are generally soluble.
Identify an aqueous solution of NaOH as a strong acid, strong base, weak acid or weak base.
strong base
Ionic compounds completely dissociate!
Nitric acid (HNO3) is used to recover serial numbers from guns. Concentrated sulfuric acid is 28.9 M. If a 500.0 mL sample of 5.75 M HNO3 is needed, how many mL of concentrated HNO3 should be diluted?
99.5 mL of 28.9 M HNO3 should be diluted.
Using the dilution equation M1V1 = M2V2, solve for V1
No need to convert volumes from mL to L!
A central atom has 3 other atoms bonded to it. One of the atoms is double bonded. There are no lone pairs. What are the electron and molecular geometries of this molecule?
trigonal planar for both
electron geometry and molecular geometry are the same when there are no lone pairs.
A student draws the following Lewis structure for bromine

Is this the correct structure?
Yes. Bromine is in group 7 and has 7 valence electrons in its neutral state. The Lewis structure for neutral Br is
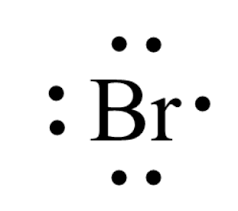 when adding 1 electron in the empty space to the right, the charge decreases from 0 to -1
when adding 1 electron in the empty space to the right, the charge decreases from 0 to -1
It is the dose at which 50 percent of the population experiences death.
What 2 compounds form when KBr and AgNO3 react? Which product precipitates?
AgBr + KNO3
AgBr precipitates
Rule: Salts containing Cl -, Br -, or I - are generally soluble. Important exceptions to this rule are halide salts of Ag+, Pb2+, and (Hg2)2+. Thus, AgCl, PbBr2, and Hg2Cl2 are insoluble.
Identify the aqueous solution of H2CO3 (carbonic acid) as a strong acid, strong base, weak acid or weak base.
weak acid
It donates hydrogen ions in solution, but will not completely dissociate.
A luminol solution is used to detect the presence of blood. What is the molarity of a luminol solution made by dissolving 15.5 g of luminol (C8H7N3O2) in water to a final volume of 90.0 mL?
0.972 M or moles per liter
First calculate molar mass of luminol.
Next use molar mass to convert from grams to moles.
Convert 90.0 mL to L
Then calculate M by dividing the number of moles by the number of liters.
A compound has 3 bonded atoms and 1 lone pair. What are the electron and molecular geometries of this molecule?
electron geometry is tetrahedral
molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal
A student draws a Lewis structure for an anion of nitrogen. Is this the correct structure? Why? Why not?

The correct structure for neutral nitrogen would be:
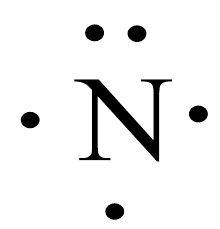
Nitrogen can only accept a total of 3 extra electrons before it has a full octet, therefore there will never be a nitrogen with a -4 charge.
14 grams
What 2 compounds form when CaS and Al(NO3)3 react? Which product precipitates?
Ca(NO3)2 + Al2S3
Al2S3 precipitates.
Rule: Sulfides of transition metals are highly insoluble.
In the following reaction of NaOH with HCl, identify the acid and base.
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) --> NaCl(aq) + H2O
HCl is the acid because it donates H+ ions to the solution.
NaOH is the base because it donates OH- ions to the solution.
A 20.0 mL solution contains 0.5 g of potassium cyanide. According to the table, is this solution saturated, supersaturated, or unsaturated?
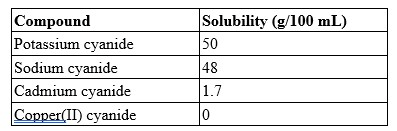
Unsaturated
because KCN has a high solubility of 50 grams per 100 mL and if you calculate the solubility of what is given 0.5g / 20.0 mL = 0.025 g/mL *100 = 25 g/100mL.
You would have to reach 50 g/100 mL to achieve saturation and > 50 g /100 mL to achieve supersaturation.
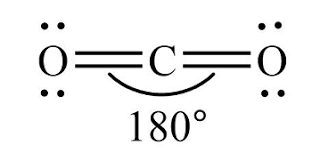
What is the electron geometry of CO2?
linear
Draw the complete Lewis structure for PCl3
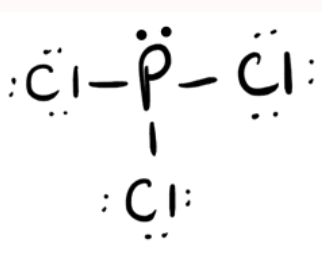
What is the toxic substance formed by metabolism of alcohol in the liver that contributes to hangover symptoms and cellular damage?
Acetaldehyde
What 2 compounds form when Na2CO3 and BaCl2 react? Which product precipitates?
NaCl + BaCO3
BaCO3 precipitates.
Rule: Carbonates are frequently insoluble. Group II carbonates (CaCO3, SrCO3, and BaCO3) are insoluble, as are FeCO3 and PbCO3.