The measure of money supply that is limited to currency and checking deposits (the most liquid elements).
M1
This is the interbank lending rate and represents the primary cost of short-term loanable funds.
Fed Fund Rate
An increase in the money supply leads interest rates to do this.
A decrease in interest rates.
Interest rates and bond prices have this relationship.
They vary inversely.
Hiding money under your bed serves as what type of money function?
Store of Value.
If GDP goes up, what happens to the demand for money?
Increases
How many Federal Reserve banks make up the Federal Reserve System?
12
This is the most immediate and effective tool the Fed uses to impact the money supply?
Open Market Operations
The Fed's inability to stimulate the economy by reducing interest rates is known as the
(a) zero lower bound problem.
(b) zero upper bound problem.
(c) negative interest rate problem.
(d) quantitative easing problem.
(a) zero lower bound problem.
What is the "price" of money?
Interest Rates
Shopping for goods by comparing prices serves as what type of money function?
Unit of Account.
As far as the Fed's mandate, there is a tradeoff between inflation and this.
Unemployment
Who is the current Federal Reserve chair ?
Jerome Powell

The Fed will most likely do this if inflation is above the target rate.
Raise Interest Rates
Name the artist who performs this song...
Jessie J -- "Price Tag"
M1 plus savings deposits, small time deposits, and market fund deposits.
M2.
If the price level in an Economy increases, what happens to the purchasing power of the dollar?
It decreases.
In contractionary monetary policy, does the Fed increase or decease the money supply?
Decrease!
Assume the economy is operating at less than full employment. An expansionary monetary policy will cause interest rates to _________, which will _________ investment spending.
(a) decrease; decrease
(b) decrease; increase
(c) increase; increase
(d) increase; decrease
(b) decrease; increase
What former member of the U.S. Congress tried unsuccessfully to "End the Fed"?
Congressman Ron Paul

Why does the US dollar have value?
Relative Scarcity (to a lesser extent, legal tender and acceptability)
The rate that financial institutions pay to borrow money from the Fed.
Discount Rate.
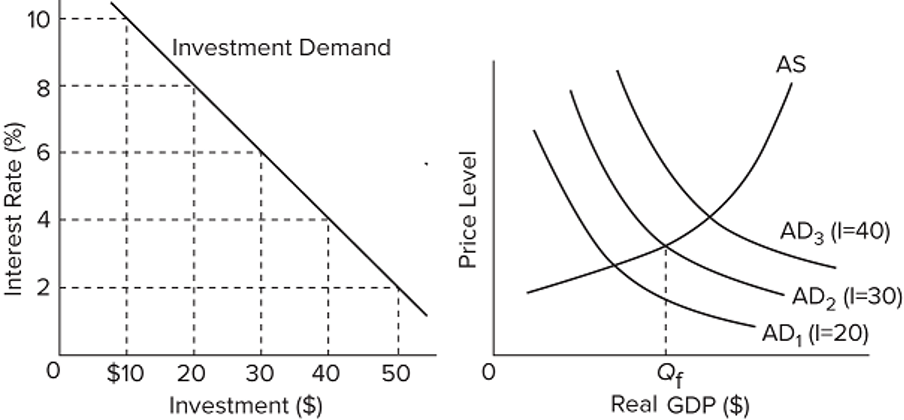
The numbers in parentheses after the AD1, AD2, and AD3, labels indicate the levels of investment spending associated with each curve, respectively. All numbers are in billions of dollars. If the interest rate is 8 percent and the goal of the Fed is full-employment output of Qf, it should
(a) increase the interest rate from 8 percent to 10 percent.
(b) decrease the interest rate from 8 percent to 4 percent.
(c) decrease the interest rate from 8 percent to 6 percent.
(d) maintain the interest rate at 8 percent.
(c) decrease the interest rate from 8 percent to 6 percent.
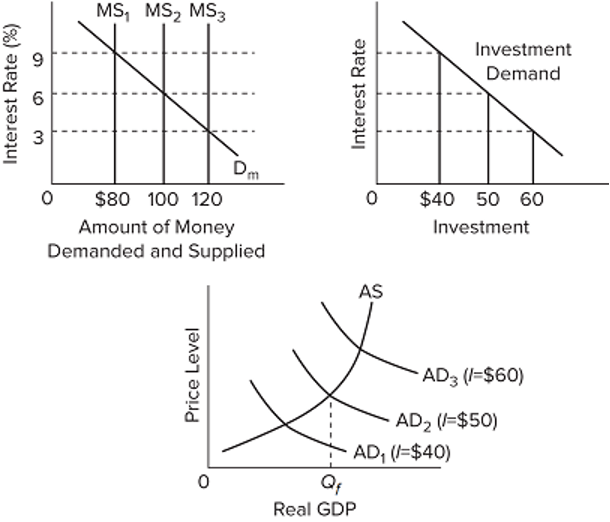
Refer to the diagrams. The numbers in parentheses after the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the levels of investment spending associated with each curve. If the money supply is MS1 and the goal of the monetary authorities is full-employment output Qf, they should
(A) increase the money supply from $80 to $100.
(B) increase the money supply from $80 to $120.
(C) maintain the money supply at $80.
(D) decrease the money supply from $80 to $60.
(A) increase the money supply from $80 to $100.
Name the band that performs this song...
Pink Floyd's "Money"