What is the function of pulmonary surfactant, and what type of cells secreted it?
Pulmonary surfactant decreases surface tension, increasing lung compliance.
It is secreted by type II alveolar cells.
Fill in the blanks!
Movement of gas occurs from areas of __________ partial pressure to __________ higher pressure.
High, low
Put the following structures in order of how urine travels through them.
Renal cortex, Kidneys, Urethra, Renal Medulla, Bladder, Renal pyramids, Minor calyx, Renal Hilus, Major calyx, Ureter
Kidneys → renal cortex → renal medulla → renal pyramids → renal papilla → minor calyx → major calyx → renal hilus → ureter → bladder → urethra
Explain the effect of aldosterone on the concentrations of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions. When is aldosterone released? What is the effect on water reabsorption?
Aldosterone is released in response to high potassium and adds more sodium/potassium on the basolateral membrane. This increases sodium reabsorption (entering blood) and increases potassium secretion (entering urine). Water reabsorption increases.
What is the function of type I alveolar cells?
1. Make up the structure of the alveolar walls and participate in gas exchange.
A patient is experiencing increased lung compliance, meaning that the lungs are able to expand more easily. They are also experiencing reduced recoil of the lungs, making exhalation more difficult. What type of lung disease are they experiencing?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or emphysema.
Are the muscles of inhalation & expiration smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, or skeletal muscle and what division of the nervous system innervates them (in broad terms)?
Skeletal muscle with somatic innervation.
List the three main components that the kidney is responsible for regulating.
1. Blood osmolarity
2. Ionic concentrations
3. Blood volume & volume of extracellular fluid
What is calcitonin? When is it released? How does it affect blood calcium levels. Be specific.
Calcitonin release is triggered by high plasma calcium levels. It is released by C cells in the thyroid gland. It increases bone formation by calcium deposits. It also decreases calcium reabsorption, causing calcium excretion.
What is dyspnea?
Hard / labored breathing.
Define lung compliance.
Lung compliance is the ability of the lungs to expand or stretch.
What are the three reasons that the respiratory system is capable of rapid gas exchange?
1. Thin membrane
2. Large surface area
3. High membrane permeability
Which two structures are responsible for REGULATED reabsorption?
1. Distal convoluted tubule
2. The collecting duct
Which two hormones increase blood calcium levels and how do they each work, specifically? When is each released?
1. 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol is synthesized from vitamin D3 from the skin. It travels to the liver, becomes 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, and then travels to the kidneys and becomes its active from by parathyroid hormone in response to low blood calcium.
2. Parathyroid Hormone
PTH is released by the parathyroid gland when blood calcium levels are low. It stimulates calcium reabsorption, activates 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol in the kidneys (GI calcium reabsorption), and stimulates bone reabsorption.
When you divide and forced expiratory volume (FEV1)/forced vital capacity (FVC), what is this measuring?
FEV1/FVC
The percentage of lung capacity expelled in the first second of exhalation - "FEV1"
BONUS (200 pts) - What are the typical values of this measure for RPD & COPD?
Which muscles contract during passive expiration?
What is the difference between pulmonary ventilation and alveolar ventilation?
Pulmonary ventilation is simply the movement of air into and out of the lungs by bulk flow. It is also called "minute ventilation" TV x RR
Alveolar ventilation is the amount of air that participates in gas exchange. (TV - DS) X RR
Define osmolarity. When osmolarity is high, what hormone should be increased in the bloodstream to counteract this, and why?
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) - also called vasopressin. This is because ADH increases the permeability of the late distal tubules and collecting ducts to water. INCREASES water reabsorption.
Osmolarity - concentration of proteins / solute in the blood
When is ANP secreted? What is its affect on sodium excretion and plasma volume?
It is secreted in response to distension / stretching of the atrial wall (high MAP).
It decreases plasma volume by increasing sodium excretion and the GFR. It also decreases secretion of both renin and aldosterone.
How would an increase in PCO2 in the blood affect the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen, and what direction would the hemoglobin - oxygen dissociation curve shift?
With an increase of PCO2 in the blood, you could assume that metabolic activity has increased, meaning that the cells need more oxygen. Affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen would decrease, causing oxygen to unload into the cells. The curve would shift to the right.
(Carbamino effect)
When the expansion of the lungs is restricted by something OUTSIDE of the lungs, but the patient has healthy lung tissue, what is this disease called? BE SPECIFIC.
Extrapulmonary Restrictive Pulmonary Disease (RPD)
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!!! Answer all parts correctly.
1. Which two muscles are inhalation muscles?
2. Which two muscles are exhalation muscles?
3. Which muscles contract during passive expiration & which muscles contract during active expiration?
4. Describe the changes in thoracic cavity volume and intra-alveolar pressure during expiration compared to inspiration.
Inhalation muscles - diaphragm & external intercostals
Exhalation - internal intercostals and abdominal
No muscles contract during passive exhalation, both exhalation muscles contract during active exhalation.
Inhalation - thoracic cavity volume increases. Intra-alveolar pressure DECREASES. High atm - low alv
Exhalation - thoracic cavity volume decreases. Intra-alveolar pressure INCREASES. High alv - low atm
Why is Bowman's capsule oncotic pressure (πʙᴄ) usually 0 mmHg in a healthy patient?
Also, does this force push or pull? Does it favor or oppose filtration?
It is usually 0 mmHg because there should not be any proteins in the filtrate. It is a pulling force that favors filtration.
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!!!
Draw the renin-angiotensin aldosterone system and explain its impact on aldosterone, ADH, blood pressure, and thirst.
Also, what causes renin to be released initially?
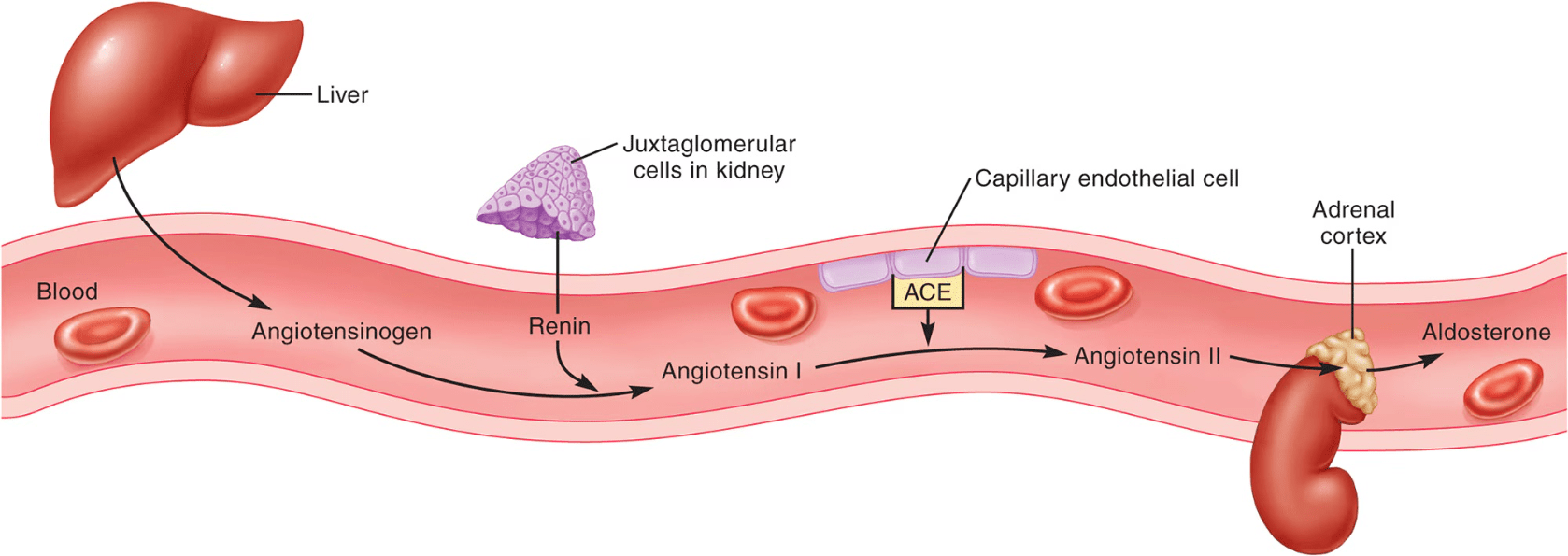 Renin would be released in situations of low mean arterial pressure (MAP)
Renin would be released in situations of low mean arterial pressure (MAP)
1. Angiotensin II increases vasoconstriction, increasing MAP.
2. Angiotensin II stimulates aldosterone secretion, increasing sodium reabsorption and therefore water reabsorption.
3. Angiotensin II stimulates ADH secretion from the posterior pituitary, which increases water reabsorption and increases MAP.
4. Angiotensin II activates the hypothalamus to increase thirst cues. (increased liquid volume increases MAP)
Give three examples of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
1. Chronic & untreated asthma
2. Chronic bronchitis (smoking... too much mucous)
3. Cystic fibrosis (thickened mucous)
4. Obstruction of alveolar ducts