What properties, the following expressions show?
(i) 23+45=45+23
(ii) 13×23=23×13
i.)23+45=45+23 shows the commutative property of addition of rational numbers.
(ii) 13×23=23×13 shows the commutative property of multiplication of rational numbers.
Check whether the linear equation 3x + 5 = 11 is true for x = 2.
LHS & RHS = 11
x=2 is correct
In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. Find x.
x = 3
From the sum of 2x2 + 3xy – 5 and 7 + 2xy – x2 subtract 3xy + x2 – 2.
2xy + 4
What is the additive identity of rational numbers?
0
Verify that x = 2 is the solution of the equation 4.4x – 3.8 = 5.
L.H.S. = R.H.S. = 5
In the given figure find x + y + z.
We know that the sum of all the exterior angles of a polygon = 360°
x + y + z = 360°
Write the following in expanded form:
(i) 70,824
(ii) 1,69,835
7 × 10^4 + 8 × 10^2 + 2 × 10^1 + 4 × 10^0
1 × 10^5 + 6 × 10^4 + 9 × 10^3 + 8 × 10^2 + 3 × 10^1 + 5 × 10^0
Using appropriate properties, solve
2/5 * -3/7 -1/6 * 3/2 + 1/14 * 2/5
-11/28
The sum of a two-digit number and the number obtained by reversing its digits is 121. Find the number if it’s unit place digit is 5.
65
In the given figure ABCD, find the value of x.
x = 140
Give the order of rotational symmetry of each of the following figures:
Solution:
(a) Order of rotational symmetry = 4
(b) Order of rotational symmetry = 5
(c) Order of rotational symmetry = 3
(d) Order of rotational symmetry = 6
(e) Order of rotational symmetry = 3
(f) Order of rotational symmetry = 4
If the cost of 4 1/2 litres of milk is ₹89 1/2, find the cost of 1 litre of milk.
rupees 19 and 8/9
A fruit seller buys some oranges at the rate of ₹ 5 per orange. He also buys an equal number of bananas at the rate of ₹ 2 per banana. He makes a profit of 20% on oranges and a profit of 15% on bananas. In the end, he sold all the fruits. If he earned a profit of ₹ 390, find the number of oranges.
300
In the parallelogram given alongside if ∠Q = 110°, find all the other angles.
angle S = 110
angle P = 70
angle R = 70
In the given figure, PQR is a triangle in which PQ = PR. QM and RN are the medians of the triangle. Prove that
(i) ΔNQR = ΔMRQ
(ii) QM = RN
(iii) ΔPMQ = ΔPNR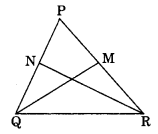
ΔPQR is an isosceles triangle. [∵ PQ = PR]
⇒ 12 PQ = 12 PR
⇒ NQ = MR and PN = PM
(i) In ΔNQR and ΔMRQ
NQ = MR (Half of equal sides)
∠NQR = ∠MRQ (Angles opposite to equal sides)
QR = RQ (Common)
ΔNQR = ΔMRQ (By SAS rule)
(ii) QM = RN (Congruent parts of congruent triangles)
(iii) In ΔPMQ and ΔPNR
PN = PM (Half of equal sides)
PR = PQ (Given)
∠P = ∠P (Common)
ΔPMQ = ΔPNR (By SAS rule)
Rajni had a certain amount of money in her purse. She spent ₹ 10 1/4 in the school canteen, bought a gift worth ₹ 25 3/4 and gave ₹ 16 1/2 to her friend. How much she have to begin with?
52 1/2
A steamer goes downstream from one point to another in 7 hours. It covers the same distance upstream in 8 hours. If the speed of stream be 2 km/h, find the speed of the steamer in still water and the distance between the ports.
30 km/h , 224 km.
How many diagonals will a tetrakaidecagon have?
14 (14-3) / 2
7 x 11
77
what mathematical numeral system do we use now?
Hindu-Arabic numerals