Identify the glands that perform the excretory function in prawns.
Antennal or green glands
What is the excretory product of reptiles?
Uric acid is the excretory product of reptiles.
______________ is the process of voiding urine from the urinary bladder.
Micturition
Atrial Natriuretic factor (ANF) can cause ___________________ and thereby decrease the blood pressure.
Vasodilation
Mention the substances that exit from the tubules in order to maintain a concentration gradient in the medullary interstitium.
Urea and sodium chloride
Differentiate Glycosuria and Ketonuria.
The presence of glucose in the urine of a diabetic patient.
The presence of ketone bodies in the urine of a diabetic patient.
What are the main processes in urine formation?
Glomerular filtration, reabsorption and tubular secretion.
Mention the substances that exit from the tubules in order to maintain a concentration gradient in the medullary interstitium.
Urea and sodium chloride
Name the blood vessel that carries blood
a) to glomerulus
b) from glomerulus
b) Efferent arteriole
Sort out the following into actively or passively transported substances during reabsorption of GFR.
Glucose, amino acids, nitrogenous wastes, Na+, water.
Actively transported substances:
glucose, amino acids, Na+
Passively transported substances:
nitrogenous wastes, water
What is the value of GFR in a healthy human being?
125ml/min or 180 litres per day
What is the driving force for glomerular filtration?
The blood pressure in the glomerular capillaries
Give the values of osmolarity of filtrate in the nephron in i) the cortex and ii) inner medulla respectively.
300 mOsmol L
1200 mOsmol L
Mention the two factors for the increase in the osmolarity of filtrate from the cortex to the inner medullary interstitium.
The proximity between the Henle's loop and vasa recta
The counter current mechansim in the above parts.
Name the layers that form the filtration membrane in a nephron.
Endothelium of glomerular capillaries
Epithelium of Bowman;'s capsule and
Basement membrane between the above.
In which part of the nephron does filtration take place? How much of blood is filtered in a minute?
Filtration occurs from the glomerulus into Bowman's capsule.
About 1100-1200ml of blood is filtered per minute.
Name the two groups of nephrons on the basis of their position in the kidney. How are they different from each other?
Juxtaglomerular Nephrons
Glomeruli are placed close to the inner margin of the cortex.
They have long loop of Henle.
Loops are found deeper in the medulla.
Cortical Nephron
Glomeruli are present in the outer margin of the cortex.
They have short loops of Henle.
Loop extends only to a short distance in the medulla.
Indicate whether the following statements are true or false:
(a) Micturition is carried out by a reflex.
(b) ADH helps in water elimination, making the urine hypotonic.
(c) Protein-free fluid is filtered from blood plasma into the Bowman’s capsule.
(d) Henle’s loop plays an important role in concentrating the urine.
(e) Glucose is actively reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule.
a) True
(b) False
ADH helps in reabsorption of water causing the urine to be hypotonic.
(c) True
(d) True
(e) True
What is micturition reflex?
The neural mechanism that cause the voiding of urine from the urinary bladder, constitute the micturition reflex.
How does the filtrate become hypertonic in the descending limb of Henle's loop?
Descending limb of Henle's loop is permeable to water, hence the filtrate becomes hypertonic as it moves down.
Explain the function of renin produced by the JGA of kidney.
Renin convert angiotensinogen to angiotensin, which increases glomerular blood pressure.
Explain the function of vasa recta.
It helps to retain reabsorbed ions and urea in the interstitial fluid of the medulla, to maintain its high osmotic pressure.

Afferent arteriole
Afferent arteriole
Bowman's capsule
Proximal convoluted tubule
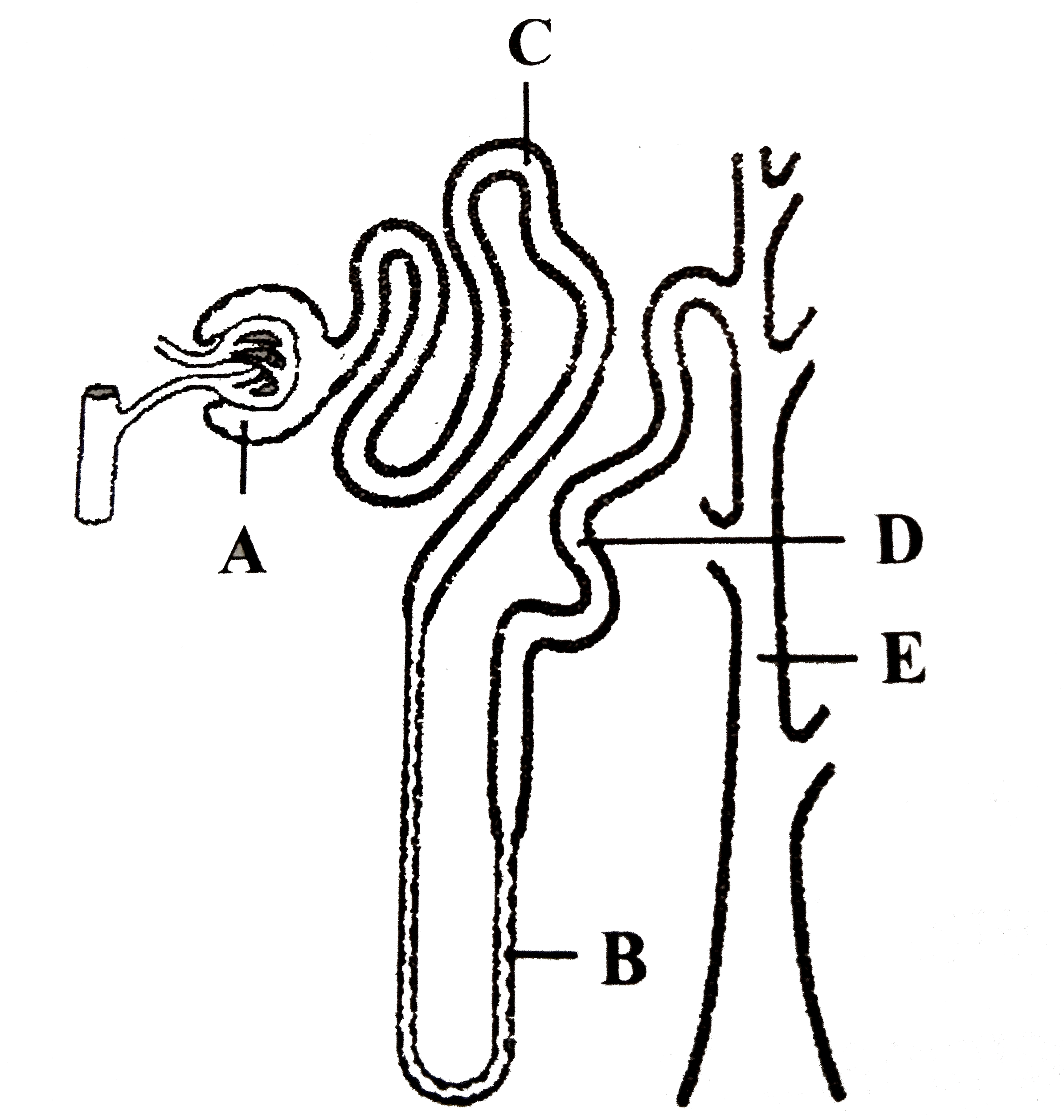
Bowman's capsule
Ascending limb
Distal convoluted tubule
Collecting duct
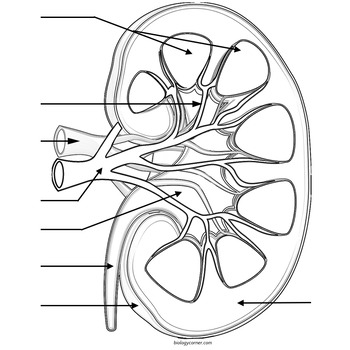
Medullary pyramid
Calyx
Renal artery
Renal vein
Renal pelvis
Ureter
Renal cortex
Renal capsule