What is the Bladder
Blood enters the kidney through this artery.
What is the renal artery?
This process transfers essential solutes back into the blood.
What is reabsorption?
This hormone makes the collecting ducts more permeable to water.
What is antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
Name the tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
What are the ureters?
These tiny structures are the functional units of the kidney.
What are the nephrons?
Which of the following materials would not usually be found in glomerular filtrate?
Water , Protein, Urea, Glucose
What is protein?
This hormone plays a critical role in regulating blood pressure.
What is aldosterone?
The structure that acts as a valve at the base of the bladder.
What is the Urinary Sphincter
Blood leaving the kidney is ______ in oxygen and ______ waste?
What is leaving the kidney is LOW in oxygen and LOW in waste?
Why is the descending limb so efficient at reabsorbing water?
What is the salty medulla that causes an osmotic gradient and water reabsorption? (passive transport)
Aldosterone increases water reabsorption by?
What is increasing sodium retention and creating an osmotic gradient?
The liver converts ammonia into this less toxic compound.
What is urea
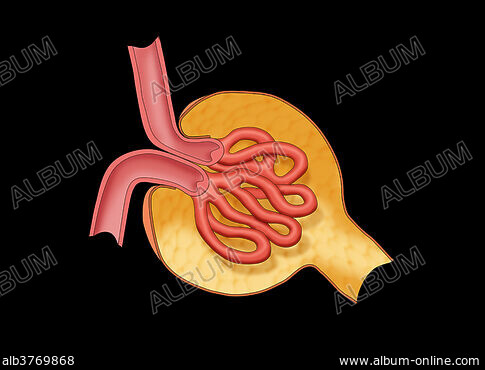 What are the two structures in the Image.
What are the two structures in the Image.
What are the Bowermans Capsule and Glomerulus?
Tubular secretion of glucose from the glomerular filtrate into the capillary bed surrounding the nephron occurs in which of the following?
What is the proximal tubule?
When a person undergoes water loss because of heavy perspiration, the loss of water from the blood will cause
What is the Increased production of ADH?
What are the three steps in the formation of urine?
What is Filtration, Reabsorption and secretion?
The high-pressure capillary bed where filtration begins.
What is the glomerulus?
By which transport process are most molecules secreted from the blood into the distal tubule?
What is active transport?
These glands release aldosterone.
What are the adrenal glands?