____________an observer will likely take what is known as "ABC data" and record the antecedents of a behavior, a description of the behavior that occurred, and consequences that follow the behavior.
What is Descriptive assessment
Typically a ______________ is conducted to determine the function of behavior.
What is a functional behavior assessment (FBA)
A ______________ works by reinforcing target or problematic behavior for a brief period of time. While this appears to be alarming and counterproductive, it allows us to conclusively demonstrate which functions (or outcomes) the target behavior is most sensitive to. This is particularly important when a behavior has been difficult to address. We compare the rate of behavior in the four experimental conditions to the baseline or control (play) condition. It is expected that the rates of behavior are lowest in the play/control condition since there is no apparent motivation for challenging behavior. Research demonstrates that there is no lasting harm to the brief periods of reinforcing problematic behavior that are necessary in a functional analysis.
What is a functional Behavior analysis?
"Say my name, say my name, if no one is around you, say ______, I love you!" Finish the lyrics.
A honey
B none of these
C sweetie
D sexy
_____________ are everyday life events that have not been systematically arranged (Cooper, Heron, and Heward, 2007).
What is Natural occuring conditions
What are the five conditions to a functional behavior analysis (FBA)?
Alone
Attention
Demand
Play/ Control
tangible
Functional Analysis is often used by researchers and practitioners as part of the FBA process. While an FBA does not have to include an FA, it can be beneficial in some scenarios. In research, an FA is used to demonstrate that behavior is motivated by a certain function, often as part of evaluating some sort of treatment. In practice, FAs can be used if results from behavior data collection are unclear, or if a behavior is severe and requires a definite determination of function before beginning treatment.
What is the difference between an FA and an FBA.
"Hey Mr. DJ, put a _________ on, I wanna dance with my baby". Finish the lyrics.Hint
A. record
B. casette
C. cd
D. not listed
What is a Record
Dr. Brown-Davis completes a ___________ of Jada’s problem behavior over 3 days. He observes Jada across her school day, including arrival and departure. He pays particular attention to the events leading up to, during, and immediately following problem behavior. He also takes careful note of the contexts in which Jada demonstrates safe behavior. He writes a narrative account of his full-day observation on the first day. On the second day, he takes a narrative account along with ABC data for each episode of problem behavior. On the third day, Dr. Brown-Davis utilizes structured ____________ methodology. This involves setting up antecedents (such as staff members ignoring Jada or taking a toy away from her) and allowing the episodes to proceed naturally from there.
What is a descriptive assessment
Based on the results of the indirect (record reviews, interviews) and descriptive assessments, Ms. Bailey decides that the following functional analysis conditions will be conducted: demand/escape + access to tangible, and a control condition. These conditions are based on the previous assessments, and are part of a synthesized contingency analysis. As a scientist practitioner, Ms. Bailey remains ready to design further conditions, isolate contingencies, or change her assessment direction based on findings.
What is a Funtional Analysis
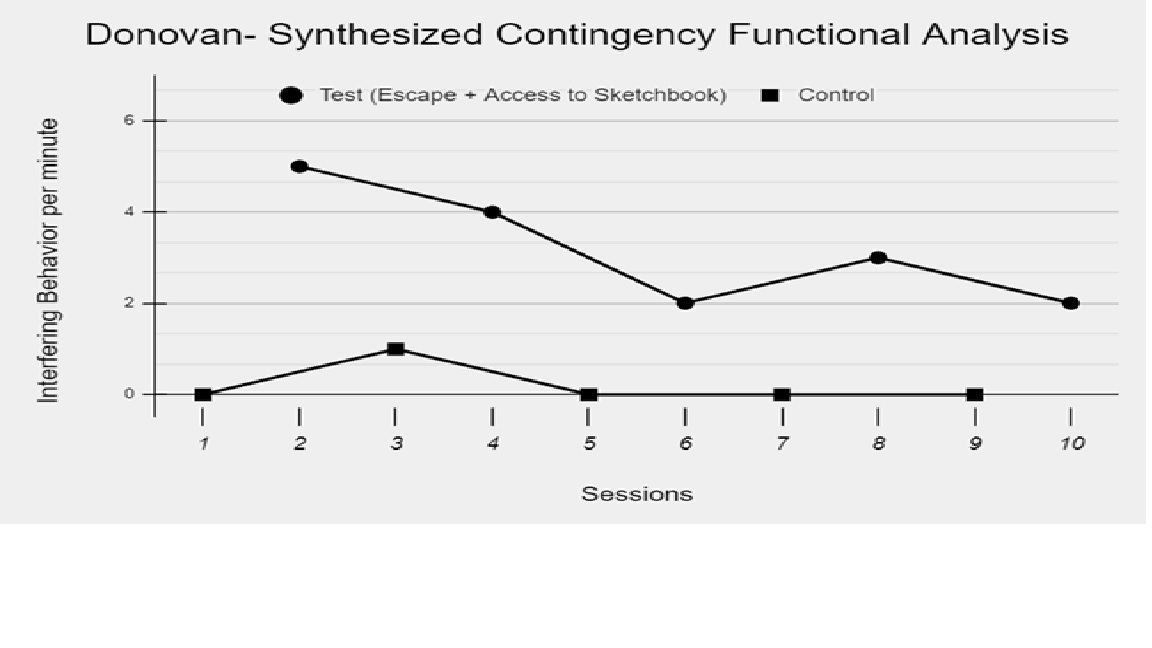
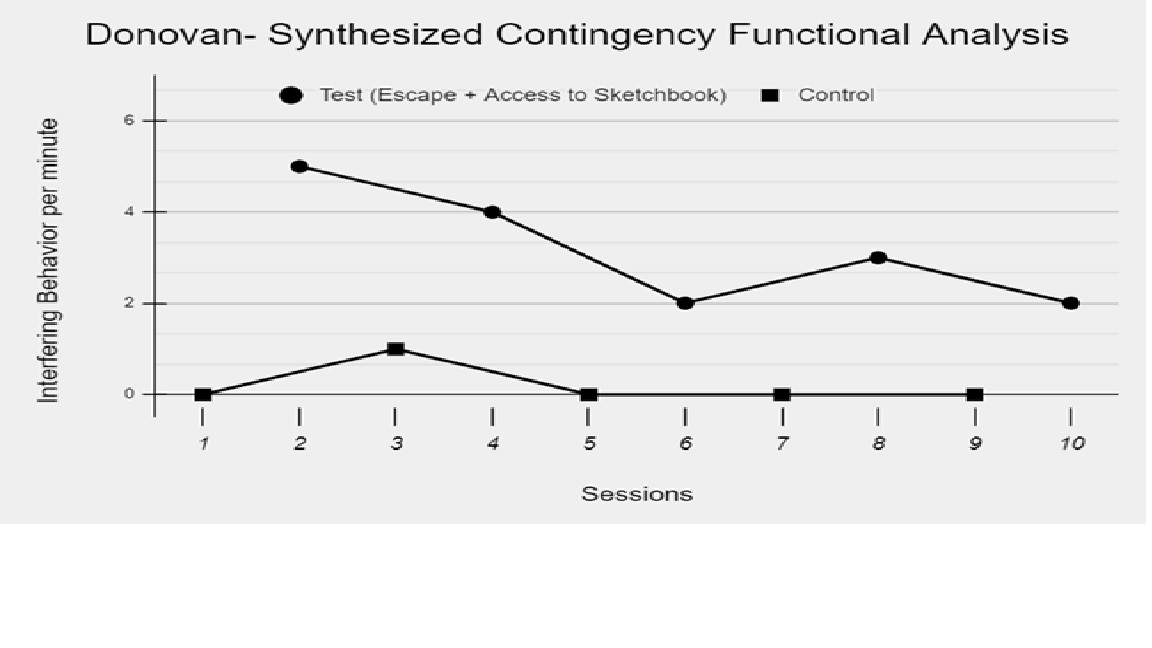
Ms. Bailey graphs and visually analyzes the data on Donovan’s problem behavior during the FA. She notices that the problem behavior occurred only one time during the control condition, meaning that the condition likely met Donovan’s needs, making problem behavior unnecessary. Ms. Bailey also sees clear differentiation between the control and test (demand + access to tangible) conditions. Overall, the pattern of responding from Donovan suggests to Ms. Bailey that Donovan’s behavior is maintained by escape from reading tasks to access his sketchbook.
"If you wanna be my _______, you gotta get with my friends!" Finish the lyrics.
______________ can be contrasted with a clinical or laboratory arrangement of variables. Essentially, an observer will take data in these conditions when the person under observation is at home or in the community doing their normal daily activities.
What is Natural occuring conditions
Based on the results of the indirect (record reviews, interviews) and descriptive assessments, Dr. Brown-Davis decides that the following functional analysis conditions will be conducted: attention, tangible access, demand/escape, and control/play. These are the four most commonly conducted sessions are part of isolated contingency analyses. As a scientist practitioner, Dr. Brown-Davis remains ready to design further conditions, or change his assessment direction, based on findings.
What is an FA?
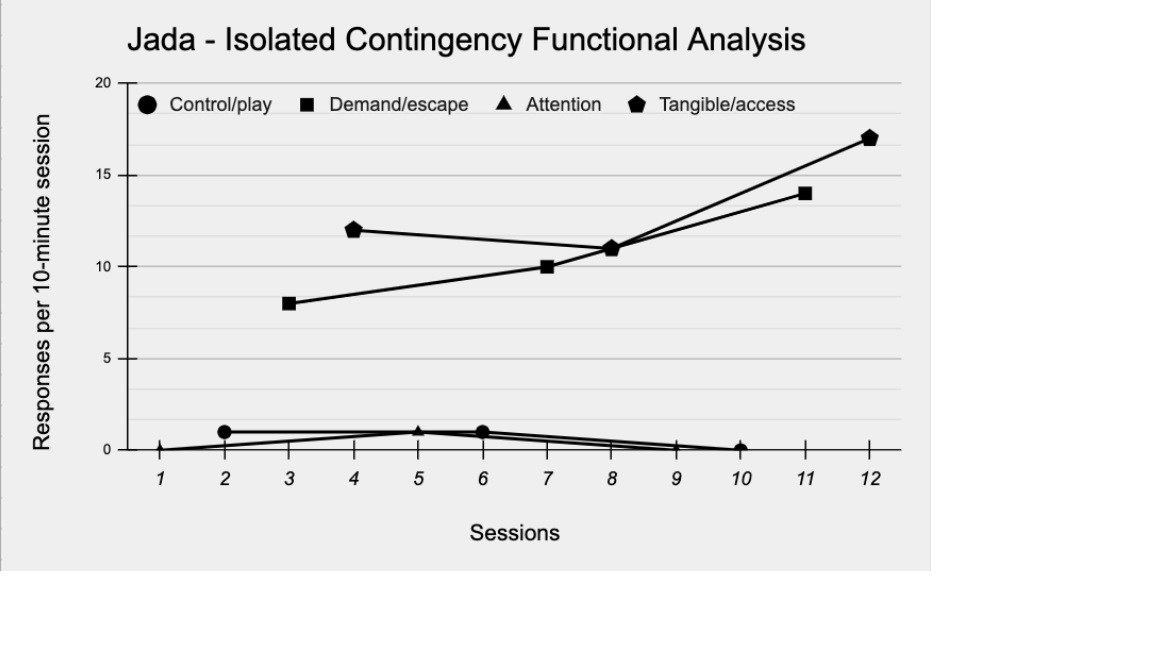
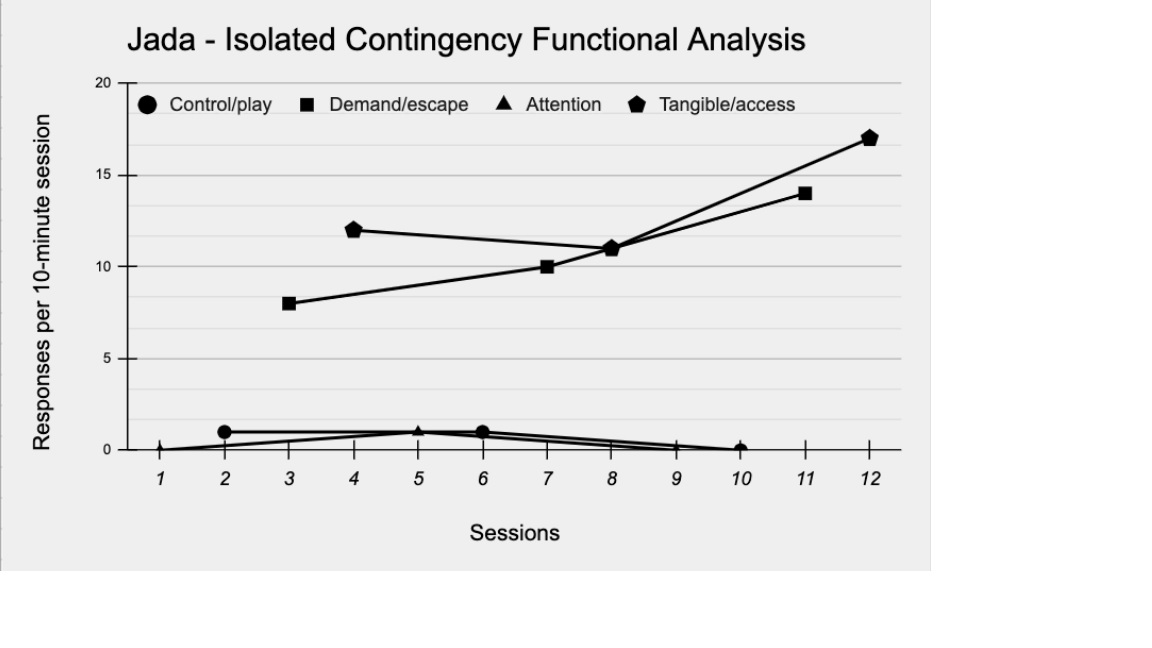
Dr. Brown-Davis graphs and visually analyzes the data on Jada’s problem behavior during the FA. He notices that the problem behavior did not occur during the play/control conditions. This suggests that the condition adequately met Jada’s needs, making problem behavior unnecessary from her point of view. Dr. Brown-Davis also sees clear differentiation between the play/control and the demand/escape conditions, and between the play/control and tangible/access conditions. He notices that low rates of problem behavior occurred during the attention condition. Overall, the pattern of responding from Jada suggests to Dr. Brown-Davis that her behavior is not maintained by automatic reinforcement. (If it were, the behavior would likely have occurred across all conditions without clear differentiation).
I bust the windows out your car And no it didn't mend my broken heart........
I'll probably always have these ugly scars But right now I don't care about that part I bust the windows out your car After I saw you layin' next to her I didn't wanna but I took my turn I'm glad I did it 'cause you had to learn
Ms. Bailey completes a __________ of Donovan’s interfering behavior over the course of 2 days. Ms. Bailey observes Donovan in several classes, making sure to include a sampling of classes that interfering behavior reliability occurs in, as well as classes that Donovan exhibits appropriate behavior. The first day, Ms Bailey simply watches and takes narrative and ABC data. The second day, Ms. Bailey utilizes a structured descriptive assessment. A summary of the assessment follows:
Donovan was observed during 4 classes each day (Math, Reading, Art, and Science). Donovan walked out of class 6 times over the course of two days. Donovan completed 4 out of 8 total assignments provided. Of the 6 times leaving class, 4 times were during Reading, and two were during Science. Donovan was gone an average of 11 minutes each time, leading to a total loss of instruction totaling 66 minutes.
Of the 6 times leaving class, presentation of work demands, specifically work demands that required a substantial amount of reading (more than 1 paragraph) directly preceded the behavior. Donovan’s behavior resulted in individually-mediated escape of the work demands and the instructional context all 6 instances of leaving class. Once in the hall Donovan would walk to the stairwell with his sketchbook and lay down and draw, at no point did he engage with other peers in the hall.
Donovan completed 4 of 8 work tasks presented over the course of the two days he was observed. 2 of the tasks were math worksheets and 2 were Art tasks. Donovan did not complete any assignments that included reading more than a paragraph of instructions/content.
What is a Descriptive Assessment
When would you use an FBA?
To determine function of the behavior.
What are some types of FAs?
The first of these is a brief FA, which provides shorter conditions to determine the possible maintaining variables of behavior. The conditions with the highest rates of problem behavior are then compared to a reversal, where an appropriate response is reinforced and challenging behavior is ignored. This rapid reversal can be used to identify whether there is a functional relationship between the challenging behavior and the reinforcer (e.g., attention, tangible item, escape, etc.)
A trial-based FA uses short, discrete trials interspersed throughout the client’s typical schedule. The client is exposed to the evocative condition (e.g. ignoring during “attention” condition) for 1 minute. If the client engages in problem behavior, the implementer provides the reinforcer for 1 minute. The frequency of the behavior in the first trial (e.g., ignoring) and the absence of behavior in the second (e.g., attention provided) is compared to determine the function.
Finally, a latency FA analyzes response latency (or time until behavior). Evocative conditions are terminated following occurrence of problem behavior and delivering the reinforcer. The time until the first challenging behavior is compared between conditions to determine the most likely function of the behavior.
Variations in FA methodology allow for different condition lengths and measurements that can be shorter than analogue FA and/or can be embedded into daily routines. Certain settings such as schools do not have resources or personnel to conduct analogue functional analyses. These variations allow practitioners in these settings flexibility, while still maintaining the internal rigor of experimental analysis.
Can you finish the lyric
First I was a afraid, I was petrified...........
Kept thinking, I could never live, without you by my side but then I spent so many nights thinking, how you did me wrong