An opening made to allow the passage of drainage.
What is an -ostomy?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 42 Table 42.2 p. 1260
This type of surgery cures the problem or condition.
What is curative?
Table 42.1 p. 1260 Ch. 42
If the patient uses Garlic or Ginkgo Biloba as a daily supplement, we need to report it during the preop education because it increases the risk of _______.
What is bleeding?
Ch. 42 p. 1264 Table 42.3
The almighty "checklist" should be completed during this phase.
What is preoperative?
From lecture & the slides for Ch. 42 and the Venn diagram we created together in class.
List four signs & symptoms of internal hemorrhage.
(Answers will vary)
What are drop in BP, increase in HR, cool/clammy skin, reduced UOP, restlessness, apprehension, pallor or cyanosis?
Ch. 42 p. 1287
A surgery for the fixation of something.
What is a -pexy?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 42 Table 42.2 p. 1260
This type of surgery is for the relief of or reduction of intensity of symptoms, and will not produce a cure.
What is palliative?
Table 42.1 p. 1260 Ch. 42
For the patient experiencing anxiety preoperatively, anesthesia may administer this class of medication to reduce the symptoms and produce a calm feeling.
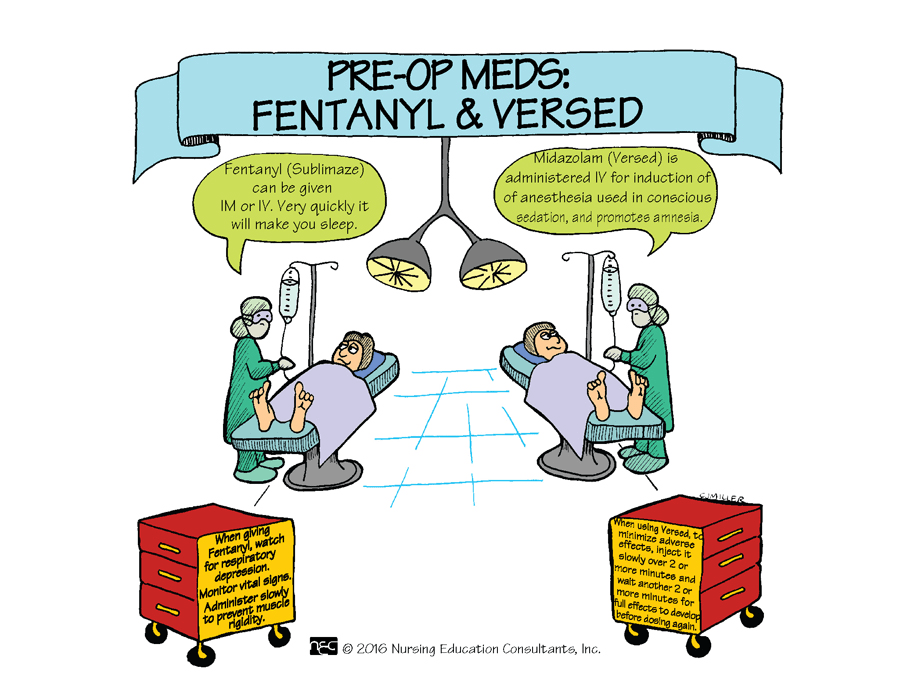
What are benzodiazepines?
Also accepted: valium, versed
Table 42.5 p. 1278
Ch. 42
Positioning of the patient occurs during this phase of surgery.
What is intraoperative?
CH. 42 p. 1281
Because lung ventilation is vital, the patient should be assisted to T, C, & DB every ________ and to use the IS _________ times every hour.
What are every 1-2 hours and use the IS 10 times each hour the patient is awake.
Ch. 42 p. 1289
An opening into something.
What is an -otomy?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 42 Table 42.2 p. 1260
What is ablative surgery?
Table 42.1 p. 1260 Ch. 42
This type of anesthesia produces amnesia, analgesia, muscle paralysis and renders the patient unable to protect his or her own airway.
What is general anesthesia?
Ch. 42 p. 1279
The patient has their artificial airway removed and the focus is on the respiratory and GI systems.
What is the post-op phase?
Ch. 42 p. 1285
List four benefits of early post-op ambulation.
(Answers will vary)
What are increased circulation, renal function, mental alertness, metabolism, urinary elimination. peristalsis, and greater availability of nutrients for wound healing as well as prevention of atelectasis, abdominal distention, paralytic ileus and thrombophlebitis?
Box 42.10 p. 1291 Ch. 42
In this type of surgery, the patient enters the surgical setting, has the surgical procedure and is discharged to home the same day.
What is ambulatory or outpatient surgery?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 42 p. 1260 Table 42.1
This type of surgery involves the complete replacement of a malfunctioning organ.
What is a transplant surgery?
Table 42.1 p. 1260 Ch. 42
Oral airways are often used on patients in the surgical suite because this is the #1 airway obstruction.
What is the tongue?
Ch. 42 p. 1280 Figure 42.5
Wound dehiscence and/or evisceration can occur during this phase.
What is post-op?
Ch. 42 p. 1288
A significant decrease in or absence of intestinal peristalsis that may occur after abdominal surgery, peritoneal trauma, or severe metabolic conditions. It often requires the patient to have a nasogastric tube placed.
What is a paralytic ileus?
Ch. 42 p. 1292
The two types of surgical seriousness are ______ & ________.
What are major and minor?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 42 p. 1260 Table 42.1
This type of surgery allows for surgical exploration for diagnosis confirmation and may involve the removal of tissue for further testing.
What is a diagnostic surgery?
Table 42.1 p. 1260 Ch. 42
Because anesthesia depresses ______ function, it may take 6-8 hours for it to return. Watch your post-op patient for distention!
What is urinary function?
Ch. 42 p. 1290
The time-out is performed.
What is pre-operatively?
Ch. 42 p. 1283
A rare genetic disorder caused by uncontrolled skeletal muscle contractions which can lead to a fatal elevated temperature is called _________________.
What is malignant hyperthermia?
Ch. 42 p. 1286
****Put this number in your cell phone
1-800-644-9737 it is the MH HOTLINE- call them if you EVER suspect your patient has MH and they will walk you through the Dantrolene protocol.