System
from A to Z
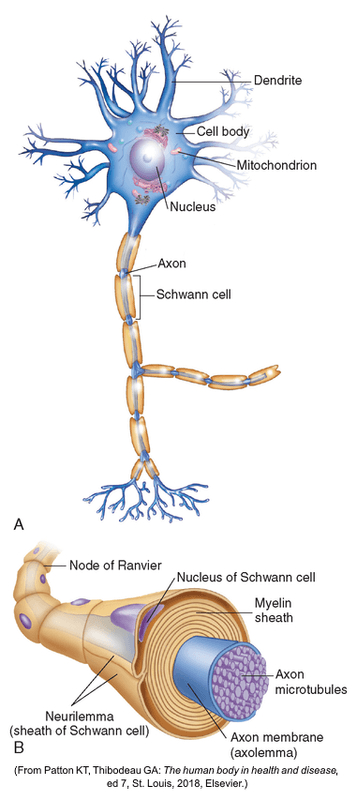
This is the basic cell of the nervous system.
What is a neuron?
This Cranial nerve (Cranial Nerve I) is responsible for the sense of smell.
What is the Olfactory nerve?
When using the mnemonic A-V-P-U to determine responsiveness, the "P" indicates that the patient is responsive to __________.
What is pain?

Often beginning in the adolescent years and presenting with an aura, this type of headache can have multiple triggers.
What are migraine headaches?
Abnormal electrical activity in the brain can result in ____________ activity.
What is seizure?
A slowing down in the initiation and execution of movement is termed ___________.
What is bradykinesia?
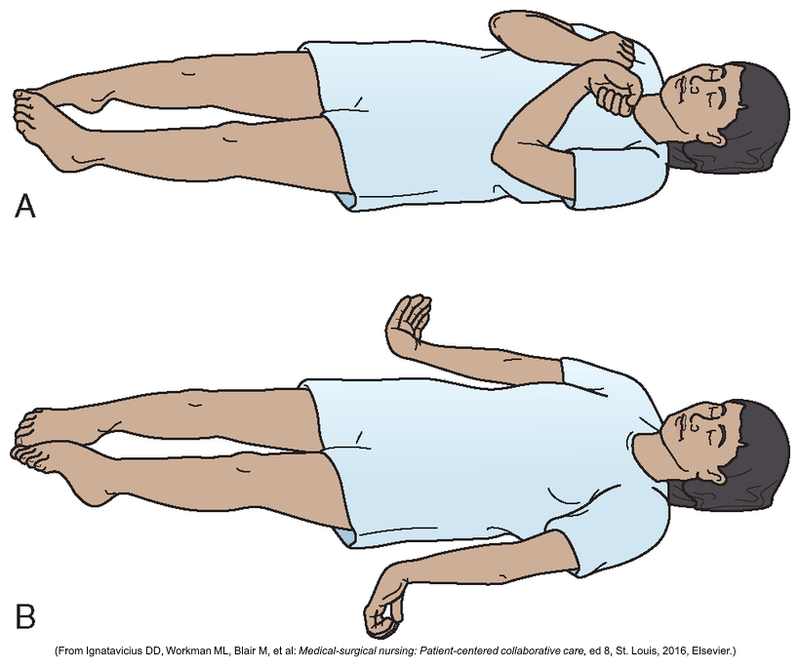
Flexion of the arms, wrists, & fingers, with adduction of the upper extremities, and extension, internal rotation and plantar flexion of the lower extremities describes this type of posturing, _____________.
What is decorticate?
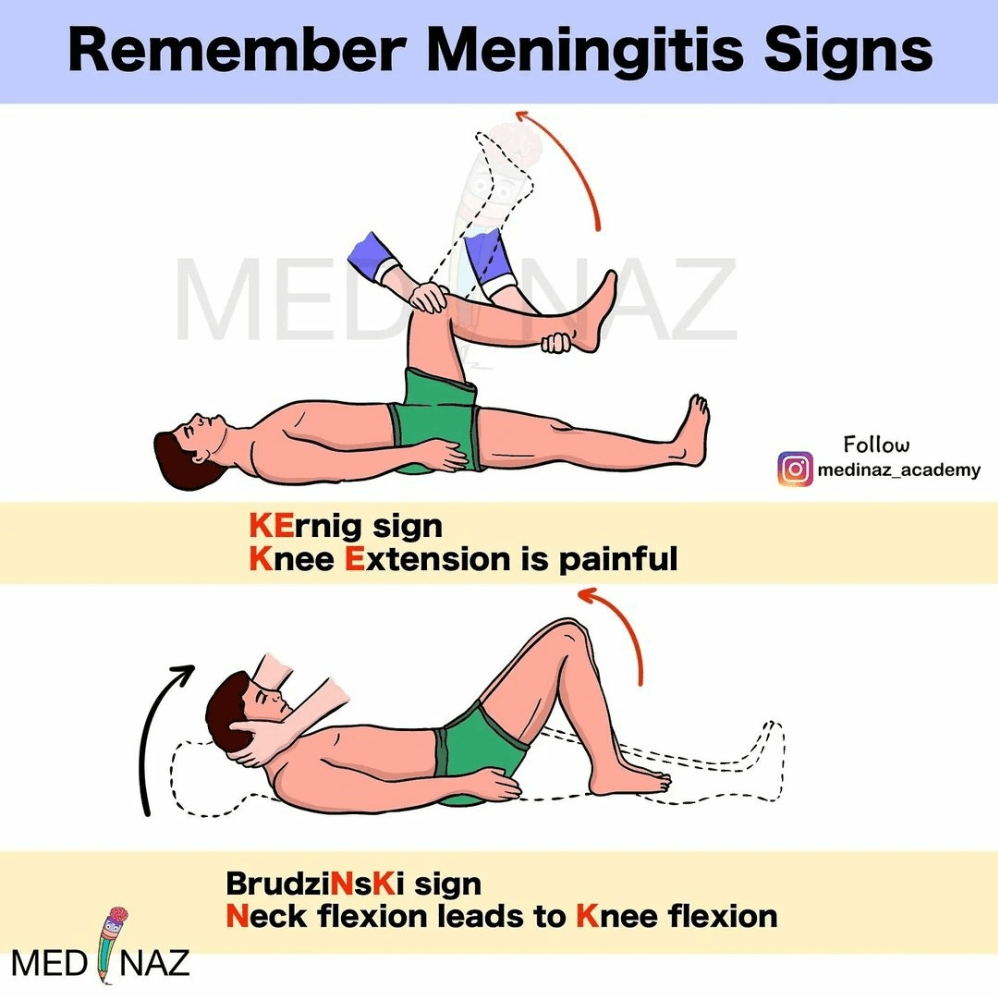
"Towards the core"; Shown below in picture "A":
This sign is elicited when the patient cannot extend the legs completely without extreme pain, ______________; this other sign is elicited when a patient's neck is flexed, the hips and knees flex also due to extreme stiffness from inflammation, ___________.
What are Kernig's sign and Brudzinski's sign?
This type of pain may result from post-herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathies, phantom limb pain, or trigeminal neuralgia.
What is neuropathic pain?
Between the neurons, there are gaps called _______, where nerve impulses get transmitted through with neurotransmitters.
What is a synapse? 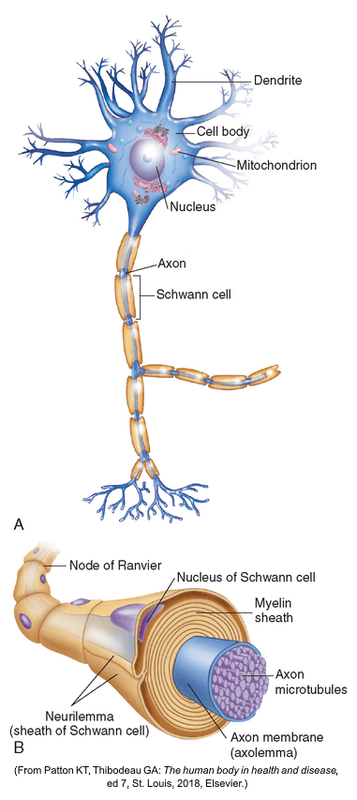
This Cranial nerve (Cranial Nerve II) is responsible for vision.
What is the Optic nerve?
The minimum score on the Glasgow Coma Scale that can be awarded is _____.
What is three?

List three possible triggers for recurring headaches.
What are: (any 3 would be accepted)
1. fatigue
2. alcohol
3. stress
4. seasonal climate changes
5. hunger
6. menstruation
7. allergies
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 16 p. 1915
This most common type of seizure involves stiffening of the body with jerking of the extremities.
What is a Generalized Tonic-Clonic seizure (formerly known as a grand mal)?
List the three components of the classic Parkinsonian triad.
What are:
1. tremor
2. rigidity
3. bradykinesia
Strokes are classified as ________ or __________.
What are ischemic or hemorrhagic?
If the meningitis is thought to be bacterial, ___________ antibiotic therapy may be ordered for close contacts of the patient.
What is prophylactic?
Bacterial meningitis is deadly. The patient should be on droplet precautions and family members are likely to be treated.
Paralysis of one side of the body is termed _________.
The two divisions of the nervous system are the CNS and the PNS. The CNS is made up of the _______________, and the PNS is divided further into the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
What are the brain & spinal cord?
This Cranial Nerve (Cranial Nerve VII) is responsible for the sense of hearing.
What is the Acoustic Nerve?
The body's sense, based on internal stimuli, of its own position & limb movements is called _____________.
What is proprioception?
Often treated with nonopioid analgesics, these headaches often arise from psychological problems related to stress, or from medical problems like cervical arthritis.
What are tension headaches?
This is the period following a seizure in which the patient is groggy, exhausted, and may be disoriented.
What is the post-ictal phase?
What is:
1. appetizing
2. cut up into small bites
3. well-balanced (fiber: fruits & veggies to reduce constipation)
4. able to be chewed and swallowed easily
5. encourage oral fluids
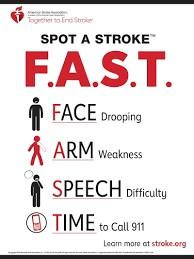
The mnemonic F.A.S.T. stands for ________, _________, ____________, ____________.
What are Face, Arms, Speech, Time?
Epidemic encephalitis is transmitted by these two vectors, __________ & ___________.
What are ticks and mosquitoes?
This type of tremor is commonly seen in Parkinson's patients.
What is pill-rolling?
This most distal area of the brain controls heartbeat, rhythm of breathing, swallowing, coughing, sneezing, vomiting and hiccups.
What is the medulla oblongata?

This Cranial nerve (Cranial Nerve X) is responsible for functions of sensations in the throat, larynx, and thoracic & abdominal organs, swallowing, and decreasing heart rate and/or increasing peristalsis.
What is the Vagus nerve?

A change in this is often the very first sign of a neurological problem or increased intercranial pressure.
List three diagnostic tests that may be utilized for diagnosing the type of headache present.
What are:
1. CT scan
2. MRI
3. Lumbar puncture (video on D2L)
The most important thing to remember when caring for a patient experiencing a seizure is ________________.
Stay with the patient. Make sure they are lowered gently onto the floor and protect their head. If possible, turn their head to one side to facilitate saliva drainage.
This is the gold standard prescription for Parkinson's disease. It improves the modulation of voluntary nerve impulses, enhancing movement and helping to decrease rigidity and bradykinesia.
What is carbidopa-levodopa?
(Brand name: Sinemet)
___________ is a total loss of comprehension and use of language, whereas __________ is difficult or poorly articulated speech.
What are aphasia and dysarthria?
List three things you can educate your patient regarding reducing mosquito exposure, thereby reducing the risk for West Nile Virus.
What are:
1. Limit outdoor activities between dusk & dawn.
2. Place mosquito netting over baby cars eats and strollers
3. Use mosquito repellants that contain DEET.
4. Install or repair window screens to prevent entry into the home
5. Store containers inside or upside down so water doesn't pool inside them to attract mosquitoes
If there is clear drainage from the nose following a head trauma, the nurse can check it for _______ with a test strip to determine if it is CSF.
What is glucose?
If a head injury or skull fracture is suspected, care should be taken to prevent the patient from becoming agitated or increasing the ICP- no loud stimulus, no coughing/ sneezing. Keep HOB at 30 degrees.
This is the largest part of the brain, divided into left and right hemispheres. Each hemisphere controls movement on the opposite side of the body.
What is the cerebrum?
This Cranial nerve (Cranial Nerve V) is responsible for sensations on the face, scalp, and teeth, and for chewing movements. It also has branches: ophthalmic, maxillary, & mandibular.
What is the Trigeminal Nerve?
The total or partial loss of the ability to recognize familiar objects or people, as a result of organic brain damage, is termed ____________.
What is agnosia?
This drug class is the first line of drug therapy now for moderate to severe headaches. They act on dilated receptors during a migraine attack and stimulating those receptors constricts cranial vessels thereby relieving the pain.
What are the -triptans?
Like sumatriptan (better known as imitrex)
List three activities persons with seizures should avoid until the seizures are under control.
What are:
1. swimming
2. driving
3. operating machinery
Due to bradykinesia, dysphagia develops in most Parkinson's patients, and all Parkinson's patients should be placed on these precautions, _____________.
What are aspiration precautions?
List three tests and three procedures the nurse can anticipate for patients who are experiencing stroke or stroke-like symptoms.
What are (tests):
1. CT scan
2. MRI
3. Carotid Ultrasound
(procedures)
1. Carotid endarterectomy
2. Craniotomy with possible aneurysm clip
3. Endovascular embolectomy
4. Medication screening for a "clot buster" drug, such as TPA
In this disorder, antibodies attack the Schwann cells, causing the myelin sheath to break down, leaving the uninsulated portion of the nerve open to inflammation. This interrupts nerve conduction and results in the classic signs of this disorder, which are muscle weakness, tingling, and numbness. If intercostal muscles become affected, respiratory failure may occur.
What is Guillan Barre Syndrome?
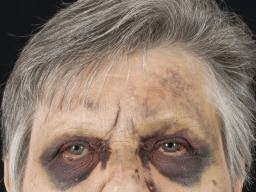
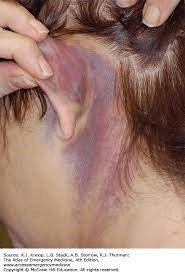
When a head injury has occurred, two ominous signs are periorbital edema & ecchymosis and postauricular ecchymosis. These two signs are better known as ____________ and ____________.
What are Raccoon eyes and Battle's sign?