Standing in an upright posture, facing straight ahead, feet parallel and close & palms facing forward.
Anatomical Position
Biomechanics is broken down into these 2 categories
Static and dynamic
This type of dense bone makes up 80% of the human skeleton and provides strength and rigidity
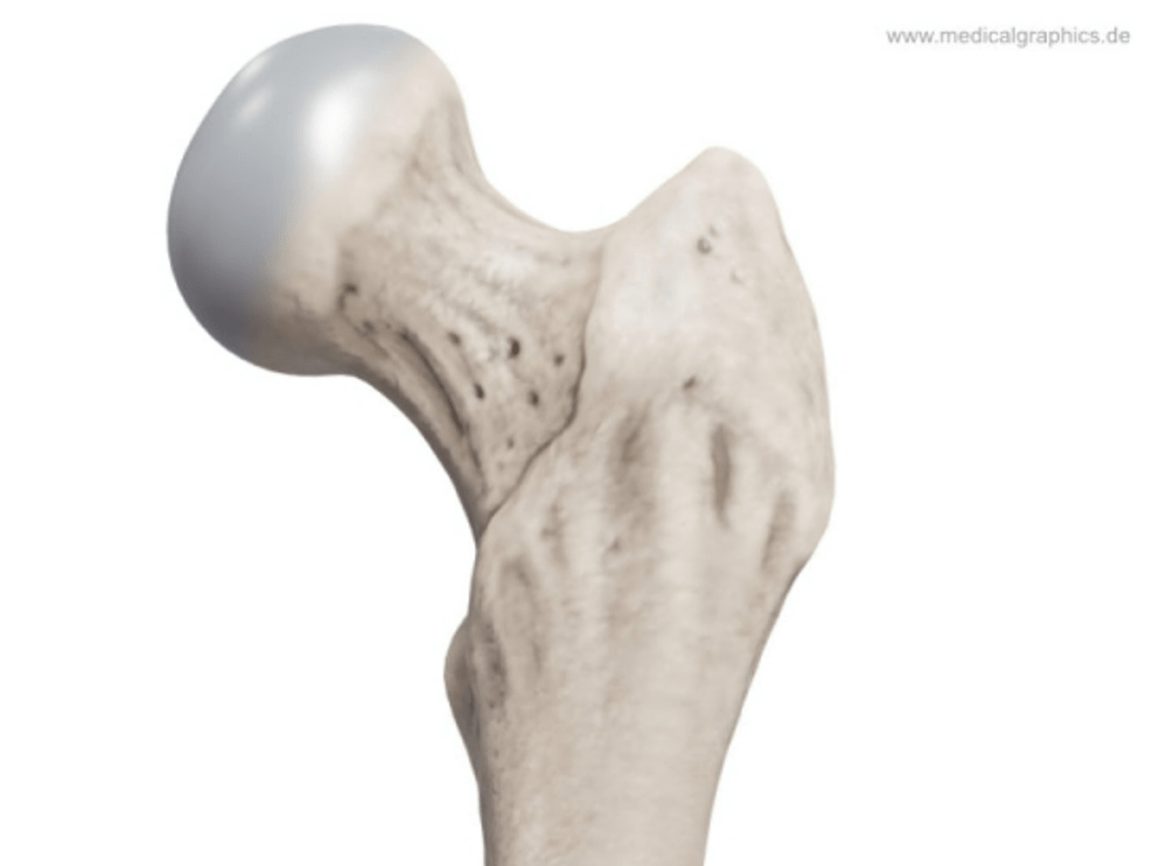
Cortical Bone
Name the red structure
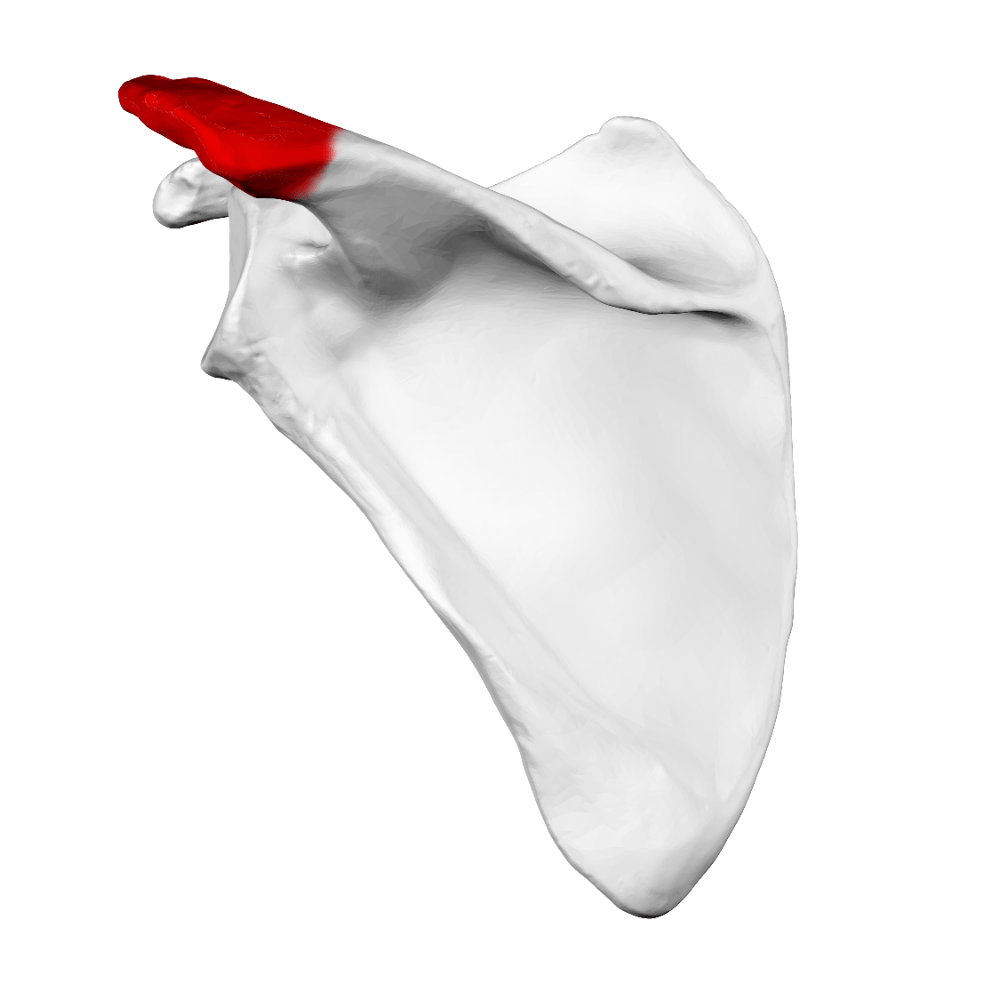
Acromion
What 2 muscle structures create a sarcomere contraction?
Actin & Myosin
Name the ideal posture curvature at each spinal level (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, & Sacral)
Cervical = Lordosis
Thoracic = Kyphosis
Lumbar = Lordosis
Sacral = Kyphosis
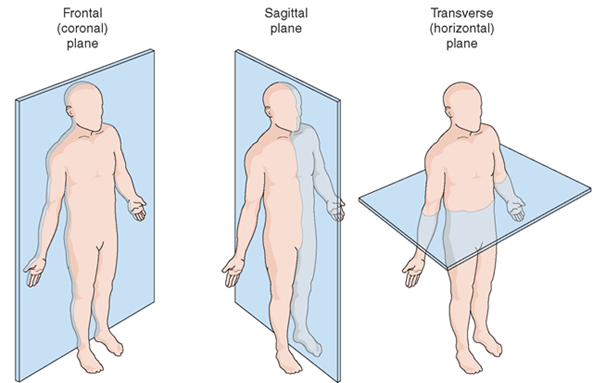
Name the planes of movement
Sagittal (Longitudinal), Frontal (Coronal), and Transverse (Horizontal)
Using a dynamometer to determine a client's amount of grip force is an example of this kinesiological principle.
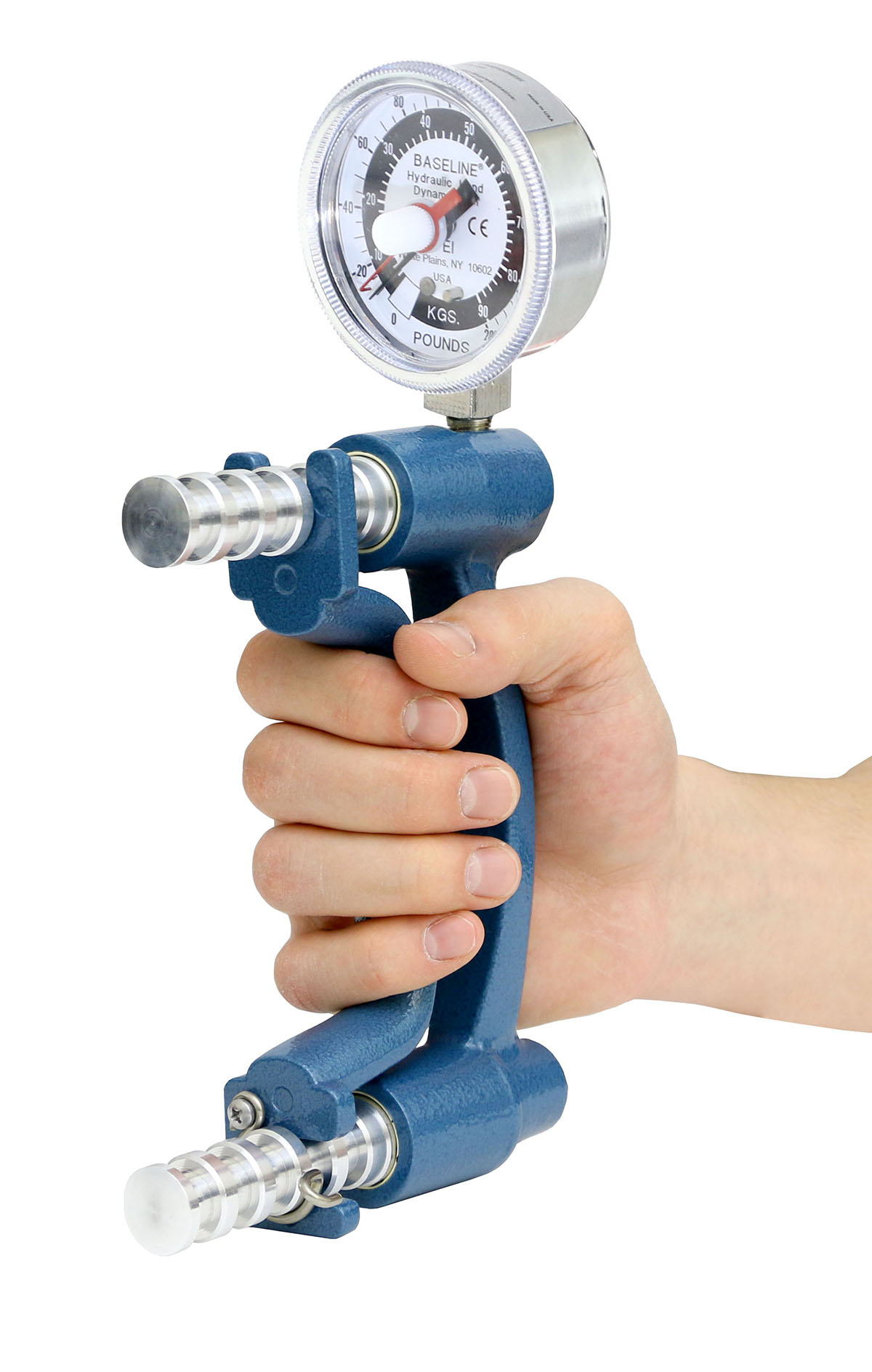

Kinetics
This cavity stores red and yellow bone marrow, makes blood cells, and stores fat.
Medullary Canal
Cervical, Thoracic, or Lumbar and how many

Thoracic/12
This muscle fiber type is responsible for short-duration and high-intensity output. It has a large diameter and provides more powerful contractions.

Type IIB Fibers
The Hunchback of Notre Dame Posture (Be specific)
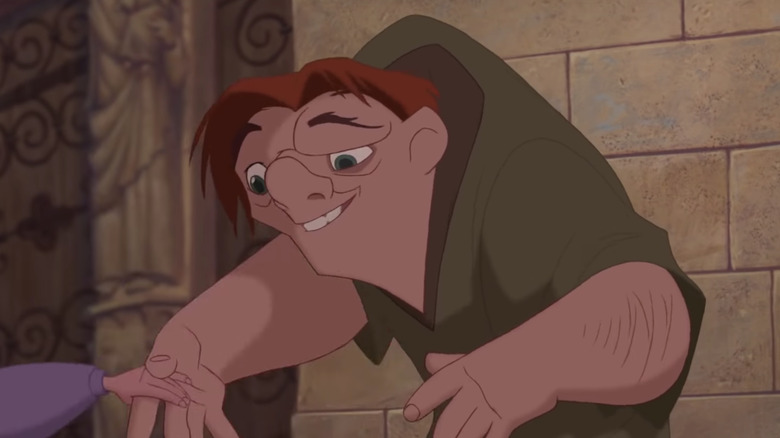

Hyper-Kyphosis
What is this movement?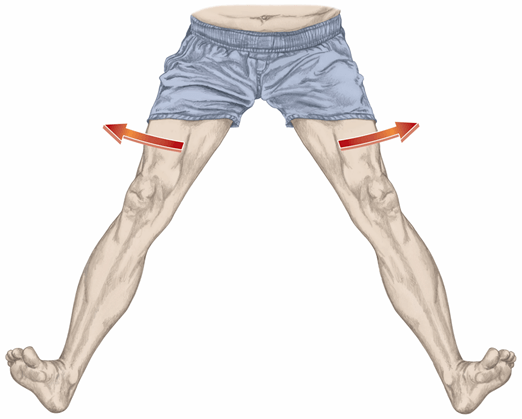
Abduction
the Arthrokinematic movement that occurs at the Glenohumeral joint.
Slide and glide occur in the _________ direction.
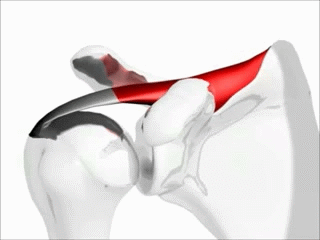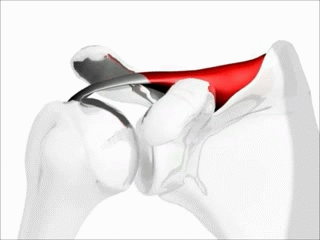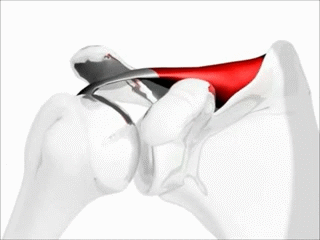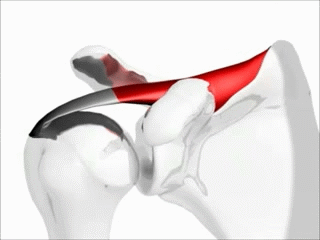
Convex surface moving on a concave surface.
Slide and Glide are in the opposite directions.
This type of joint is triaxial with movements in all 3 planes.
ball and socket
What 2 muscles work together to extend, adduct, and medially rotate the shoulder?

Latissimus Dorsi & Teres Major
This type of muscle is part of the autonomic nervous system, does not have striations, and is not under voluntary control.
Smooth/Visceral Muscle
Posture in motion
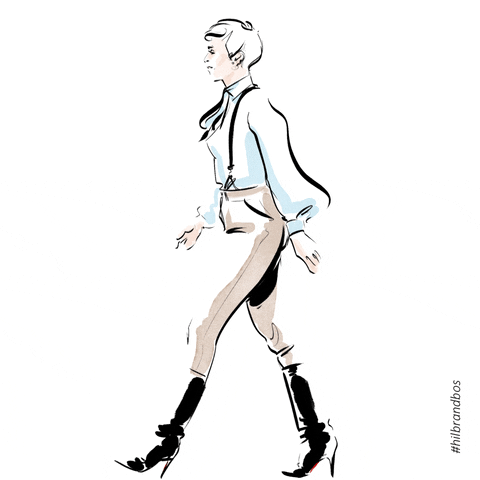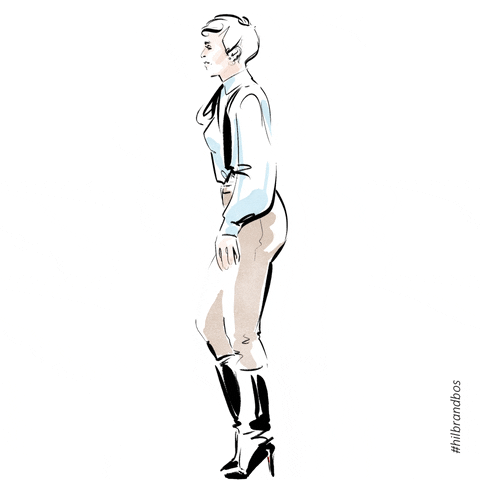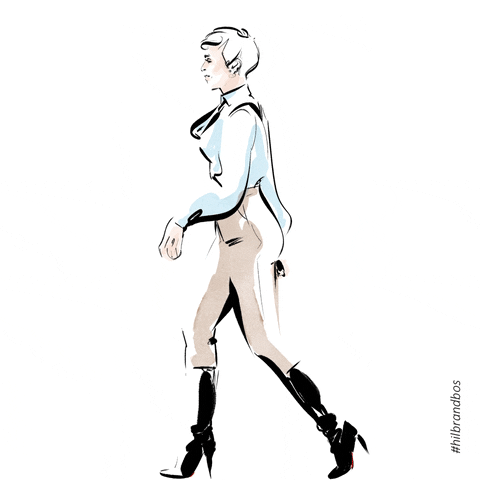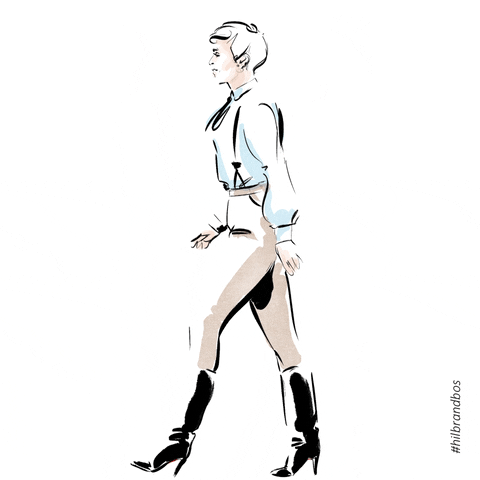
Gait/Ambulation
The arms, legs, pectoral, and pelvis girdle are considered part of the skeletal system
Appendicular
What 2 force concepts do we need to consider when working with a client from sit or stand from a chair?
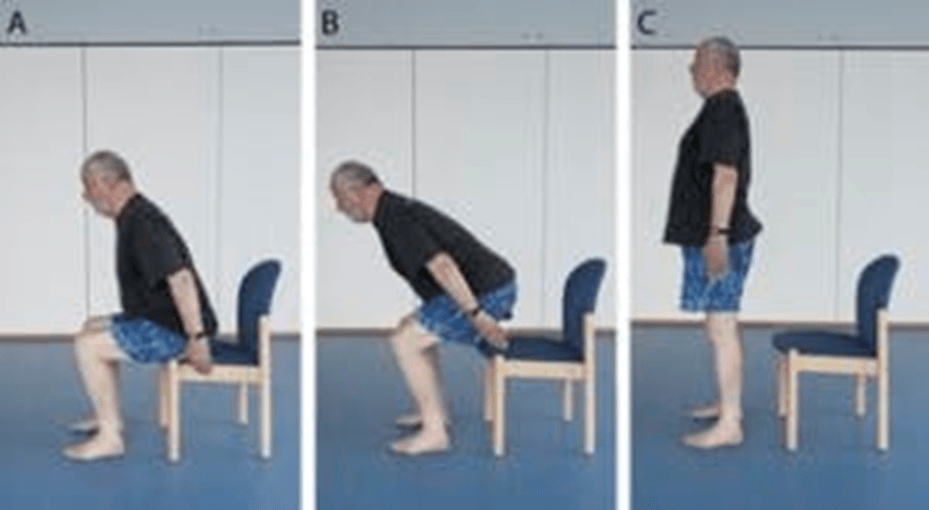
Center of Gravity
Base of Support
This bony landmark is considered a cavity and is characteristic of round, cup-like depressions found on the anterior side of the scapula.
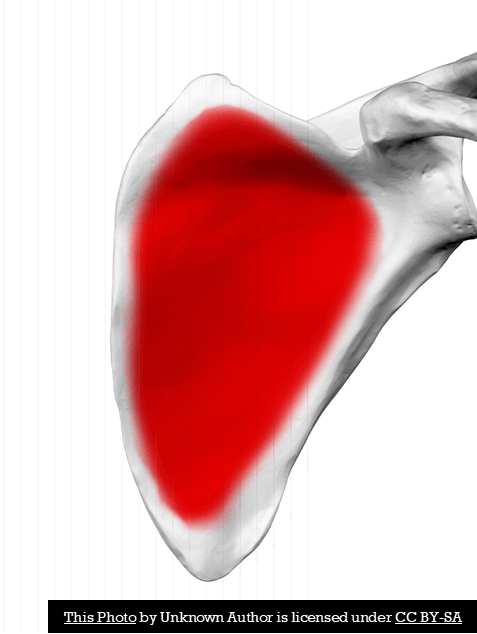
Subscapular fossa
Name this muscle, its function, and its group
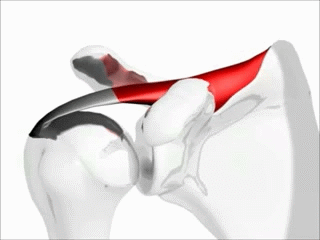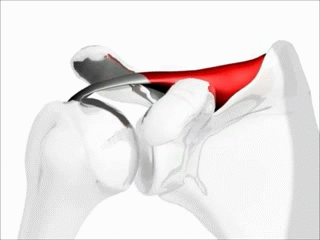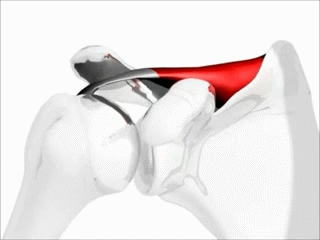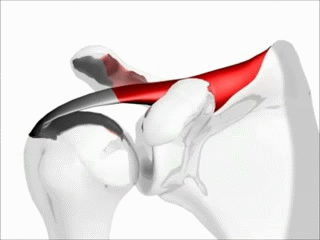
Supraspinatus, abduct the shoulder, rotator cuff muscles
This isotonic muscle contraction is characteristic of lengthening a muscle against external resistance. The muscle acts as a break to decelerate motion
Eccentric
This posture concept refers to the position of the body in relationship to the center of gravity (COG) and base of support (BOS). Stability is maintained if the COG is maintained within the BOS.

Balance
This body system is the communication and control center. It is considered the "headquarters" and senses, interprets, and responds to the body's needs.
Nervous system
Name the lever class

3rd Class
These fibrous bands of connective tissue connect muscle to bone. They are flexible but not elastic. They can tear, rupture, or strain.
tendons
Name the erector spinae group from lateral to medial
Iliocostalis, Longissimus, and Spinalis
The semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles are two of the three hamstring muscles. What bony landmark is their "origin" attachment?
Ischial tuberosity
Name the 5 phases of the gait cycle
Heel strike, Flat foot, Mid-stance, Heel off, Toe Off