True or false: all cells have ribosomes
True! all cells need proteins to function so they all need ribosomes which produce proteins
What structure prevents plant cells from exploding?
the cell wall
What is the yellow part of the diagram?
**DOUBLE POINTS** What are the black pieces?
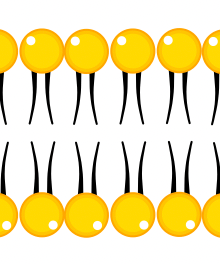
The phospholipid head
**Phospholipid tails
What does hydrophilic mean?
*FOR DOUBLE POINTS* Is the phospholipid head or are the phospholipid tails hydrophilic?
water-loving
*the phospholipid head
What does hydrophobic mean?
water-fearing
What type of solution was the celery put in?

Hypertonic
Can plant cells shrivel or burst?
**FOR DOUBLE POINTS** Why?
No
**The plant cell's cell wall prevents extreme changes in shape such as bursting or shriveling
The cell membrane allows certain substances to easily pass into or out of the cell, but not other substances. Which term applies to this aspect of the cell membrane?
semi-permeable
Name 3 differences between plant cells & animal cells
- plant cells have a cell wall
- plant cells have chloroplasts
- plant cells have a large central vacuole, animal cells have multiple small vacuoles
Cells are small to maximize their ______ ____ to _____ ratio
Cells are small to maximize their *surface area* to *volume* ratio
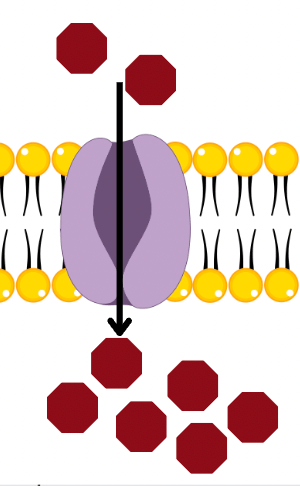
What kind of transport is this?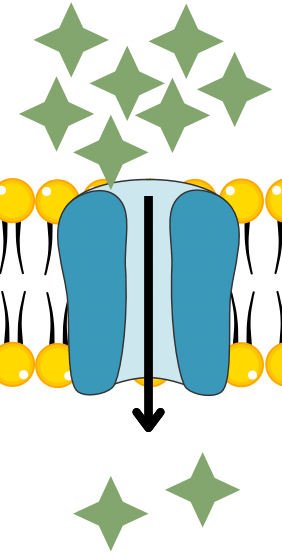
Facilitated Diffusion, the membrane contains a protein channel that helps substances move across the membrane
_________ __________ describes how the cell only lets some materials in & some materials out of the cell
selective permeability
Fill in the missing boxes using the terms: more, less, equal
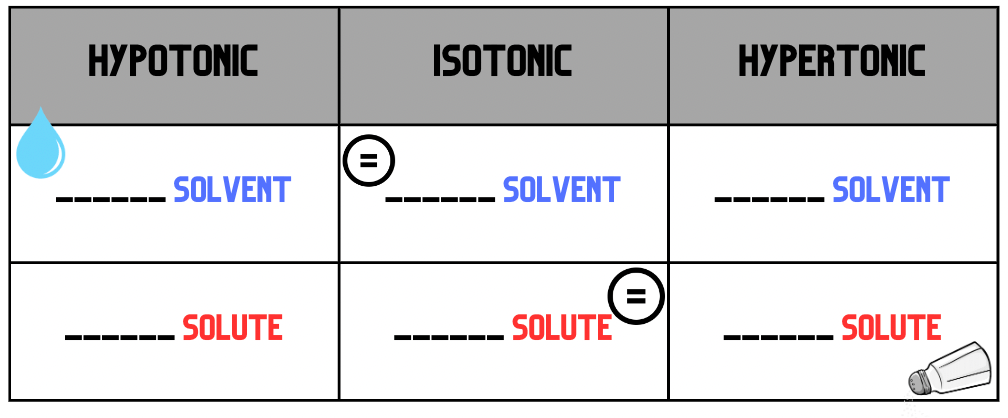
HYPOtonic - more solvent, less solute
ISOtonic - equal solvent, equal solute
HYPERtonic - less solvent, more solute
What kind of solution was this plant cell put in?
**DOUBLE POINTS** What is the term to describe what happens to the cell membrane?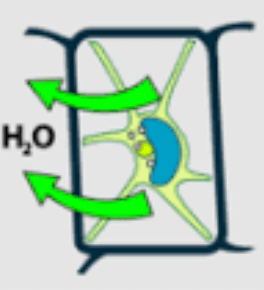
Hypertonic
**Plasmolyze
The chloroplast absorbs sunlight and creates glucose, a simple sugar. The ___________ then uses the sugar to create immediately available energy.
Mitochondria
How do plant cells/plants get glucose?
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY: (only answer once the first question has been answered correctly)
How do animal cells/animals get glucose?
Plant cells produce glucose via photosynthesis in the chloroplast.
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY:
Animals consume food to get glucose.
Which cell shape would most efficiently transport nutrients/O2 into the cell & transport waste out of the cell?
Cell B
Name the 3 types of passive transport.
*FOR DOUBLE POINTS* - Define all 3
Simple Diffusion, Osmosis, and Facilitated Diffusion
High to low concentration movement of small molecules, high to low concentration movement of water, high to low concentration movement of molecules with help (ex: transport protein)
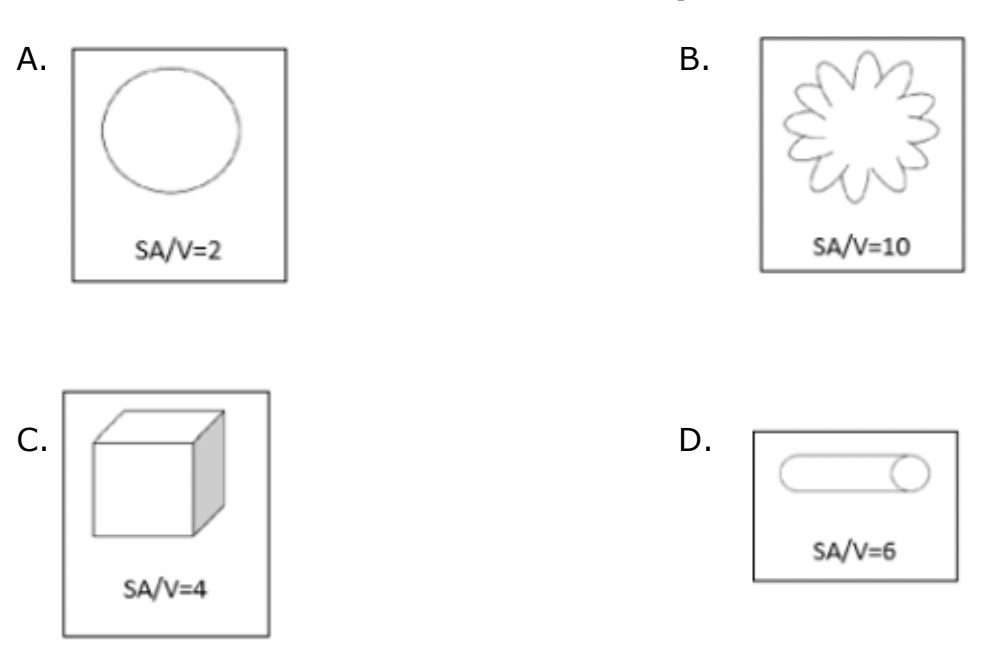
What is the blue structure called?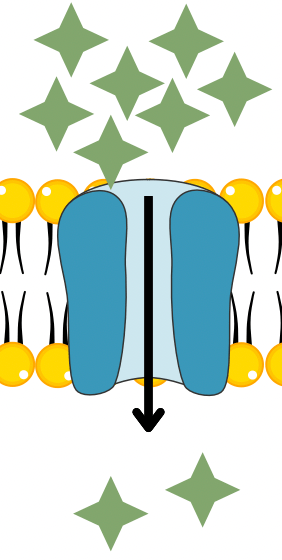
A channel protein
What type of solution has cell A been placed in?
Hypotonic
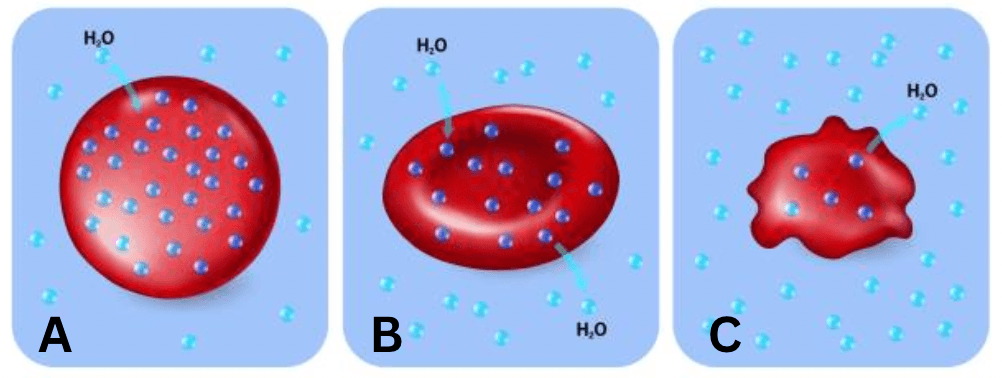
The black cells and white cells move using passive transport. What direction(s) will the white molecules move?
**DOUBLE POINTS** What direction(s)
White cells will diffuse to side A.
**Black cells will move both directions to maintain dynamic homeostasis
Your cells break down waste & remove it from the cell. Which specific organelle is responsible for breaking down waste?
lysosomes
Name at least 2 differences betweek PROkaryotes and EUkaryotes
- pro have no nucleus, euk have a nucleus
- pro have no membrane-bound organelles, euk have membrane-bound organelles
- pro are always unicellular, euk can be unicellular OR multicellular
When cells get too big they struggle to: (pick 2)
a - transport nutrients & oxygen (O2) into the cell
b - have space for all organelles
c - maintain their cell membrane
d - remove waste from the cell
A & D
Is dialysis active or passive transport?
Passive Transport
A sodium-potassium pump functions to pump sodium out of the cell AGAINST the concentration gradient. What type of transport is this?
Active transport, molecules are moving AGAINST (up) the concentration gradient
What key term describes what happened to the red blood cell?
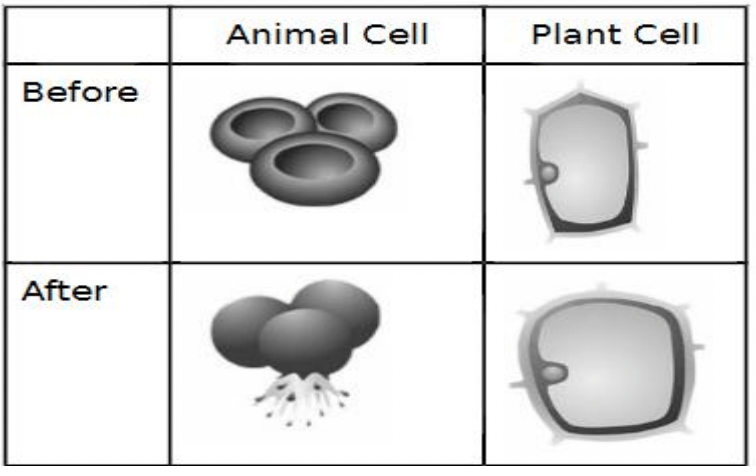
lyse; lysis - the disintegration of a cell by rupture of the cell wall or membrane
A dialysis bag is placed in a beaker. Below is the weight of the bag at the start of the experiment and after 30 minutes. Is the solution HYPERtonic or HYPOtonic?
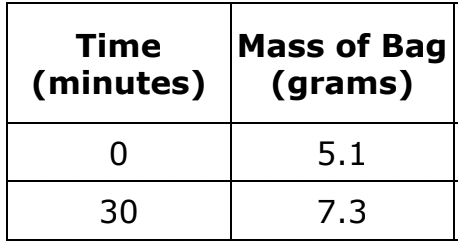
The solution is HYPOtonic.
- items are not able to be synthesized, sorted, and secreted/sent out
- nutrients are not able to reach their destinations
- proteins are not synthesized/put together, enzyme death could lead to cell death
The image below shows a theory where prokaryotic cells engulfed each other to form eukaryotic cells. The chloroplast and mitochondria used to be independent cells. What theory is this?
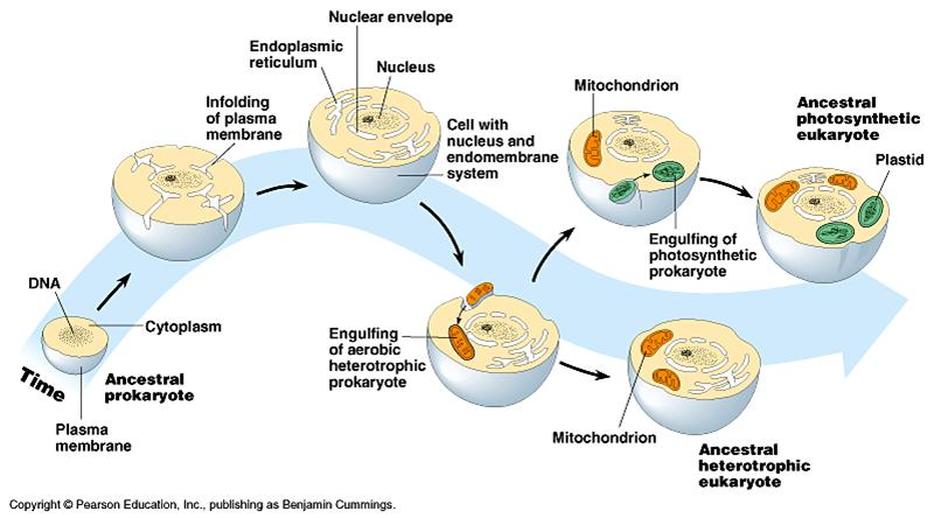
Endosymbiotic theory
What do membrane proteins do? (select 3 answers)
a - transport substances across the membrane
b - to make food for the cell
c - to provide structure for the membrane
d - to act as membrane receptors & cell markers
e - to produce energy for the cell
a, c, & d (transport, structure, receptor/marker)
What molecule is missing?
ATP, this is active transport so energy is required
Name the 3 types of active transport.
**DOUBLE POINTS** Define each type.
Simple Active Transport, Exocytosis, Endocytosis
Active transport - the movement of molecules from LOW to HIGH concentration with the use of ATP (energy)
EXocytosis - The removal of waste from the cell using a vesicle, waste EXits the cell
ENdocytosis - Substances are brought into the cell where the cell membrane surrounds the material
What is an experiment that could show the impact of a HYPERtonic solution on an animal cell? What would the researcher see?
**DOUBLE POINTS** Include the use of a HYPOtonic solution in your experiment.
*open response; example: placing an animal cell in a salty solution. The cell would shrivel due to water flowing out of the cell into the salty solution.
**open response; example: placing an animal cell in a pure water solution. The cell would swell and possibly lyse due to water flowing into the cell.
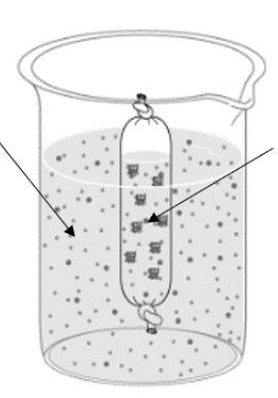
What is the BAG compared to beaker C?
**DOUBLE POINTS** What is the BAG compared to beaker A & B?
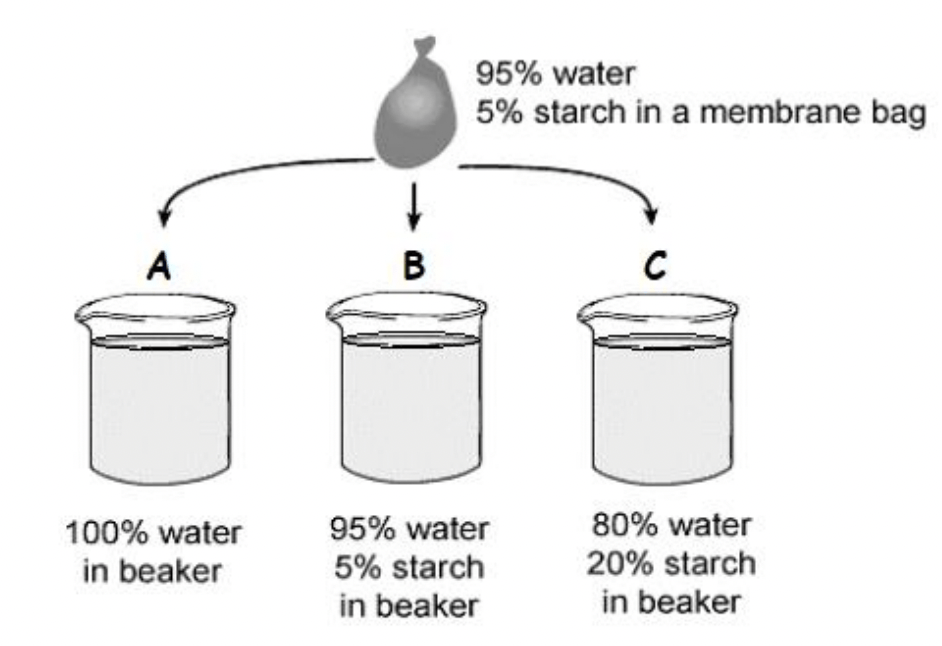
HYPOtonic
**The bag is HYPERtonic to beaker A and ISOtonic to beaker B