Three shunts in the fetal circulatory system
Foramen ovale
ductus venosus
ductus areteriosis
What type of shunting is characteristic of cyanotic disease?
Right to left shunting.
-right sided pressure exceed left sided pressures.
Cardiogenesis begins in this week of gestation.
Week 3
Which direction is the blood abnormally flowing through the heart.
Left to right
What causes the change in fetal circulation to shift from the placenta to the lungs
The clamping of the umbilical cord.
true or false:
Most genetic mechanisms of causation are multifactorial
true
The connection of the right and left atria
foramen ovale
True or False:
Symptoms of obstructive defects depend on the site and severity of the stenosis.
True
Week 7
True or False:
Acyanotic defects decrease pulmonary blood flow.
False
- Acyanotic defects increase pulmonary blood flow because blood is shunting from the left (high pressure side) to the right into the pulmonary system.
True or false:
The fetal lungs are aerated prior to delivery.
False
-Fetal lungs are not aerated until after birth.
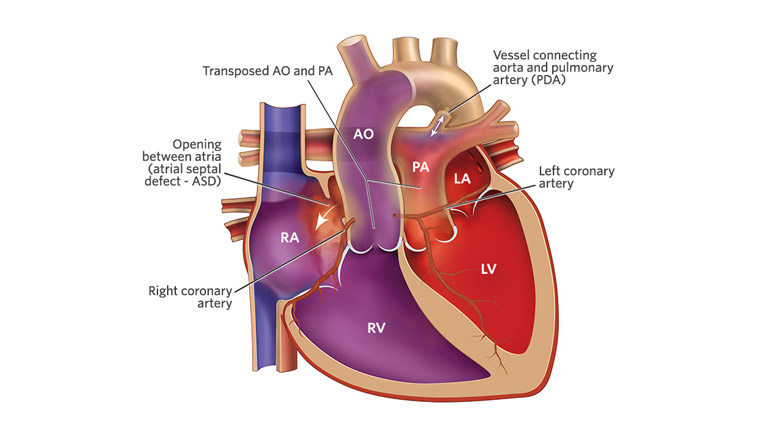
Transposition of the Great Arteries
-a condition where the aorta arises from the RV and the PA arises from the LV.
- results in two separate, parallel circuits in which unoxygenated blood is continuously flowing through the systemic and oxygenated is flowing through the pulmonary.
- incompatible with life unless a communication exists. (DA, FO, or VSD)
Ductus Arteriosus
Joins the Pulmonary artery to the Aorta (conjoins the arteries)
What is this disease and what is its main characteristics?
Tetralogy of Fallot
-Most common cyanotic heart defect 5-10%
1.) a large Ventricular septal defect that is high in the septum
2.) and overriding aorta that straddles the VSD
3.) pulmonary stenosis
4.) right ventricular hypertrophy
Fetal shunts
ASD - atrial septal defect
the abnormal communication between both atria
What delivers oxygenated blood and nutrients to the fetus.
Acquired heart disease are abnormalities that occur after birth. The most common associated heart diseases in children are:
- kawasaki disease
- HTN
- Rheumatic heart disease
- Myocarditis or Obesity?
Ductus Venosus
Connects the inferior vena cava to the umbilical vein (connects the veins)
Which disease is this and is it obstructive or cyanotic?

Aortic Stenosis
CAN LEAD TO SUDDEN DEATH!
- obstructive
- narrowing of the aortic outflow tract
This begins when the septum primum and the septum secundum grow towards the area of the endocardial cushions.
Atrial septation

Arterioventricular canal defect (AVC defect)
Abnormalities in both the atrial and ventricular septa and the AV valves.
How does resistance effect the fetal blood circulation?
Fetal blood follows the path of least resistance. Since there is high resistance in the lungs and low systemic resistance, the blood diverts through the ductus arteriosus to the aorta and throughout the body.

Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
- abnormal development of the Left sided cardiac structures, resulting in obstruction to flow from the LV outflow tract.
- underdevelopment of Aorta, aortic arch, LV and mitral atresia/ stenosis.
When does the closure of the ducts take place?
FO : functionally at birth/ anatomically several months later
DA: functionally at 15 hours/ anatomically first several weeks
DV: within one week after birth
What is this disease and is it cyanotic or obstructed?
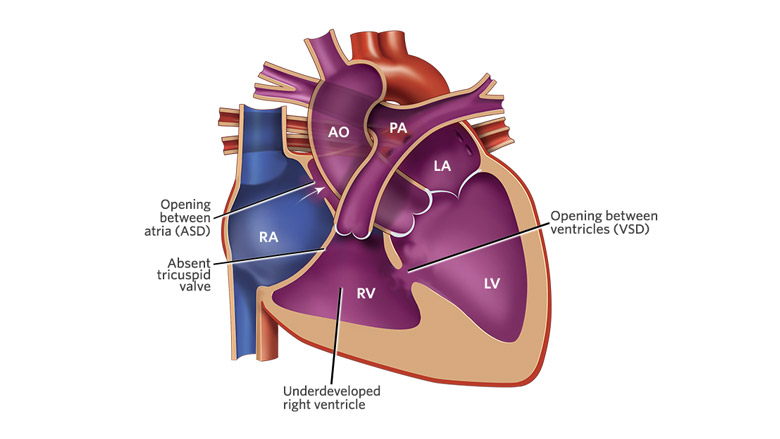
Tricuspid Atresia
- Cyanotic
- consists of an imperforate tricuspid valve, resulting in NO communication between the RA and RV
- other defects that are characteristic - septal defect, hypoplastic or absent RV, enlarged mitral valve and pulmonary stenosis.
This begins with the fusion of the muscular ridge at the apex, endocardial tissue and the bulbar ridges in the bulbar cordis.
Ventricular Septation
blood shunts from the PA to aorta.
PDA - patent ductus arteriosis
What are three significant post natal changes that occur?
1.) thinning of the right ventricular myocardium
2.) systemic vascular resistance increases
3.) The left ventricular myocardium becomes thicker and more dominant.
What is a symptom of heart failure that is specific to children?
Failure to thrive (FTT) - caused by poor feeding/sucking
- manifestations are otherwise the same in children and adults.

DA
What is this disease and is it obstructive or cyanotic?
BONUS - What is the severe form of this disease called and how is it different?

Pulmonary stenosis
- obstructive
-narrowing of the pulmonary flow tract
BONUS- pulmonary Atresia
- involves complete blockage of the RV into the pulmonary vein. (Now blood flow is dependent on a patent ductus arteriosus)
True or false:
The heart arises from the mesenchyme and begins as an enlarged blood vessel with a large lumen and a muscular wall
True
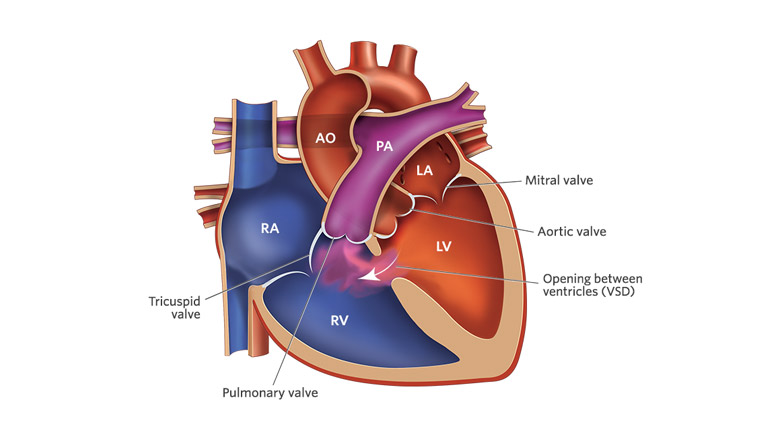
VSD - Ventricular Septal Defect
Abnormal flow of blood between the ventricles. Also the most common type of congenital heart lesion.
Postnatal HR, cardiac output and systolic BP?
HR: 100- 180 bpm
Cardiac output: high
Systolic BP: 39- 59mmHg (reflects low SVR)
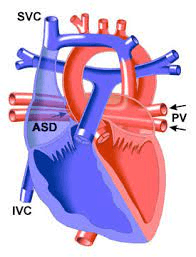
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection
- occurs when the pulmonary veins abnormally connect to the right side of the heart either directly or through one or more systemic veins that drain into the RA.
Foramen Ovale
What is the disease and is it obstructive or cyanotic?

Coarction of the aorta
- narrowing of the lumen of the aorta that impedes blood flow.
- obstructive
What are genetic risk factors associated with CHD?
Trisomy 18 (99%)
Trisomy 21
Trisomy 13
Cri du Chat syndrome
turners syndrome
Kleimfelter Syndrome
What is the gold standard for definitive diagnosis of structural and functional cardiac disease
ECHO - echocardiogram
- other tools for evaluation include physical exam, plotting a child's growth, ECG and chest Xray.
oxygen consumption is doubled at birth.
Environmental risk factors and medications that could cause CHD:
maternal conditions:
viral infections (rubella), ETOH, Drugs, DM, advanced maternal age, metablic disorders (PKU and Hypercalcemia), and autoimmune disorders (lupus)
Medications:
Anticonvulsants, ACE inhibitors, lithium, retinoic acid, and warfarin