The use of filters in recording and displaying EEG data is important in producing...
A readable, interpretable EEG
What does the notch filter out?
Activity produced by the surrounding electrical field. (60 Hz)
Another name for low frequency filter is __________.
High pass filter.
Another name for high frequency filter is _________.
Low pass filter
HFF and LFF are typically combine to create a specific _________.
Impedances should be under ____________.
5 killiohms
A frequency response curve is a graph that plots ______ against _________.
Frequency, amplitude
Time constant is defined by the amount of time it takes for the waveform to return ________ of the way to baseline after deflection.
2/3
Describe the EEG below.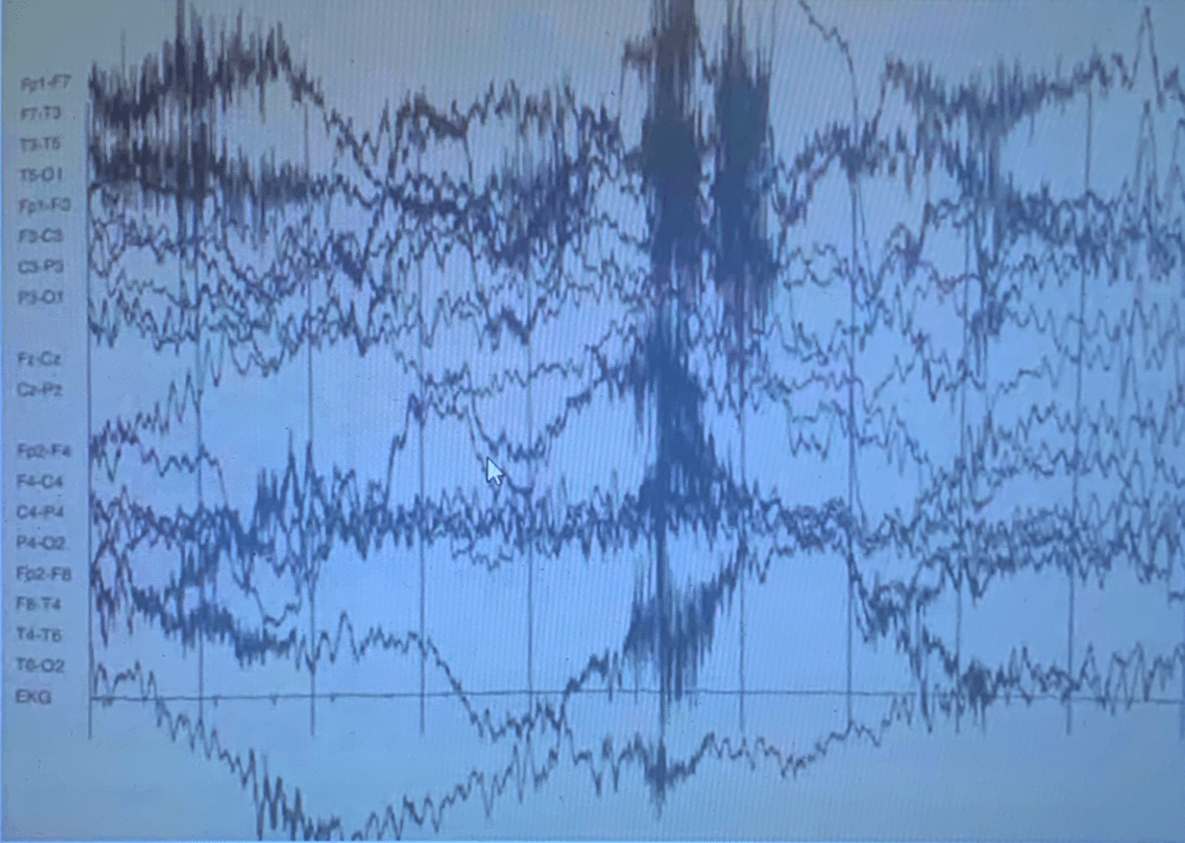
No filter used in this EEG
Muscle artifacts prevalent throughout the recording
Overlapping, not on horizontal line, bottom is not on baseline (going downwards)
Filters can diminish the ________ of waveforms.
Amplitudes
EEG filter setting are ____ to ____ Hz.
1 Hz, 70 Hz
Outside of North America the common notch frequency is ______.
50 Hz
The standard setting for a Low Frequency Filter is ____.
1 Hz
High Frequencies filter out...
Muscle Artifacts
A bandpass filter is best described as....
A range of frequencies between the unwanted high and low frequencies that is allowed to pass through the filter set up.
If the impedance is correct you can conclude that...
The hookup is correct as well.
The curved lines represent...
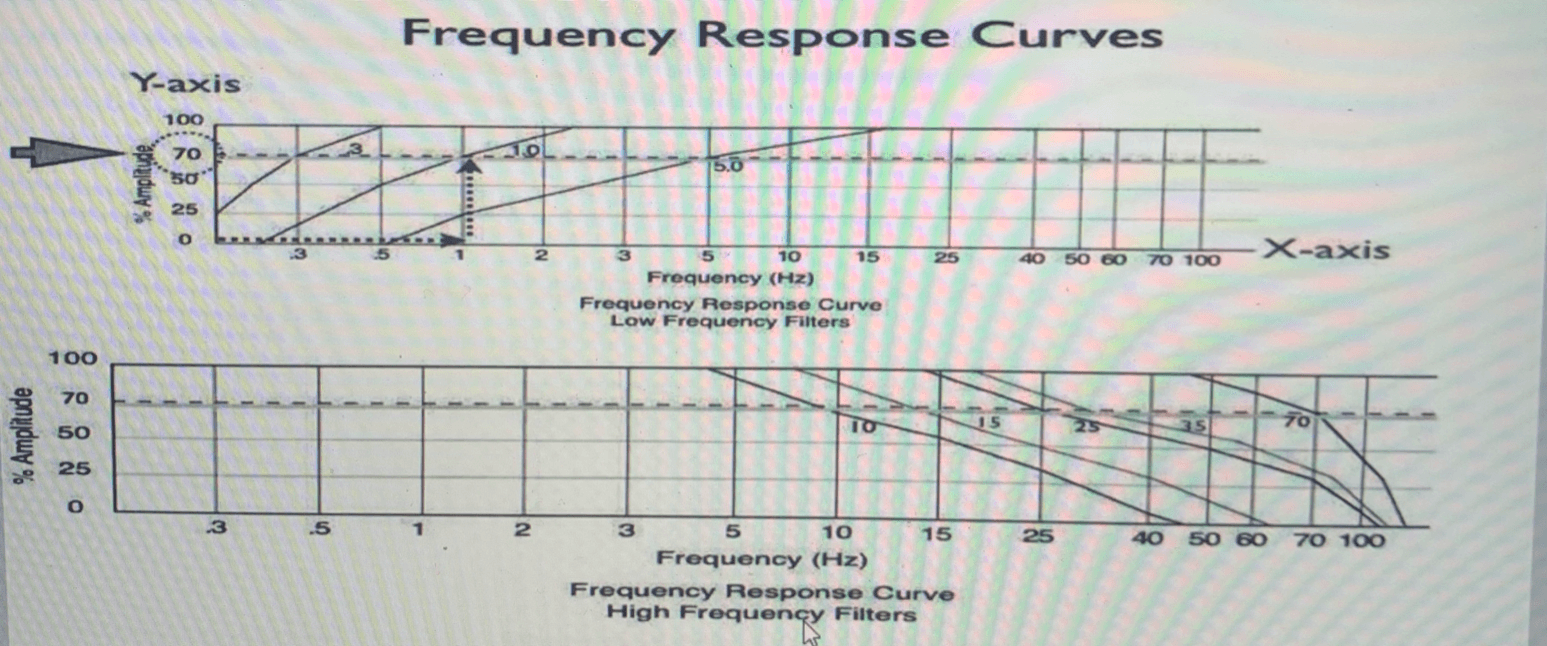
The filters
Time constant is expressed in _________.
Seconds
In this EEG is a use of filter in place? Explain.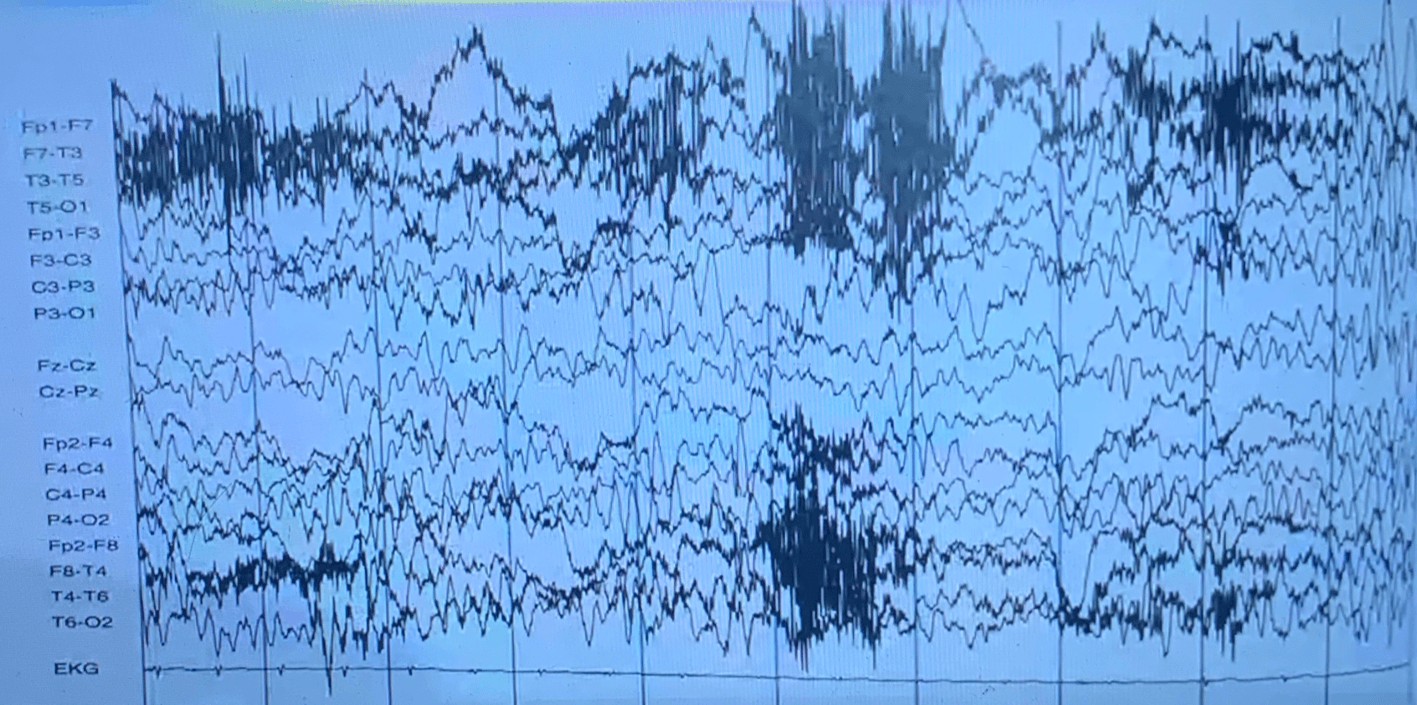
Yes the use of a filter is in place this can be depicted because there is a readable baseline and The amplitude of the muscle artifact is reduced throughout the recording
What are three factors to decrease the amplitude of a wave?
1. Frequency
2. Filter
3. Impedance
What are the three types of filters used?
1. Low frequency filter
2. High Frequency Filter
3. Notch Filter
Why is the notch for one specific frequency?
Standard alternating current.
______,________, and _______ are removed by a Low Frequency Filter.
Skin, motion, sweat
70 Hz
The formula for a bandpass filter is...
Why does the strategy of "more is better" not always hold true with using filters?
Implicit to the act of filtering the EEG signal is the potential loss of information.
The X-Axis represents ...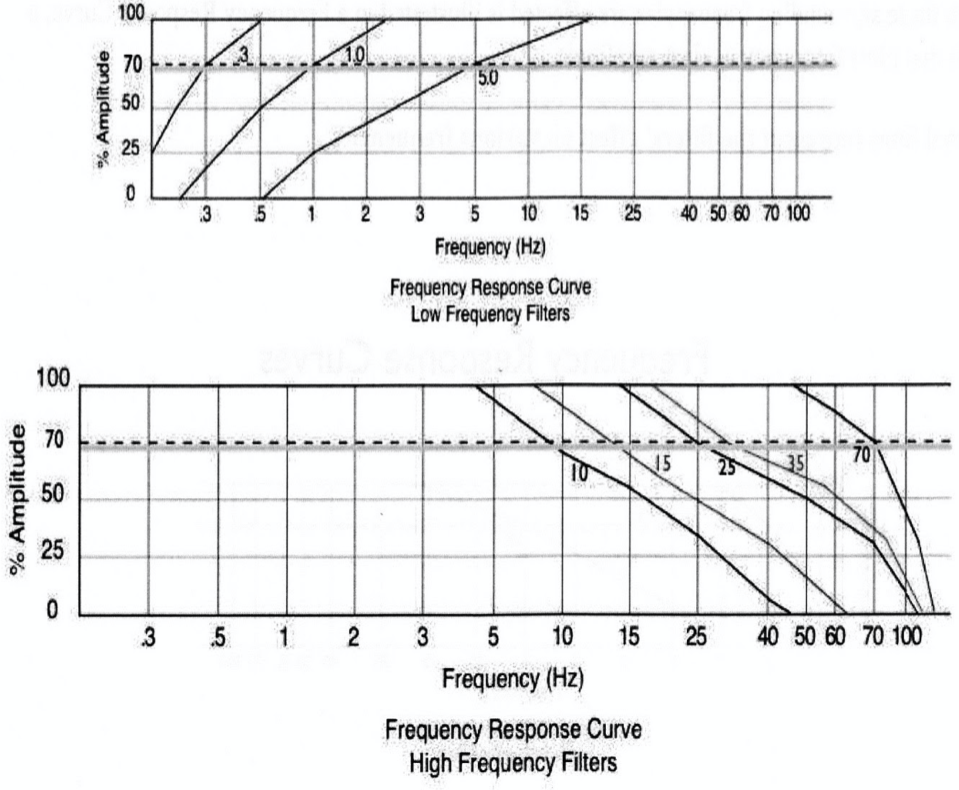
Frequencies of activity (Hz)
Time constant is the product of the ________ and the _______ of those two elements in the RC circuit.
resistance, capacitance
What is seen in the sixth second of this EEG? LF 1 Hz
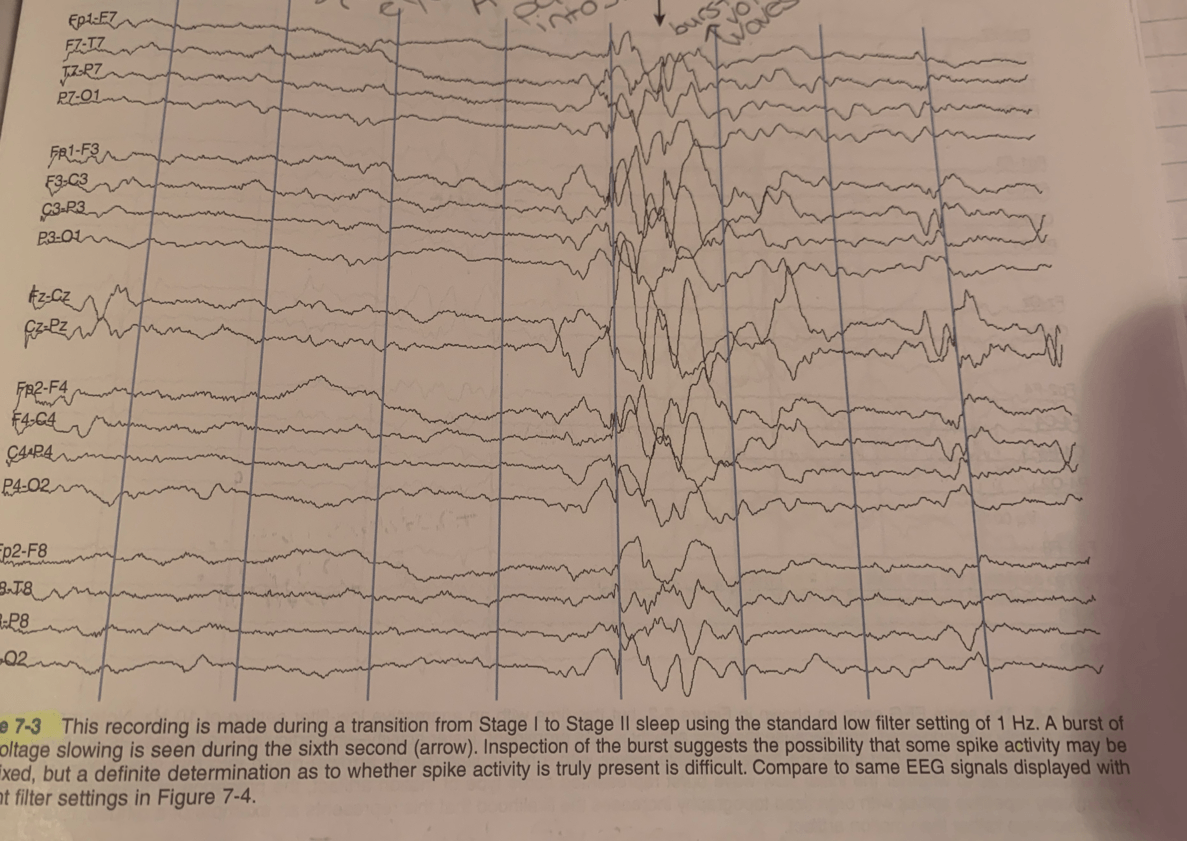
After 6 seconds the patient goes into sleep.
A Burst of high voltage slowing is seen in the sixth second. Burst suggests that there is a possibility that some spike wave activity may be intermixed, but definite determination if spike activity is truly present is difficult
The most cortical activity of clinical interest is between ___ and ___ Hz.
1Hz, 30 Hz
What are three advantages of filters?
1. Used to "clean up" EEG tracing
2. Certain filter settings can be used to accentuate particular types of EEG activity
3. Most ideal filter design would be one that removes all of the electrical noise and artifacts from the EEG and only allows true cerebral waves to pass through
A 60 Hz filter will effect an EEG by ...
electrical interference
When standard low-frequency filter settings (1 Hz or below) are used the main effect is...
to help keep each EEG channel within its horizontal area, eliminating large drifts upward or downward into the space of other channels
What will happen when there is use of overly aggressive HFF’s?
Attenuate the height of high-frequency waves and change the morphology.
What is the bandpass set up pictured below?
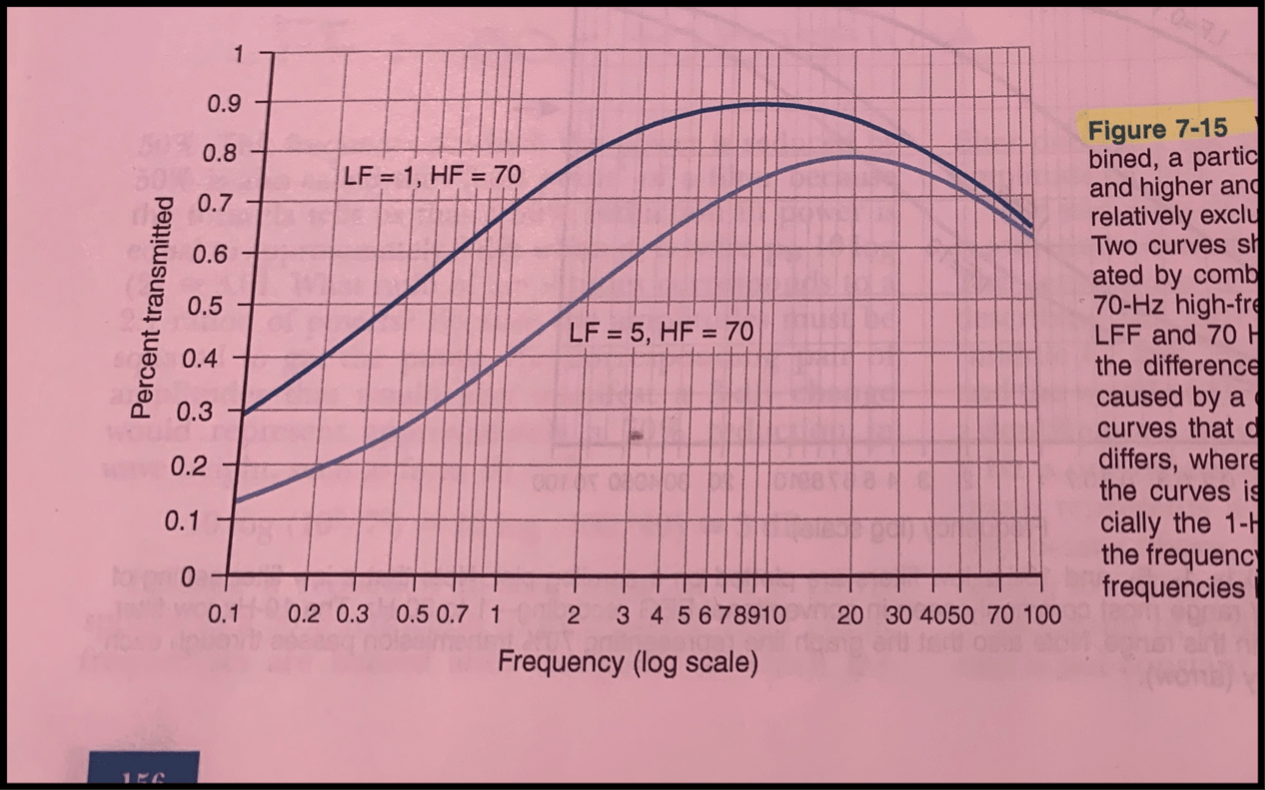
LFF= 1 Hz, HFF = 70 Hz (top curve)
LFF= 5 HZ and HFF= 70 Hz (bottom curve)
Some filter settings can change the ______ of brain waves to show waves that are not really there.
shape
Y- axis represents...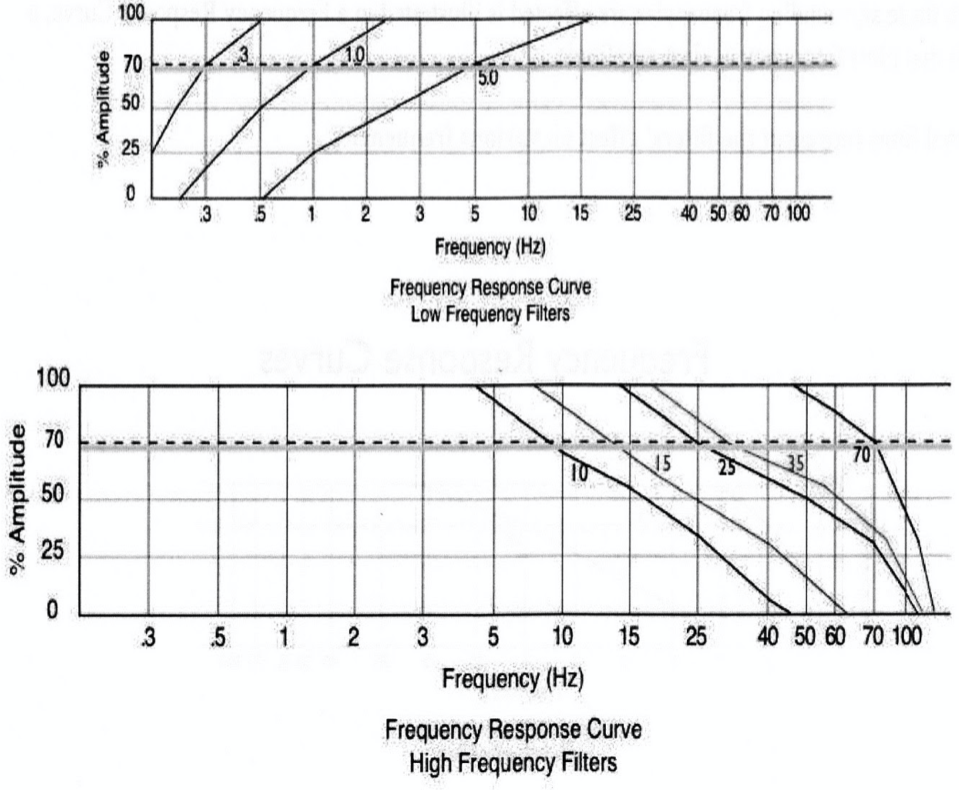
Amplitude (% of true amplitudes seen)
τ= R X C
τ stands for ____________
the number of seconds it takes for a square wave to fall by 63% of its original value
Aggressive LF 10 Hz used. What is displayed?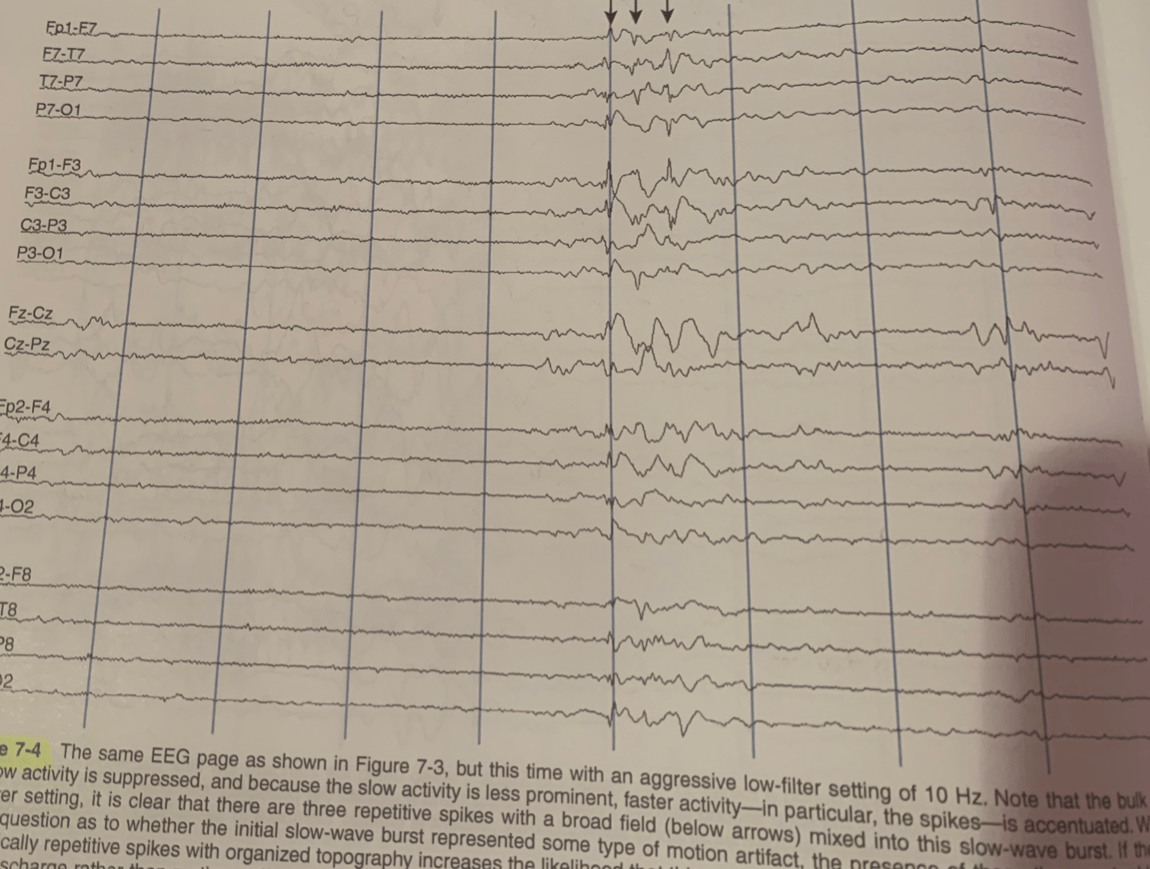
Bulk of slow activity is suppressed
3 repetitive spikes (below arrows)
Presence of these 3 repetitive, rhythmic spikes with organized topography increases the likelihood that this represents an example of a diffuse, repetitive spike-wave discharge rather than motion artifact
High and low frequency filters are based on simple RC circuits, circuits that include both a _______ and a ___________.
resistor, capacitor
What is the most ideal filter design?
One that removes all of the electrical noise or artifacts from the EEG and only allows true cerebral activity to pass through. (doesn't exist)
The ideal notch filters transmission curve shows a ____ response for all frequencies except ______ frequency of the filter, where there is a notch in the curve denoting near complete attenuation of any waves at that particular frequency.
Flat, nominal
Aggressive use of low frequency filter can bring out _________.
spike-wave discharges
Roll-off characteristic, but logically, the curve rolls off in the ______ direction of LFF’s, falling off toward the direction of ________ frequencies.
opposite, higher
This diagram shows....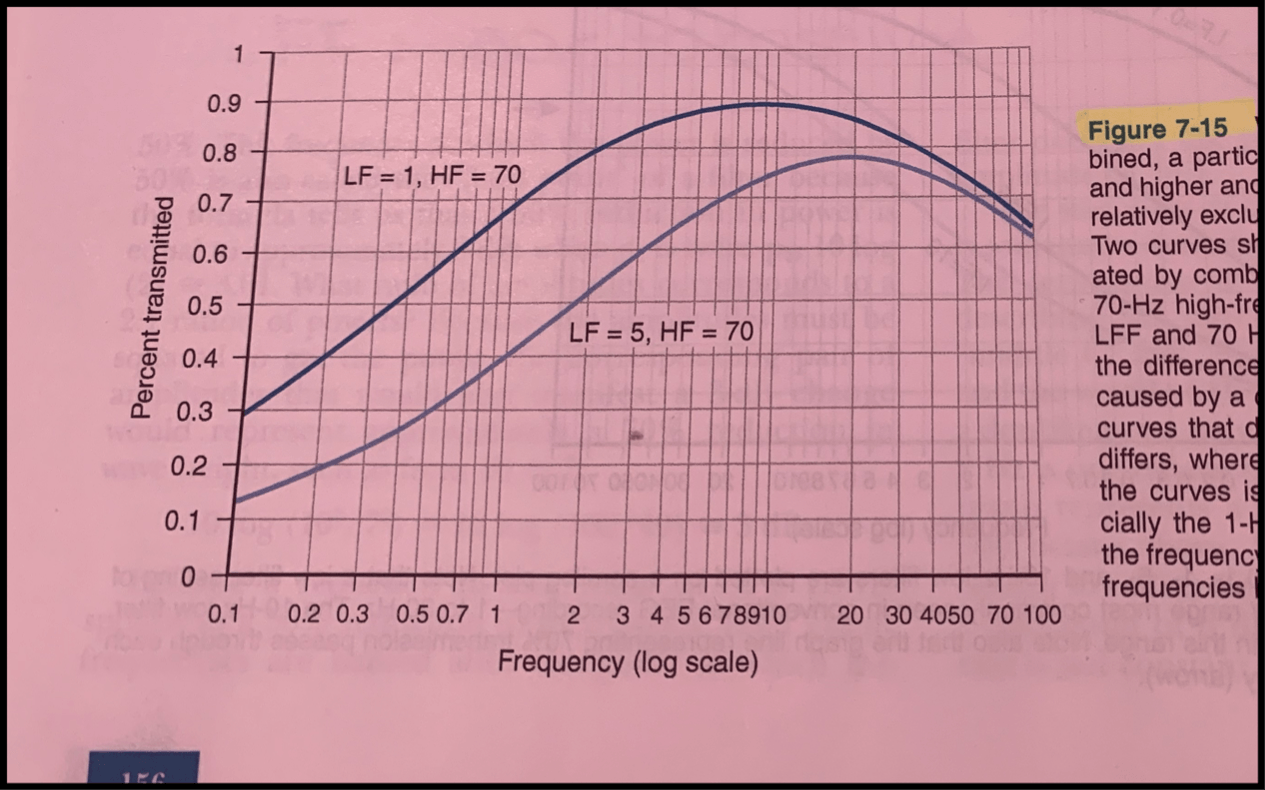
A difference between the two bandpasses caused by a change in the LFF used.
An over-zealous filter can overly “clean” the EEG, which filters out and causes a disappearance of waveforms that may be of interest to the reader of the EEG.
The graph depicts how a particular _______ will affected a particular _________.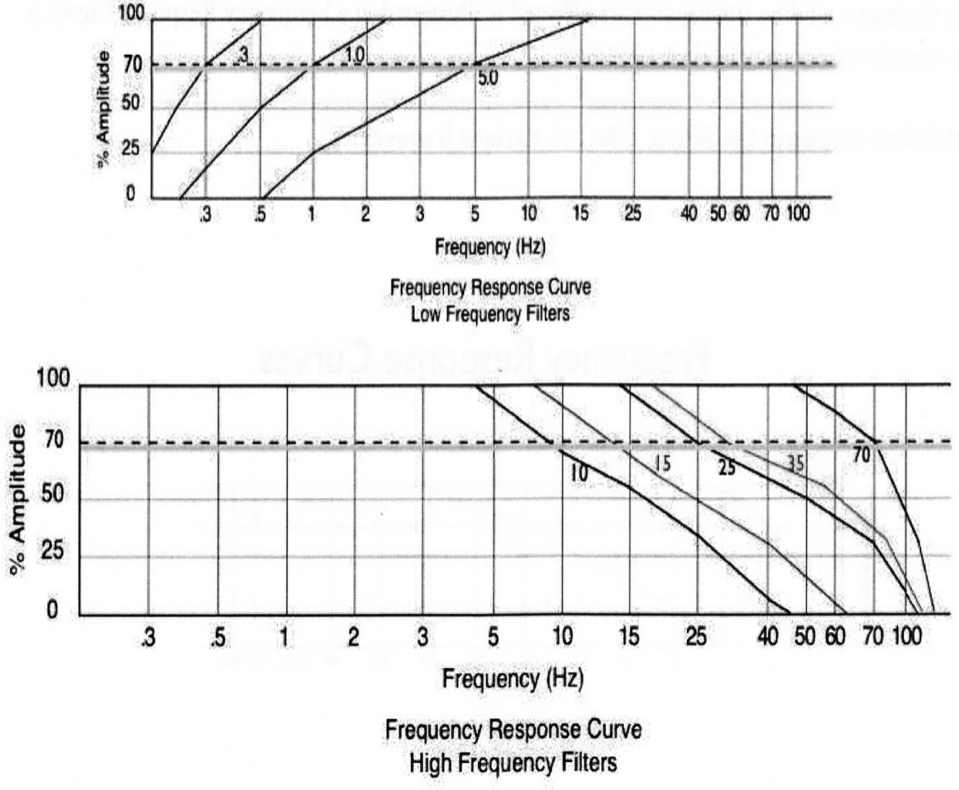
Filter, frequency
A short time constant eliminates _______.
slow waves
What is shown when a low filter is applied to the square wave output?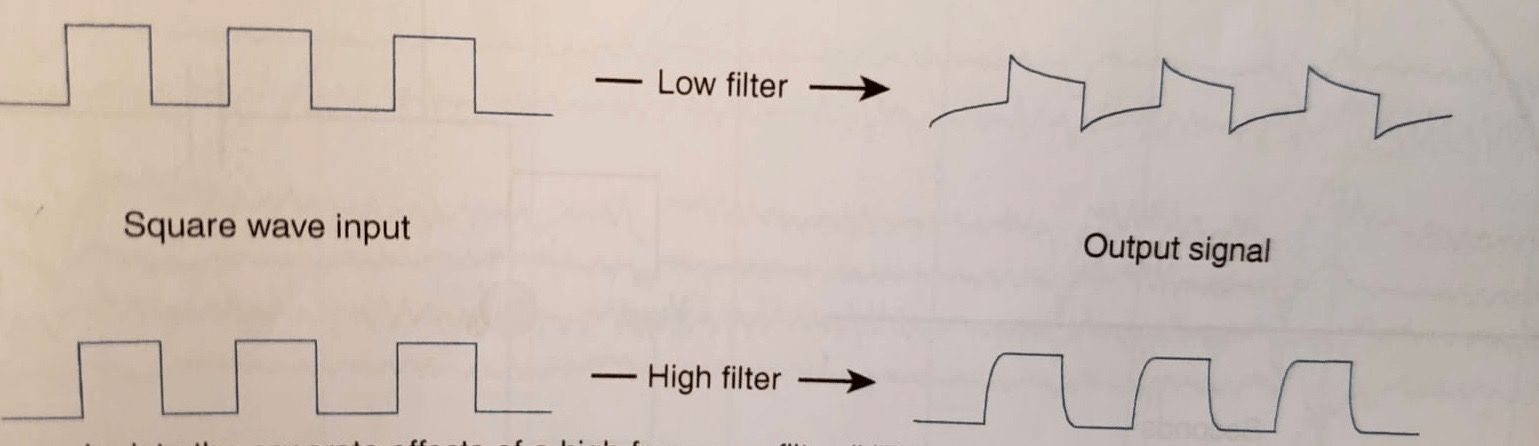
When a Low filter was applied to the square wave input the output signal changed by:
-horizontal line deflecting downwards
-horizontal line decreases towards the baseline
Skin: _____ Hz
<1
Rather than be used to reject spurious activity, occasionally filters are used to...
bring out certain EEG activity that may otherwise be hidden in other, high voltage activity
Notch-filters, filter out _______, rather than a frequency range.
activity
More Aggressive use of Low frequency filters initially begins to attenuate _____ frequencies.
delta
HFF's allow ______ activity to pass through.
low frequency
Left side of the curves display....
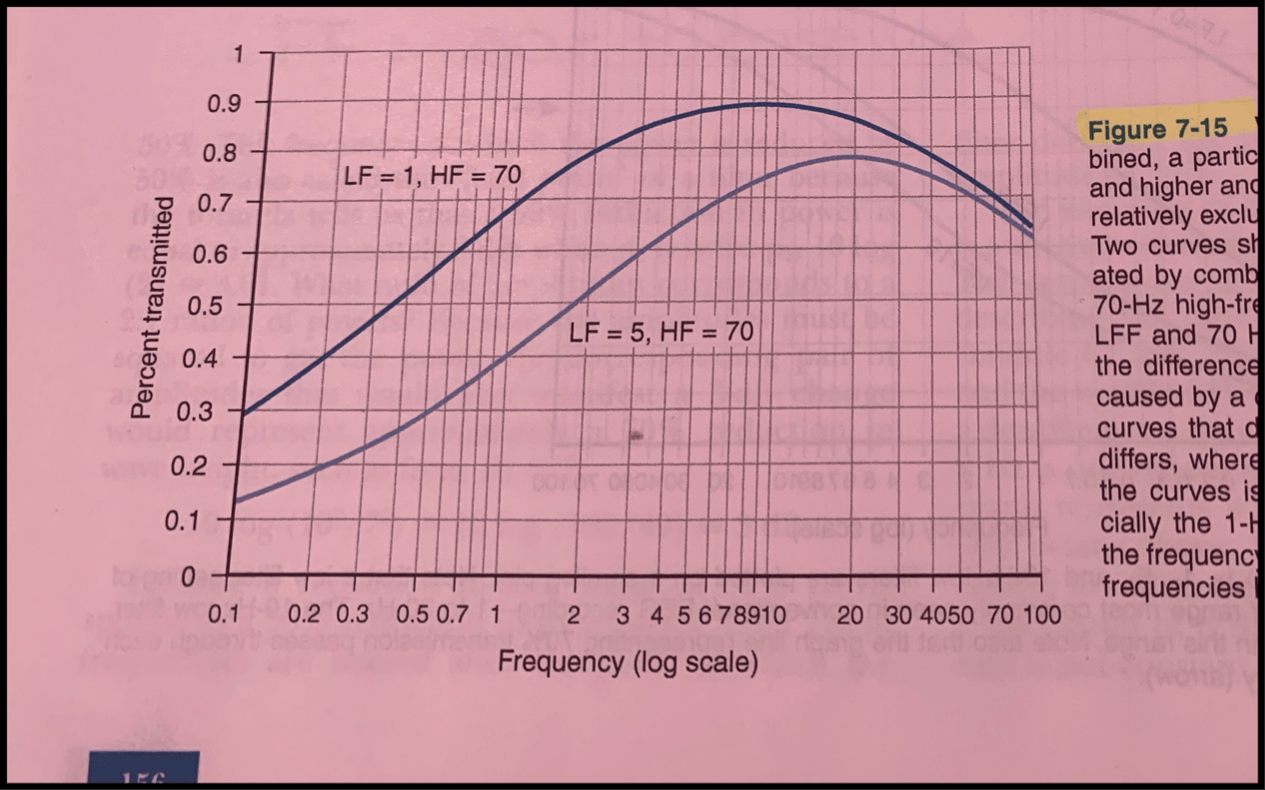
The filters effect on low frequencies differ
When there is a presence of 60 Hz artifact in an electrode that is an indicator for ...
Poor electrode contact
------ line in the graph below represents...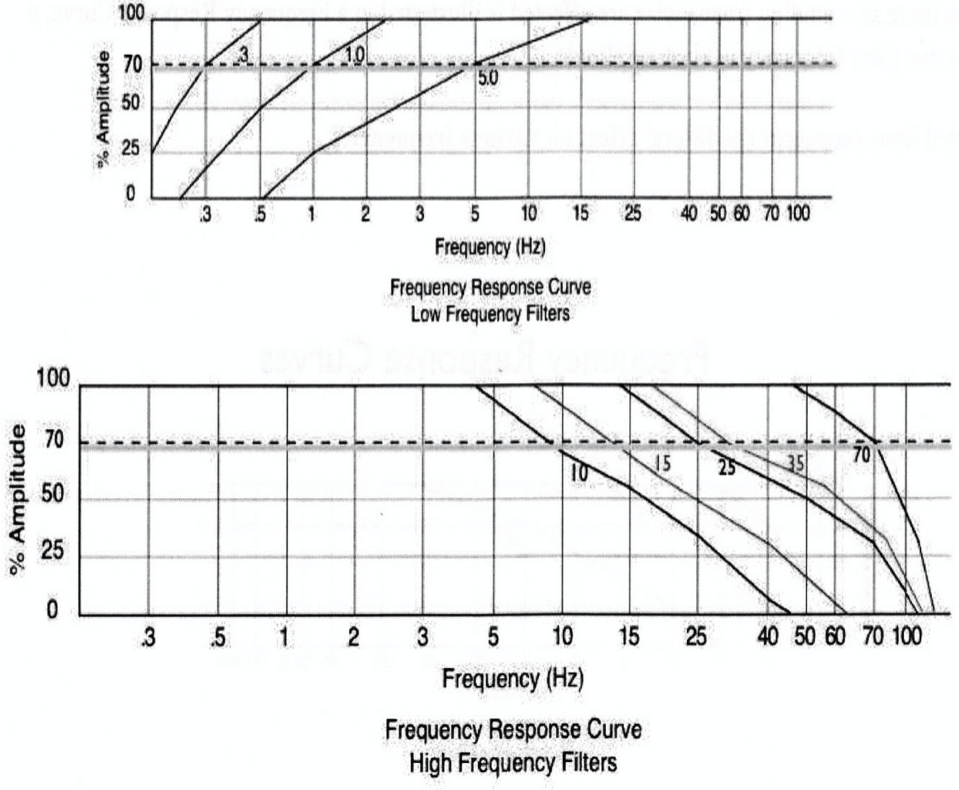
The cutoff frequency
τ= R X C
R stands for ________________
resistor decreases the current
What happens to the square wave output when a high filter is applied?
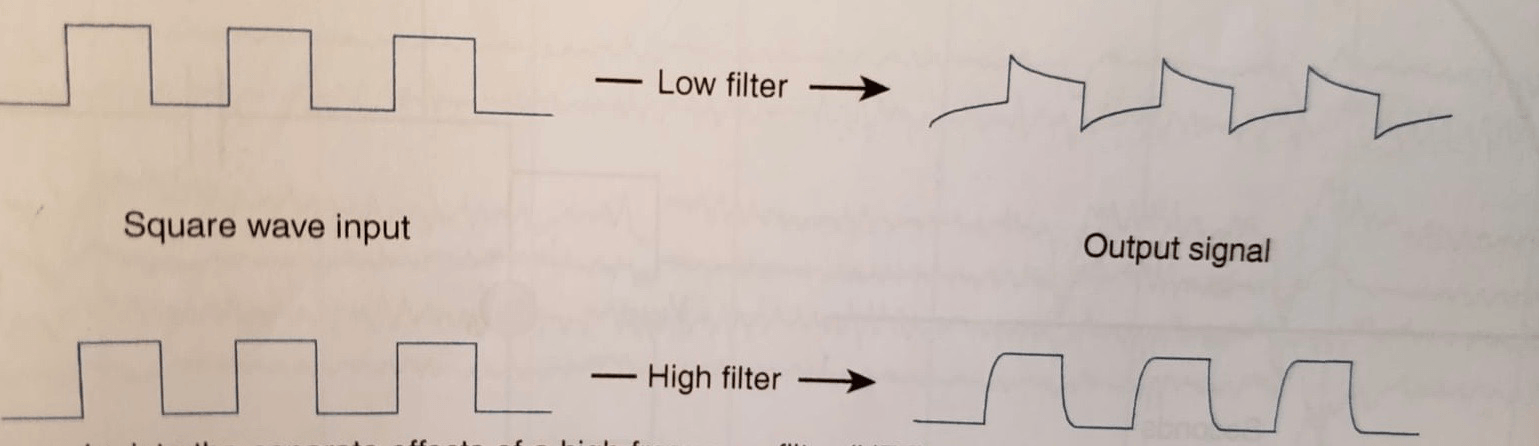
When a high filter is applied the vertical component of the square becomes rounded off, which changes the shape.
How would one avoid solely relying on filters to remove an artifact for example, if a sweat artifact/ muscle artifact is shown what should one do?
If there is a sweat artifact: try fanning a patient, loosening their clothing, or using air conditioning to cool the room down so they are more comfortable
If there is a lot of muscle artifact: try coaching the patient to relax and try repositioning their pillow
What can a filter be named after?
A particular frequency or after its time constant.
List the steps to prevent a 60 Hz Artifact.
1. Ground Outlet
2. Never use an extension cord
3. No machines- except EEG
4. No electronic/cell phone use
5. Hookup:SAME impedance bilaterally
When a low frequency filter encounters a sine wave that happens to be exactly at its cutoff frequency, it cuts down the _______ of the wave by approximately _______.
amplitude, 30%
HFF eliminates muscle artifact, but also can eliminate __________.
spikes
The right side displays....
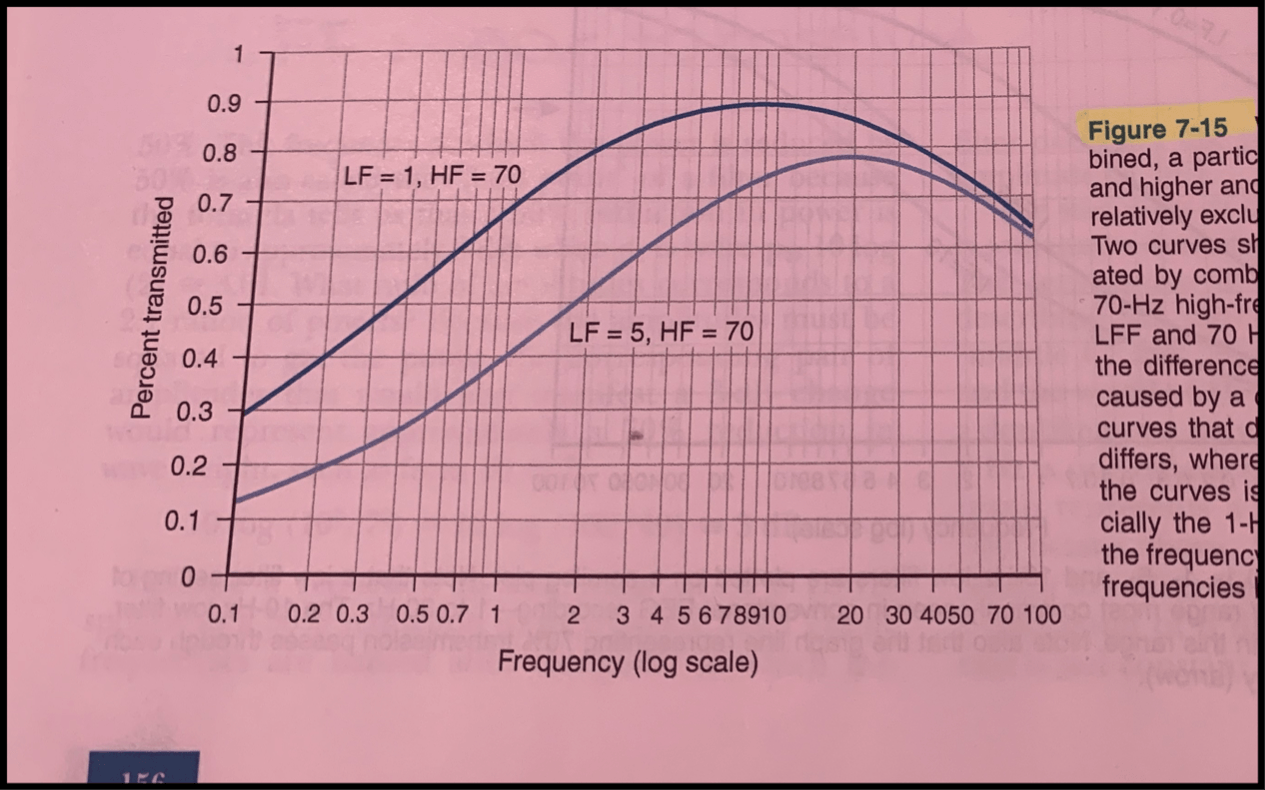
High frequency portion of the curves is similar
An improperly attached electrode may have a tendency to show...
Voltages that are too high/low and may also be prone to include other noise/artifact in the recording
List the proper steps needed to be taken to be able to read a frequency response curve.
1. Find the frequency of activity on the X-axis
2.Follow that point upward until it intersects with the curve (filter)
3. Follow intersecting point to the left of the graph to where it intersects with the Y-axis = value of how much of the waveform’s actual amplitude will be seen
τ= R X C
C stands for _____________
capacitor stores electricity
True or False:
Picture below is a muscle artifact.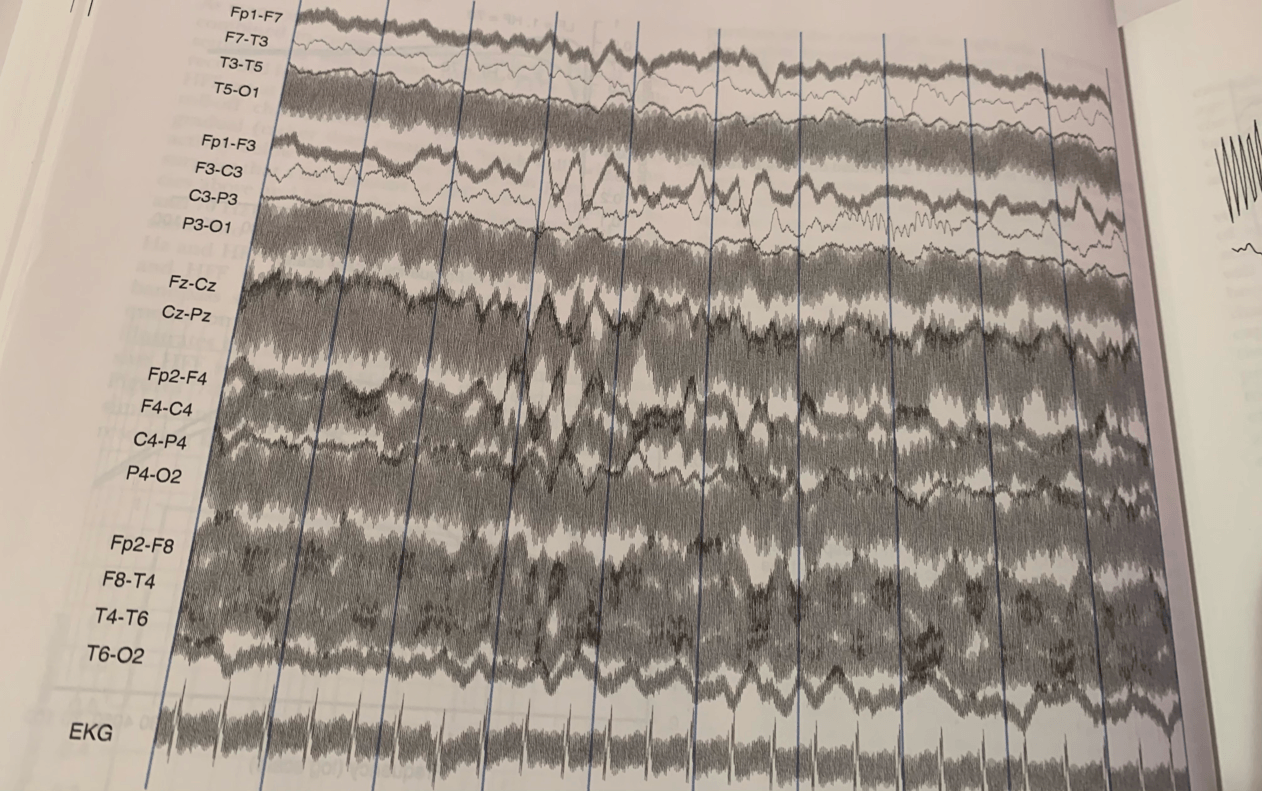
False:
60 Hz Artifact
Selecting an appropriate filter requires ...
1. Knowledge of important cortical rhythms to record in any particular patient at any one time
2. Knowledge of what artifacts look like
3. Being able to depict how the filters will affect both of the above activities
The Goal of a filter is ...
To accentuate brain activity and attenuate extraneous artifactual activity.
True/ False:
Notch Filters have a very high rejection for a very narrow band around 60 Hz.
True
LFF allows ______ potentials to pass unaffected.
faster
In a routine recording of a HFF of 15 Hz what will be shown?
The spike activity is greatly attenuated.
Waves with frequencies below 5 Hz are _____________.
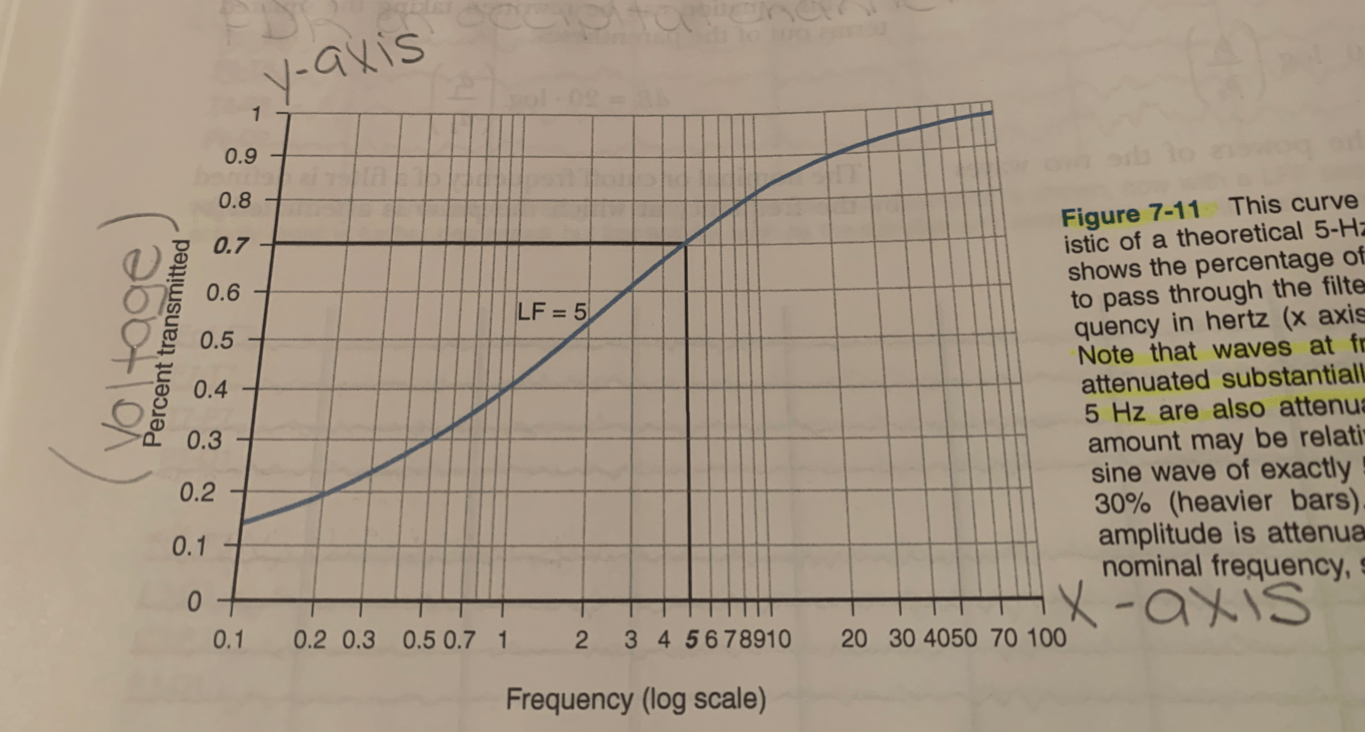
attenuated substantially
True/False:
Electrolyte solution/paste is applied on top of the electrode to facilitate recording of electrical currents.
False:
Electrolyte solution/paste is applied under the electrode to facilitate recording of electrical currents.
Which the filter setting will record the greatest
amplitude of a 50 Hz wave?
70 Hz
Amount of time it takes for the deflection to return to __________ of the way back to the __________ once a square wave voltage has been input to that pens corresponding amplifier
63%, baseline
How can the 60 Hz artifact obscured in these channels be distinguished from muscle artifacts? 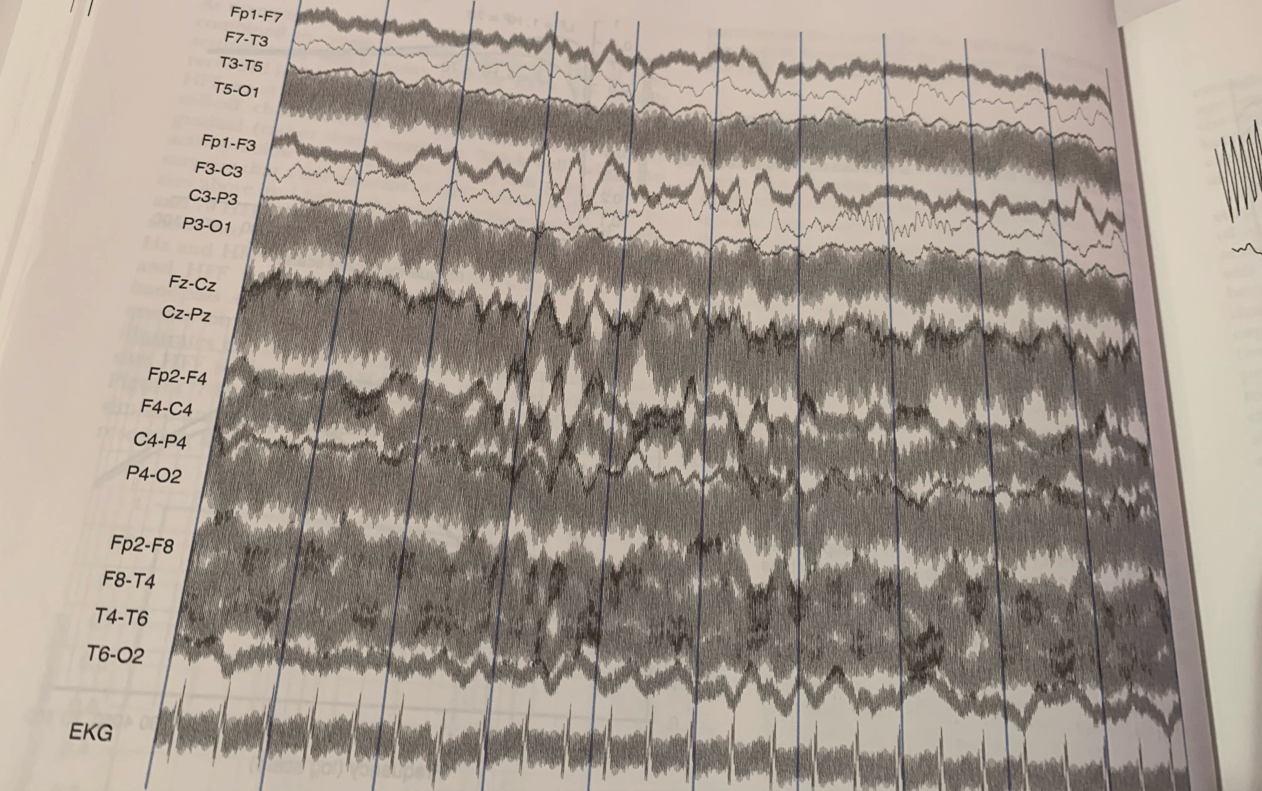
A highly regular, sinusoidal appearance is depicted and the amplitude of the 60 Hz artifact stays steady in each channel.
Low frequency filter of 5 Hz: eliminates sweat artifact, but also eliminates ___________.
Any slow activity
To select an appropriate filter one must...
- Have knowledge of important cortical rhythms to record in any particular patient at any one time
- Know what the artifacts look like
- Know how the filters will affect both of the above activities
50 and 60 Hz Notch Filters are most useful when...
The field of AC current from the electrical wiring and outlets that surrounds the patient contaminates the record.
What impact will a low filter have on an EEG?
It will affect the amplitude (50 mv)
Voltages will decrease, altered morphology (sharp contours will become rounded off), and sleep spindles, spikes, and sharp waves will be shown at 10-30+ Hz
The curve represents...
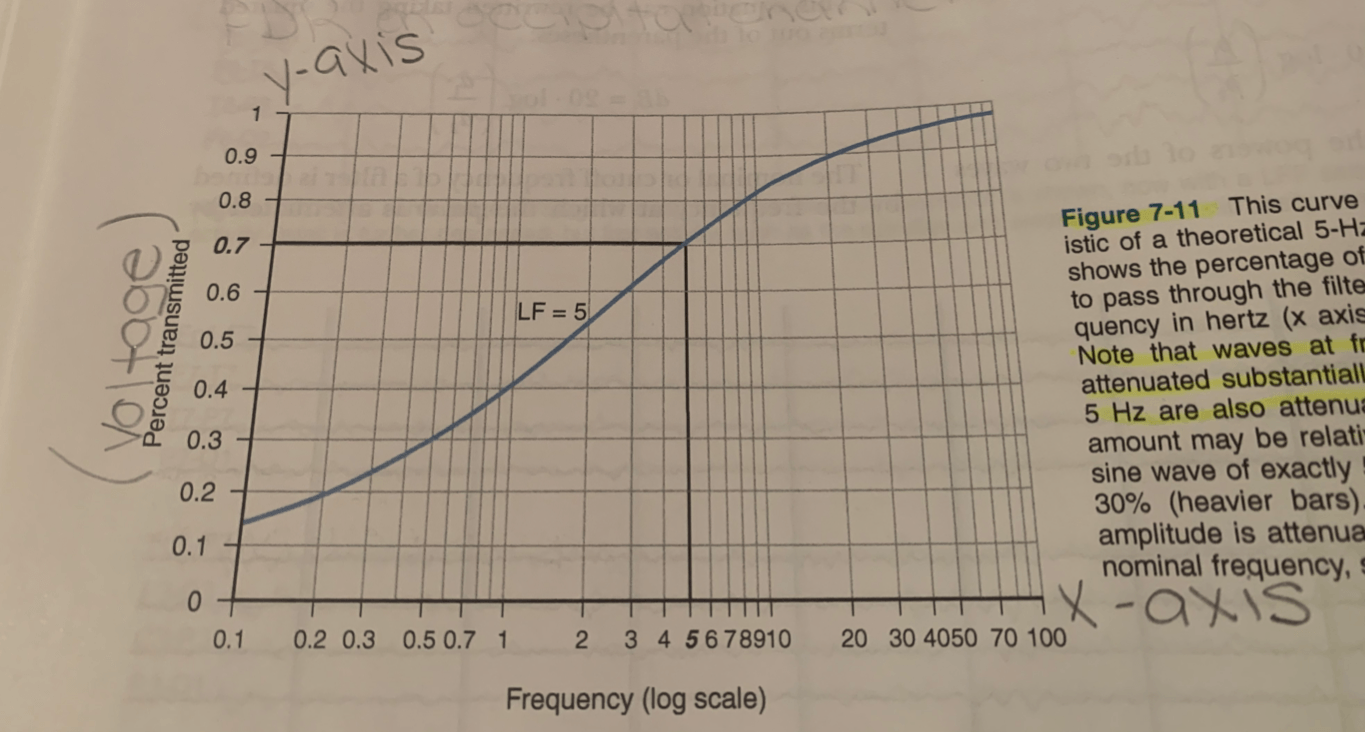
sine wave of exactly 5 Hz attenuated by about 30%
What happens if the two electrodes being compared have the same amount of 60-Hz-artifact?
Then we will not see it in the channel.
The activity of a 2 Hz wave will be displayed at ___% of its true amplitude if you use a 5 Hz LFF to record it.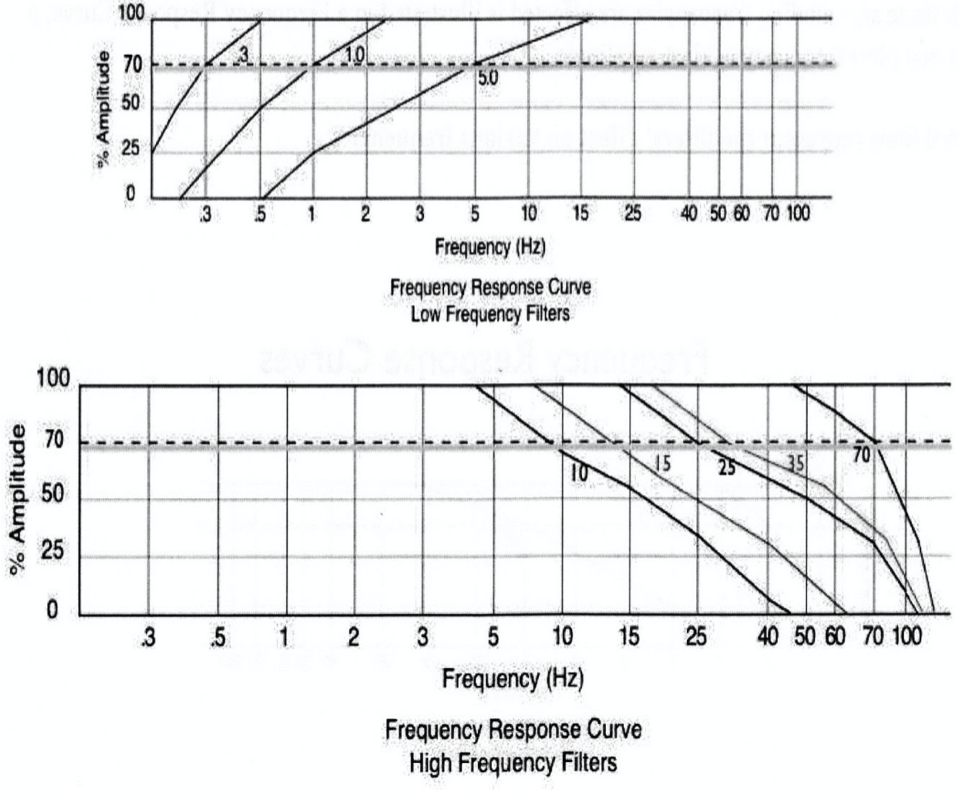
38%
As the time constant gets longer, or the LFF _____________ the timing of waveforms shift out to the right, becoming later in _____________.
decreases, time
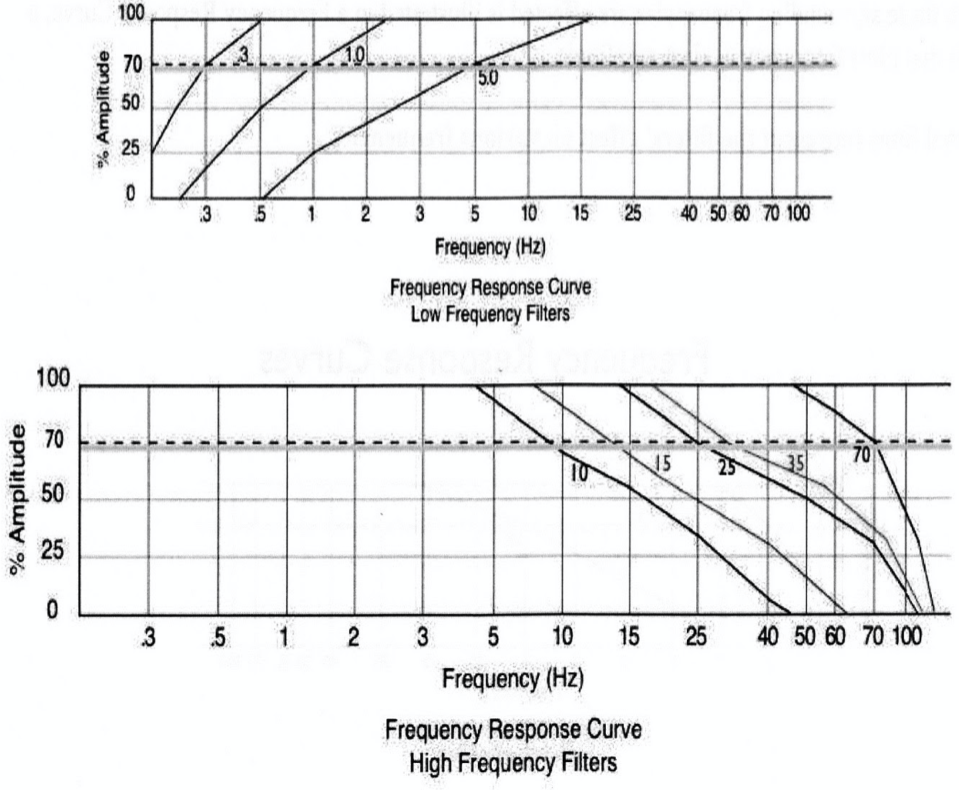
This graph represents roll off characteristics for HFF's with cutoff frequencies of....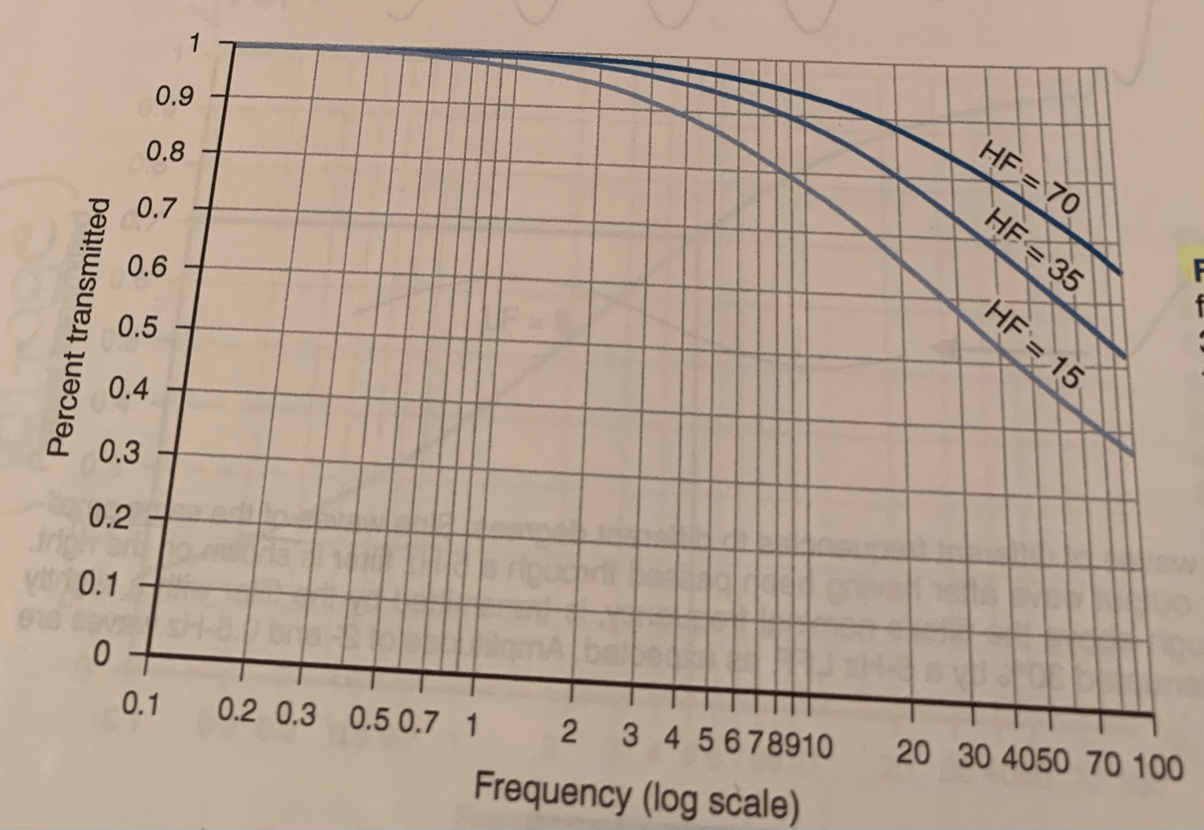
70 Hz, 35 Hz, 15 Hz
What impact will a high cut filter have on an EEG?
Affects the amplitude
Filters limit the _________ range and the machine will remain _________ and ________.
frequency, sensitive, accurate
60 Hz Filters reduce amplitude of waves in the 60 Hz range, what is in this range?
Electrical activity
What is the difference when using a LFF of 0.5 Hz rather than a LFF of 1 Hz?
0.5 Hz frequency allows more slower rhythms to be seen than 1.0 Hz which can be used when a patient has had a brain tumor of stroke.
What is a pitfall of using a High Frequency Filter?
Makes high frequency noise look more like sine waves (brain waves).
This graph displays...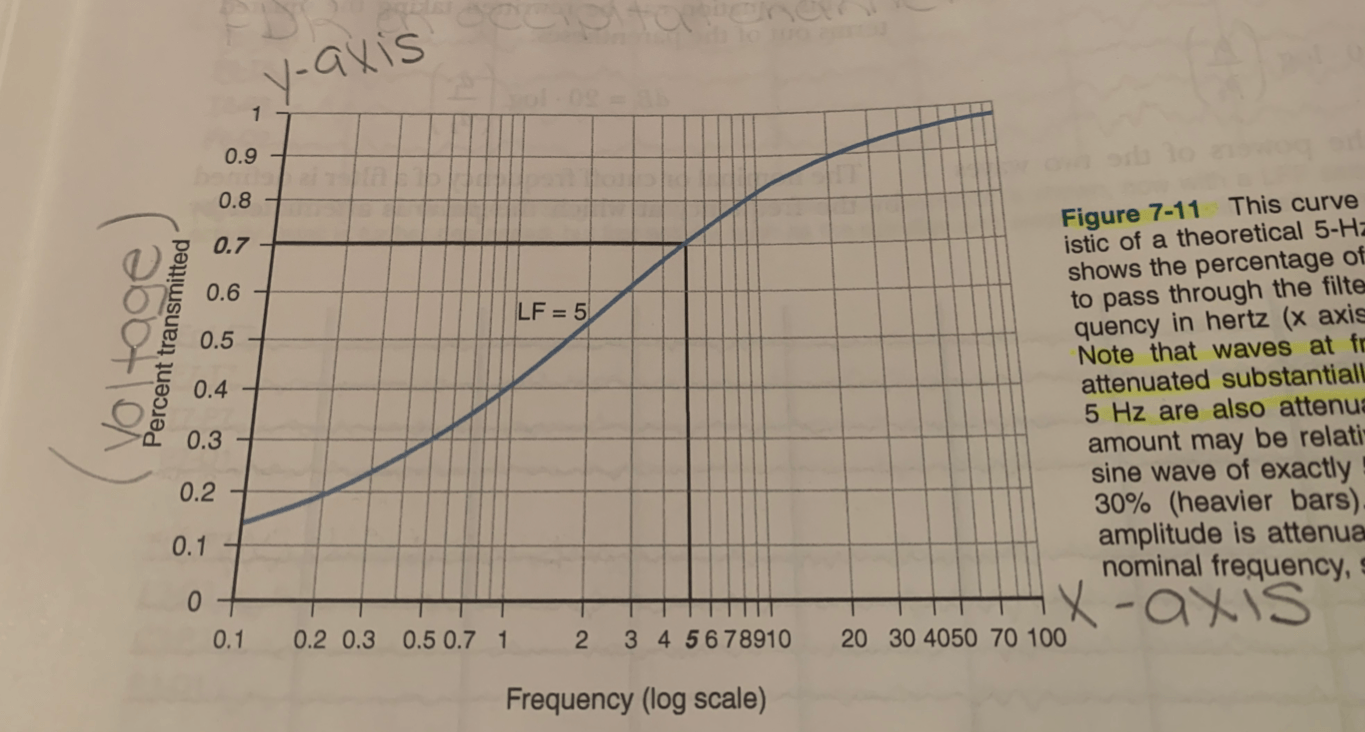
The % of a pure sine wave that is allowed to pass through the filter (y-axis) as a function of its frequency in hertz (x-axis)
If a 60 Hz activity is present all over the head, whey do we usually not see it in the tracing?
Because the activity cancels out during the subtraction of one electrode from another.
A 50 Hz frequency will be displayed at about ___% of its original true amplitude.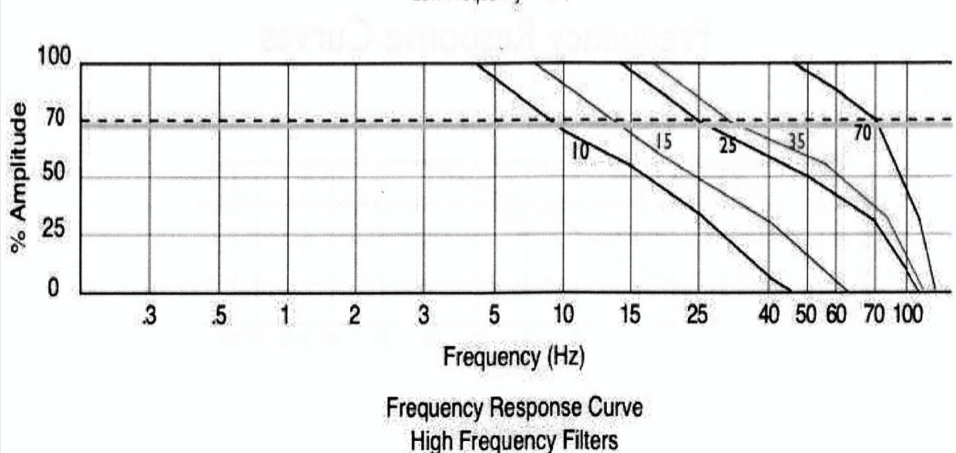
15%
As the time constant gets longer, or the LFF decreases the timing of waveforms shift out to the right, becoming later in time. This causes a change in ______________ and ______________.
timing and wave morphology
Each roll-off curve passes through the point of ___% transmission at its respective cutoff frequency. Frequencies lower than the cutoff frequency are attenuated by less than __%.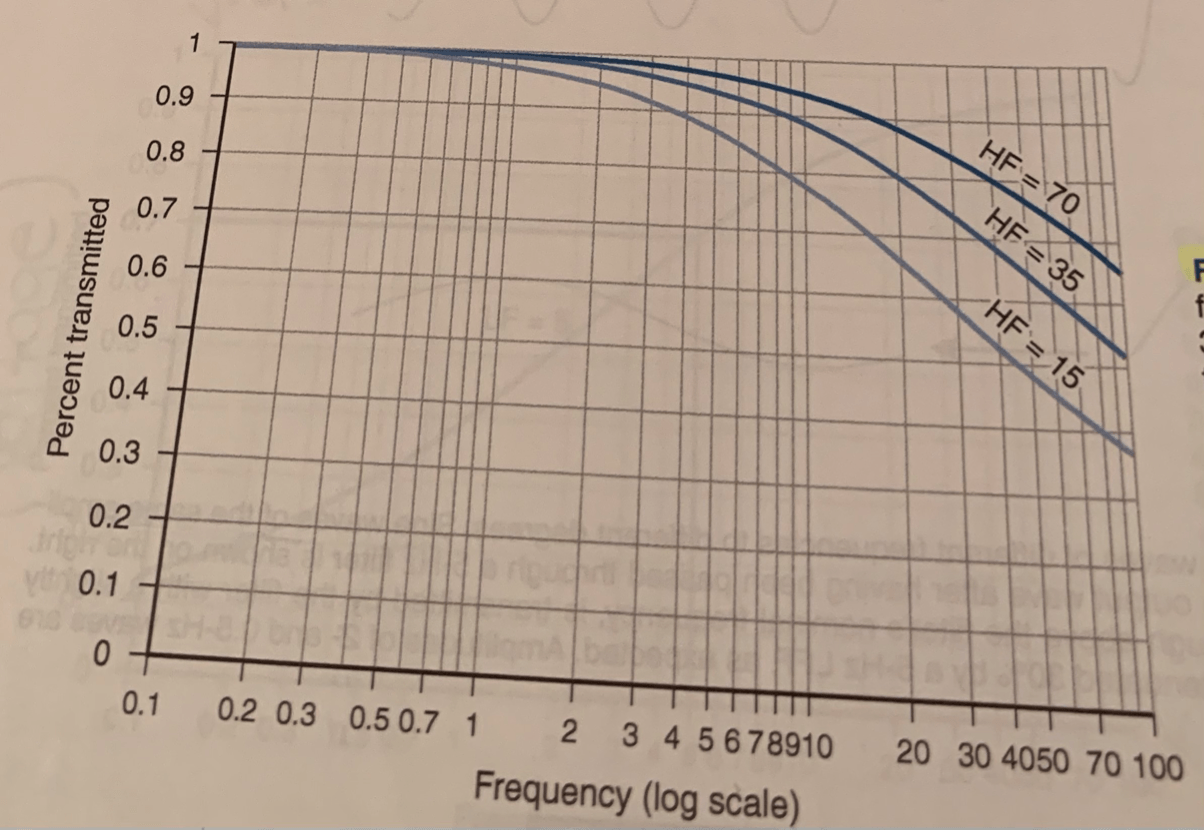
70%, 30%
When might using a low frequency filter setting of 0.5 Hz be useful and why?
When a patient has had stroke or a brain tumor because 0.5 Hz allows more slower rhythms to be seen.