The removal of particulate matter from
a liquid or gas stream. This is typically
achieved by passing the liquid or gas through
or past a porous barrier or membrane.
Filtration is only effective for the removal of
non-dissolved, or suspended, solids.
Filtration
Corrosive capability of a liquid.
Affected by the presence and concentration
of hydrogen and hydroxides in the fluid.
pH
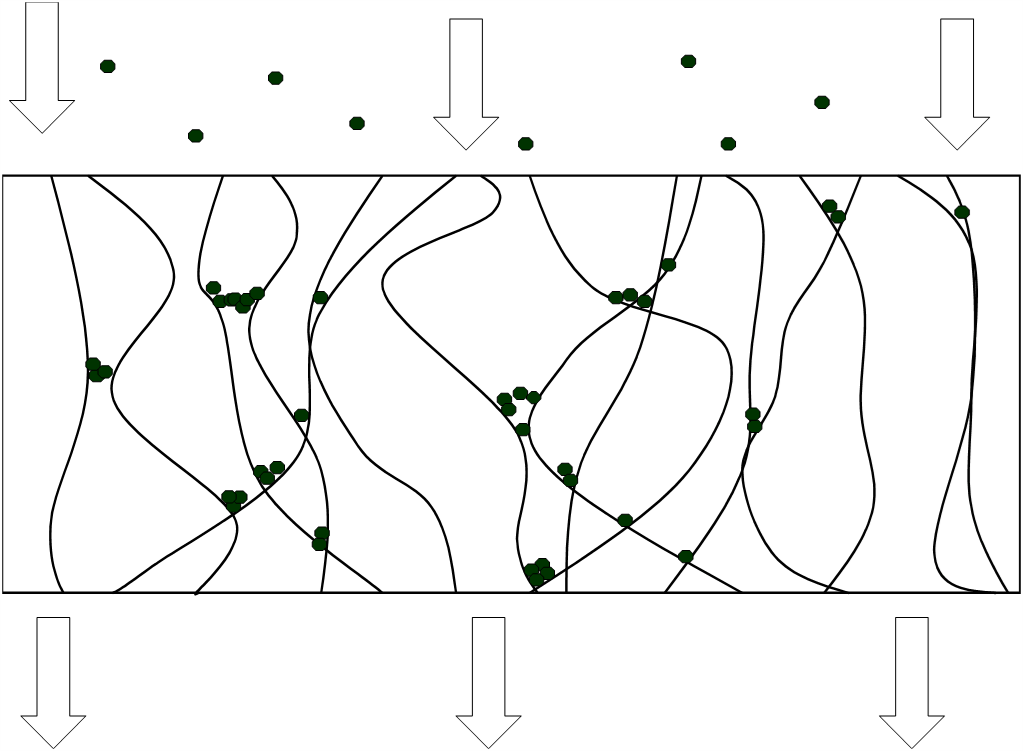
Particulate matter is captured within a matrix.
Includes sand media and RFR cartridge filtration.
Depth Filtration
To remove water from a semi-solid
(sludge) material to increase the % solids
content of the solids phase
Dewatering
Effective in the removal of essentially
all free and dispersed, non-emulsified oil,
and settleable solids from oil water mixtures
OWS
Solids that are suspended within the
fluid stream and have not chemically
bonded with the fluid. Typically
expressed as mg/L or ppm. Generally
removable with filtration depending
on the character of the solids,
the fluid, and influence of additives
and physical characteristics.
TSS
Total Suspended
Solids
Chemical compounds based on carbon
chains or rings and also containing
hydrogen with or without oxygen,
nitrogen, or other elements.
Organic Compounds

Particulate matter is accumulated
on a barrier.
Includes bag filtration.
Cake Filtration
To make water clear by removing
particulate impurities through settling in
static or non-turbulent water flow
Clarification
Will remove non-emulsified hydrocarbon
levels up to?
20%
Solids that have chemically become part
of the liquid on a molecular level.
Examples of this would be salt or
sugar or coffee color. Typically
expressed as mg/L or ppm.
Dissolved solids cannot be removed
from liquid with filtration alone.
TDS
Total Dissolved
Solids
Chemical compounds that do not contain
carbon as the principal element; i.e.
Metals or rocks
Inorganic compounds
Up to 50 ppm TSS
Bags
Cartridge
Sand filters
Name 3 types of
Filtration boxes.
Weir Box
Tube Settler
Dewatering Box
This attracts small droplets of oil that
combine with one another until they are
large enough to float up and be caught
by the skimmer bar.
PVC coalescing pack media
A measurement of water clarity determined
by how much light is absorbed, reflected,
or passes through a fluid sample.
More sediment or particles =
higher readings. Water clarity is
an important factor in determining the
impact of discharged water on the
receiving water body.
NTU’s:
Nephelometric Turbidity Units
Living organisms that remove dissolved
oxygen from water/fluid either as
a direct result of biological processes,
or by interference with the populations
of oxygen producing organisms.
Bacteria and algae are examples.
BOD:
Biological Oxygen
Demand
Up to 100 ppm TSS
Bag
&
Sand filters
140 gpm is the max
flow for this type of
Equipment.
Tube Settler
Term attracts oil
Oleophilic (oil loving)
Refers to applying industry accepted
best approach to solving problem.
BMP:
Best management practice.
Chemical Oxidants or Compounds that
remove oxygen as they dissolve and
chemically react with water or interfere
with populations of oxygen producing
organisms. Decaying organic matter such
as animal and food wastes are examples
COD:
Chemical Oxygen
Demand
Up to 500 ppm TSS
Sand filters only
Test to determine if a
dewatering box will
work on a certain
application
Bucket test
The OWS works by
the difference of the
two liquids
Specific gravity