Geosphere: rocks, mountains
Hydrosphere: water
Atmosphere: air
Anthrosphere: human
5. How would a natural disaster affect an area's carrying capacity? (pg 35)
Carrying Capacity decreases because there is less food and other resources
11. If organisms are leaving/dying in an area, what is that doing to the biodiversity of that area? (pg 32)
Biodiversity is decreasing
16. Where is ATP made within the cell? (which organelle?) (pg 114)
Mitochondria
21. Explain the difference between a food chain and a food web
Food chain: the series of energy being consumed
Food web: several food chains together
2. List how the biosphere is organized, from smallest to largest (1-5). pg 11
Organism, Population, Community, Ecosystem, Biome, Biosphere
6. Identify three things that are density-independent limiting factors. (pg 36)
Weather
Natural Disasters
Human Activity
12. What is a climax community? (pg 50)
the final stage of succession with several different species
17. What is the difference between thylakoid and mitochondria? (pg 98)
Thylakoid: where photosynthesis takes place
Mitochondria: where cellular respiration takes place
24. A _____________ consumer eats/consumes Secondary Consumers.
tertiary
3. List 3 biotic factors and three abiotic factors. (pg 12)
Biotic: plants, animals, humans
Abiotic: air, water, sunlight
7. Identify three things that are density-dependent limiting factors. (pg 36)
Competition
Predation
Parasitism/Diseases
13. If biodiversity is high, what does this mean for the stability of the ecosystem? (pg 49)
When biodiversity is high, the ecosystem is very stable
18. What are the inputs for Cellular Respiration? The outputs? (pg 113)
Inputs: Oxygen, Glucose
Outputs: Water, Carbon Dioxide, ATP
26. If a snake has 4623.1 J of energy, how much did the rat have before it was eaten?
46, 231 J of energy
4. How do scientists measure population density (formula)? (pg 26)
# of individuals
______________
area
8. What type of population growth do we see when resources are abundant? (pg 34)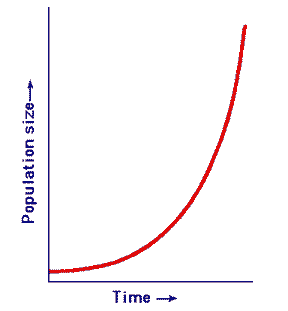
Exponential Growth
10. When does primary succession begin? When does secondary succession begin? (pg 50-52)
Primary Succession--> begins with rock
Secondary Succession--> begins with natural disaster like a fire
19. What organisms undergo the process of cellular respiration? Photosynthesis? (Pg 96 & 114)
Cellular Respiration: plants & animals
Photosynthesis: plants
27. What is the difference between a heterotroph and an autotroph?
Autotroph: an organism that receives energy from the sun
Heterotroph: an organism that consumes other organisms