This mechanism of evolution requires differential survival and reproductive success (fitness) among the offspring
What is natural selection?
A population is in Hardy-Weinberg __________ when it is not evolving.
This is what a node represents on a phylogenetic tree.
What is a common ancestor? (or divergence event)
Substances that dissolve easily in water are said to be
What is hydrophilic?
The simplest carbohydrate molecule, produced during photosynthesis
What is glucose?
This mechanism of evolution gives way to the variation within a species and is considered the "raw material" of evolution
What is mutation?
Straight hair is a homozygous recessive trait. The hardy-weinberg symbol that would show this is
What is q2 ?
This evidence is more exact and reliable than morphological evidence in constructing a tree.
What is molecular/DNA/genetic evidence?
Water is a slightly charged molecule because of its ____ bonding
Polar
The ____________ of a molecule will determine how it ____________ in the cell/organism.
structure / functions
A trait or behavior that helps one survive and reproduce in its environment.
What is an adaptation?
Within a population of butterflies, the color brown (B) is dominant over the color white (b). And, 40% of all butterflies are white. What is the value for q to the hundredths place?
0.63
When looking at a phylogenetic tree, species are more closely related if:
They share a more recent common ancestor than other the organisms shown in the tree.
Hydrophobic substances will have intramolecular bonds that are mostly
nonpolar covalent
The process that bonds single monomers into larger, more complex organic molecules. 1 water is lost for each new bond formed.
What is dehydration synthesis?
In order for speciation to take place (new species form), groups of individuals must first be ________ from one another.
What is reproductively isolated?
Within a population of butterflies, the color brown (B) is dominant over the color white (b). And, 40% of all butterflies are white. Calculate the frequency of heterozygous individuals.
0.47 (0.4662)
A branch on a phylogenetic tree represents this.
What is a lineage?
The polarity of water allows it to make this kind of bond between different water molecules
hydrogen bonding
What are enzymes?
The disproportionate representation of a certain allele due to a population at one point being reduced to a select few individuals that had a high representation of this allele. The Askenazi Jews are an example of this. During WWII, their populations decreased significantly. By chance the remaining population had a high number of the allele that codes for the deadly disease, Tay-Sachs.
What is genetic drift (bottleneck effect)?
After graduation, you and 19 of your closest friends (lets say 10 males and 10 females) charter a plane to go on a round-the-world tour. Unfortunately, you all crash land (safely) on a deserted island. No one finds you and you start a new population totally isolated from the rest of the world. Two of your friends carry (i.e. are heterozygous for) the recessive cystic fibrosis allele (c). Assuming that the frequency of this allele does not change as the population grows, what will be the incidence of cystic fibrosis on your island?
What is 0.25%?
Which species is least related to the rest and what is your evidence?
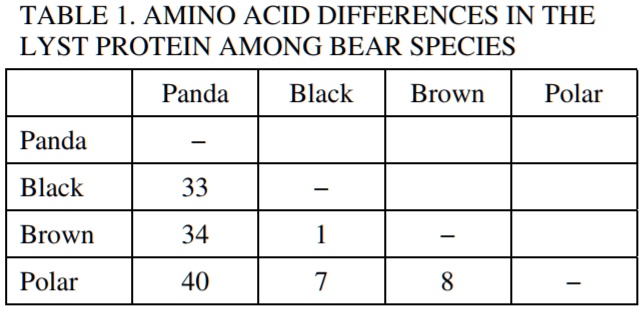
The panda- it has the most amount of amino acid differences across all of the other species.
Water coheres more strongly to itself than to the air above it. This creates..
What is surface tension?
Nucleic acids are composed of chains of different types of nucleotides. Because there are different nucleotides, a genetic code can be constructed from their sequence in a strand of DNA or RNA. These are the different nucleotides (letters) in a DNA molecule.
What are adenine (a), cytosine (c), guanine (g), and thymine (t)?