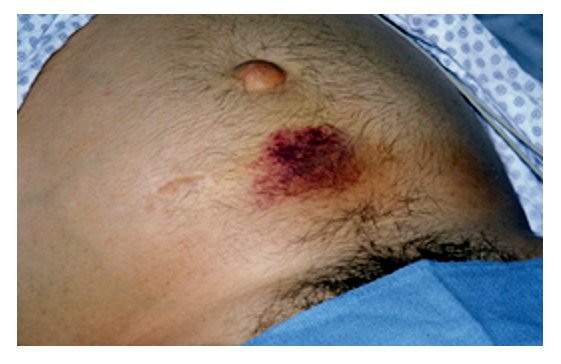
What is Cullen's Sign?
Obvious yellowing of the skin, sclera, and mucous membranes
What is jaundice?
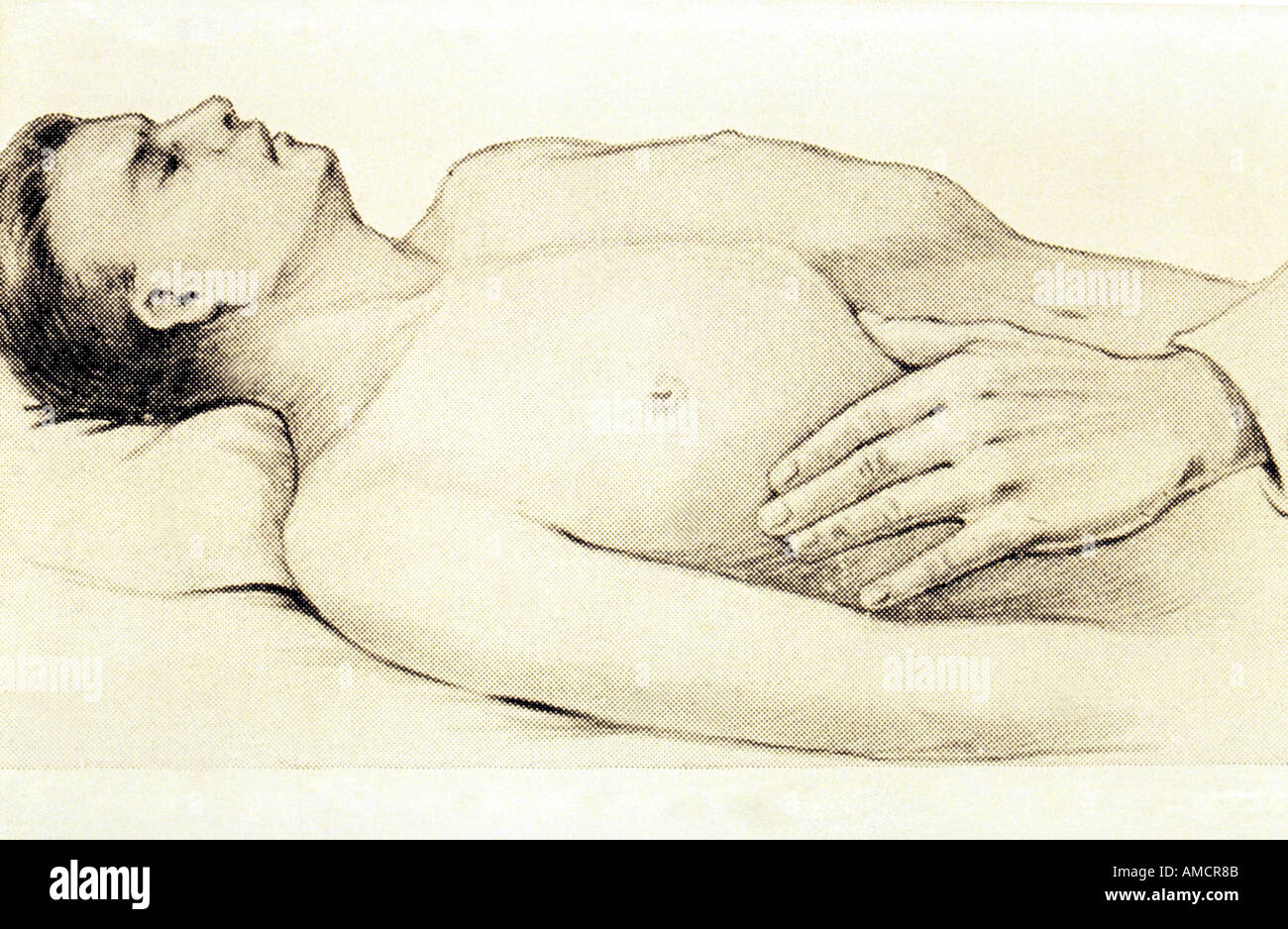
What is a Murphy's sign?
What is the treatment for Pancreatitis?
NPO
Rest
Antibiotics
Fluids
No fresh flowers or fresh fruits (canned or cooked foods).
No raw or uncooked meats, poultry or fish
Limit visitors
Avoid sick people
Avoid crowded places
What are precautions for Neutropenia?
Fragile, thin veins that become distended and tortuous due to portal hypertension.
What are Esophageal Varicies?
Low sodium and lean protein diet is best for these patients
What is Cirrhosis?
Electric razors
Soft tooth brush
Limit or reduce venipuncture. Apply pressure for at least 5 minutes post lab draws
Monitor for dark tarry stools
What are precautions for thrombocytopenia?
Common causes of acute pancreatitis?
What are alcoholism, gall stones, biliary/pancreatic obstruction and trauma from surgical manipulation of biliary tract?
Chronic pancreatitis has normal to moderately elevated levels
What are amylase and lipase?
Cognitive syndrome that stems from unfiltered or unbroken down toxins that lead to metabolic abnormalities- such as disorientation, confusion, flapping of arms or Hepatic Coma.
What is hepatic encephalopathy?
Warm and bright red palms of the hands
What is palmar erythema?
Interventions for ICP?
What is
Do not cough or sneeze?
Elevate HOB.
Avoid jerky movement
Head should be in midline, do not bend
Do not strain to have BM.
Provide quiet and calm environment (dim the lights).
The most rapid reliable imaging technique to diagnose acute pancreatitis and causative factors
1. Oral fecal route- Self resolving
What is Hep. A?
A poor prognostic indicator of liver failure with the symptoms of sudden oliguria, elevated BUN and creatinine levels, and increased urine osmolarity
What is hepatorenal syndrome?
Severe neck stiffness causes a patient's hips and knees to flex when the neck is flexed. Indicates meningeal irritation.
What is Brudzinski's sign?
Medications given to reduce ammonia levels and prevent/treat hepatic encephalopathy
What is lactulose and nonabsorbable antibiotics?
The two most important nursing plans for the acute pancreatitis patient
What are pain management and promotion of nutrition and hydration?
What are risk factors for breast cancer?
Genetics. BRCA gene +
Family history
Obesity.
What are some of the S/S of ICP?
Restlessness, disorientation and confusion
Headache. N/V
Cushing Triad (irregular slow respirations HTN and bradycardia)
A coarse tremor characterized by rapid, nonrhythmic extensions and flexions of the wrists and fingers
What is asterixis?
1. Profile of a female with Cholecystitis?
2. Teaching that you will do for this patient?
1. Fair, Fertile, Fat, forties
2. Life style modification (diet, exercise).
Labs to trend in the acute pancreatitis patient
What are amylase, lipase, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and alanine aminotransferase (ALT)?
A rare, inherited disease that causes the progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the brain.
Strange and uncontrolled movements that are either slow or wild and jerking are-one of the clinical manifestation of this disorder
What is Huntington's disease?