What lobe in the brain is responsible for hearing?
Temporal lobe
What nerve is responsible for the movement of most of the muscles in the tongue?
Hypoglossal nerve
What are the meninges?
Dura mater, Arachnoid mater, & Pia mater
What functional group opposes or reverses particular movement?
Antagonist
What is this called?

Transversus abdominis
What's the difference between gray matter and white matter?
Gray matter: short, nonmyelinated neurons and cell bodies
White matter: myelinated and nonmyelinated axons
What type of nerve is this?
Facial nerve
What is the function of meninges?
To protect and cover the spinal cord and brain, otherwise known as the CNS (central nervous system). They also provide a support system for blood vessels.
What pattern of arrangement is G?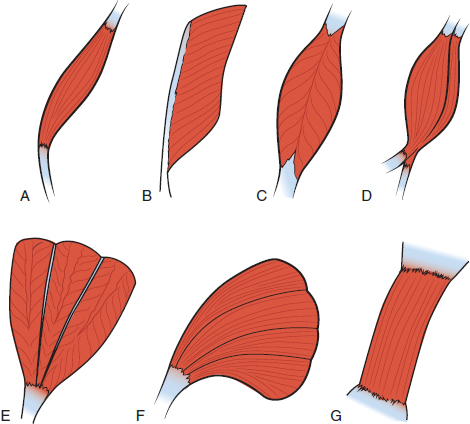
Parallel
What are the projection fibers that radiate through cerebral white matter to the cortex?
Corona radiata
What part of the brain is this (orange)?
Brain stem
What is the largest cranial nerve with both motor and sensory functions?
Trigeminal nerve
What is the pia mater?
the innermost layer closest to the brain tissue
What is this called?
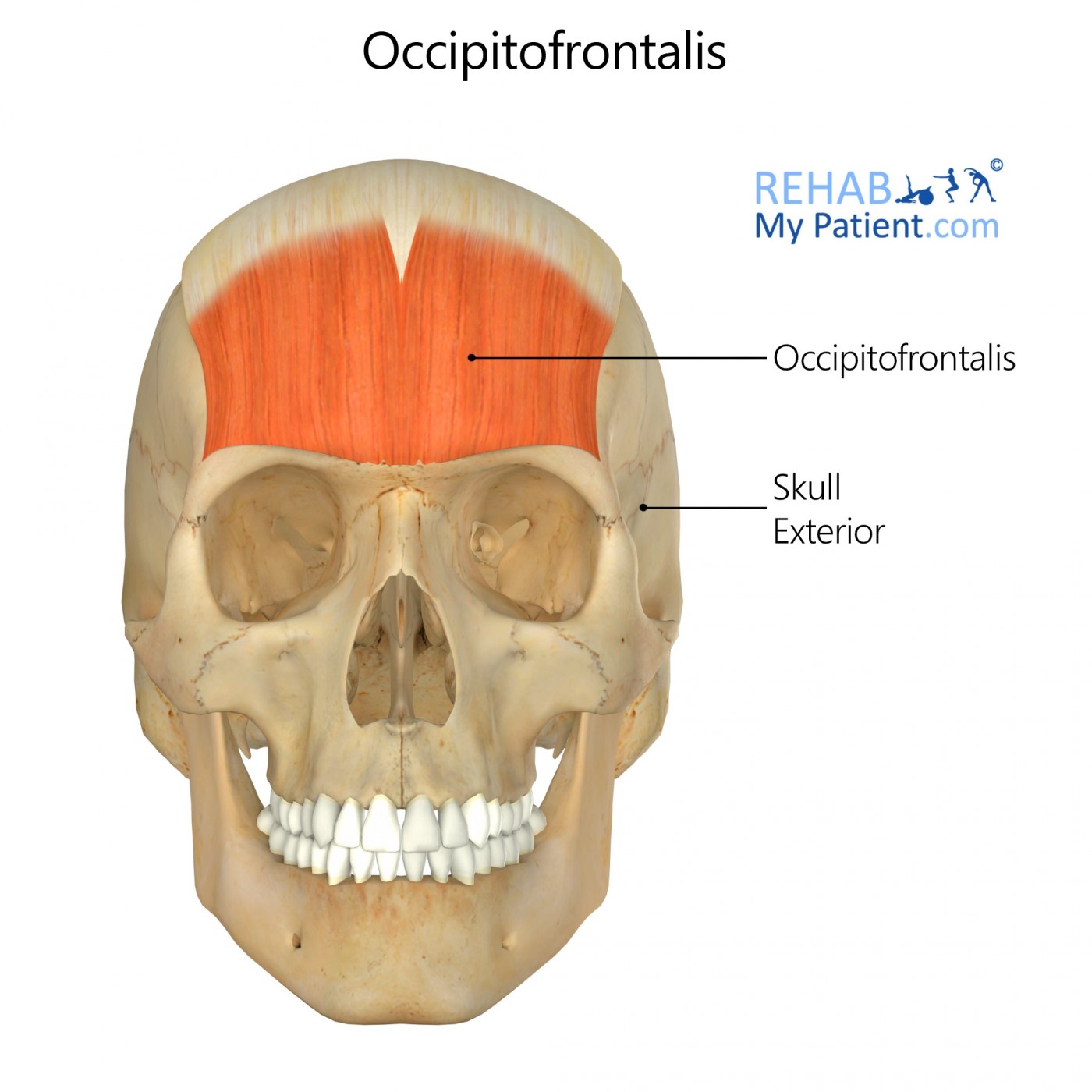
Frontal belly
What is the hypothalamus responsible for?
Gland in the brain that controls the hormone (endocrine) system
What ventricle is this (in red)?
Fourth ventricle
What is the optic nerve?
The sensory nerve that involves vision.
What is the subarachnoid space within meninges?
It's the space between the arachnoid and the pia mater filled with cerebrospinal fluid that cushions and protects the brain and spinal cord.
What is this called?
Platysma
What muscle is this?

Rhomboid major
Cerebral cortex
What nerve provides muscle function and pupil response?
Oculomotor nerve
Which menix contains a drainage system that allows blood the leave the brain and allows cerebrospinal fluid to re-enter circulation?
Dura mater
What are the prime movers of jaw closure?
Temporalis and masseter
What part of the brain is located between the midbrain and medulla oblongata?
Pons