Creates concentration gradients for Sodium and Potassium.
What is the Sodium Potassium Pump?
The subunit of a G protein protein that is active when bound to GTP.
What is alpha subunit?
Phase in the cell cycle when DNA is replicated.
What is the S phase?
Enzymes that remove phosphate groups from substrate
What is phosphatase?
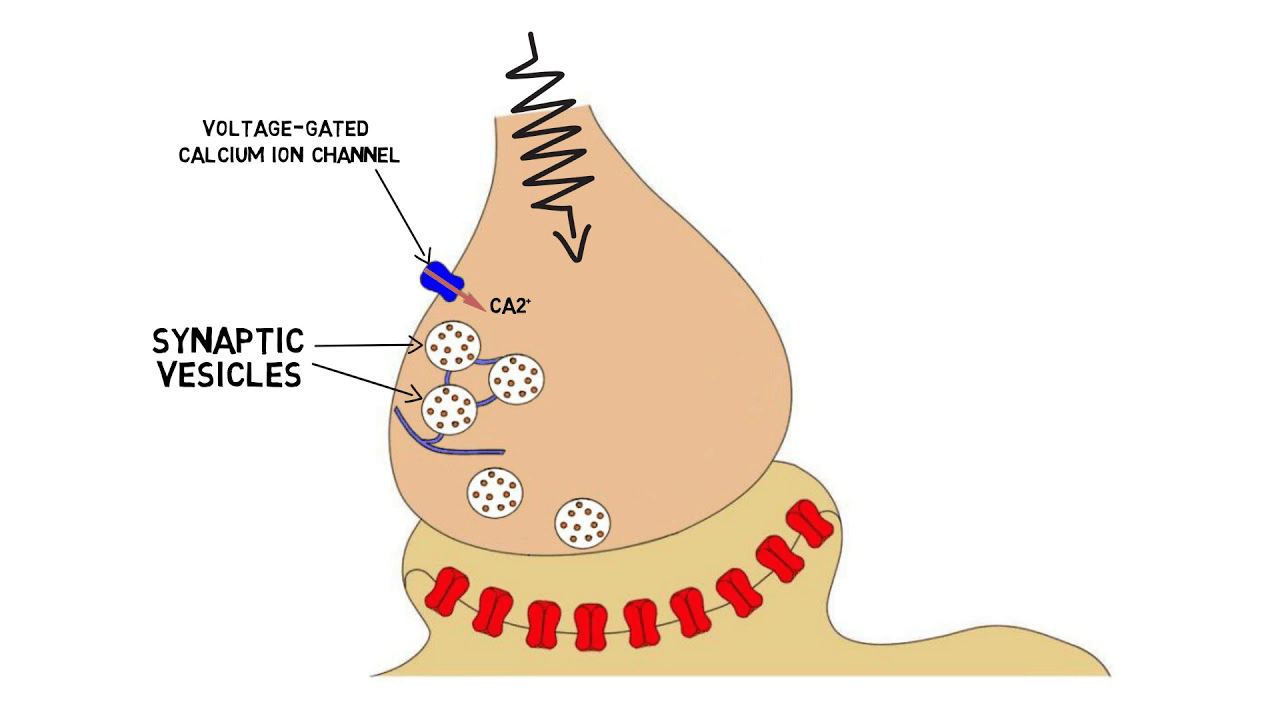
It's the ion responsible for neurotransmitter secretion in response to an action potential.
What is calcium?
Signal molecule that causes cell to carryout an action.
What is a first messenger?
Two identical chromatids that are formed by replication of a chromosome, are joined by a centromere
What are sister chromatids?
Can halt cell division in both the G1 and G2 phases of the cell division cycle
What is p53?
Ion responsible for depolarization during an Action Potential.
What is Sodium?
Generated by adenylyl cyclase and activates PKA.
What is cAMP?
The nucleus envelope breaks down during this stage.
predefined cell suicide, where the cell actively destroys itself by shrinking, maintaining a smooth functioning in the body
What is apoptosis?
Molecules that diffuse passively across the plasma membrane.
What are hydrophobic molecules?
Proteins that link intracellular signaling cascades activated by receptor tyrosine kinases
What are Ras proteins?
Stage in mitosis where each pair of chromosomes is separated and pulled toward opposite ends.
What is Anaphase?
Drive the events of the cell cycle by partnering with a family of enzymes called the cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks)
What are cyclins?
Transporter that allows for the transport of Glucose into the intestinal epithelium.
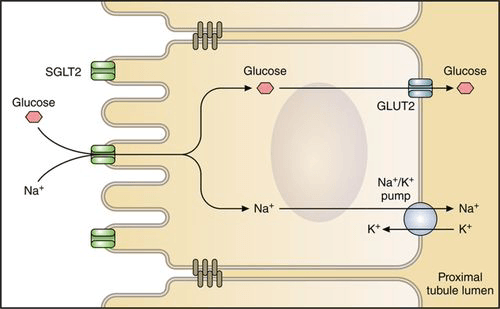 What is the Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter?
What is the Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter?
Produces the second messengers Inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and Diacylglycerol (DAG).
What is Phospholipase C?
The principal microtubule-organizing center seen in mitosis.
What is the centrosome?
Membrane channels that mediate the cell-to-cell movement of ions and small metabolites
What are gap junctions?