What is the primary intracellular cation? The primary extracellular cation?
Primary intracellular cation: K+
Primary extracellular cation: Na+
What is the name and function of the hard covering found on the outside of bones?
The periosteum contains blood vessels and nerves and helps provide an anchoring point for tendons and ligaments.
What is the function of the nervous system?
Collect, synthesize, and respond to information from receptors
T/F - the intestines have both latitudinal and longitudinal layers of muscles to help with peristalsis.
True
Identify the periosteum.
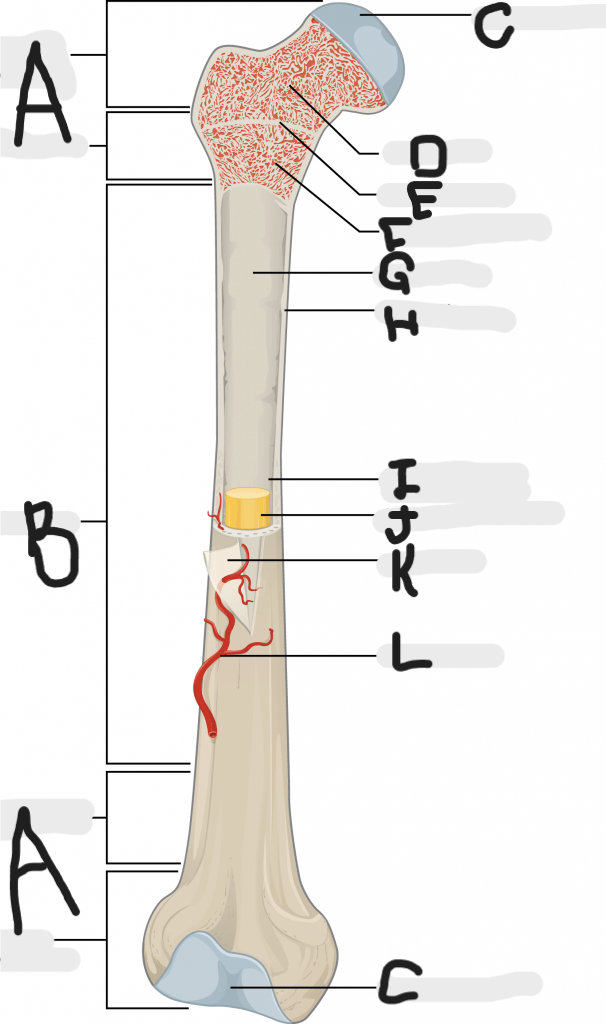
The periosteum is represented by K.
A hypotonic solution has a _______ concentration of solute than inside a cell.
lower
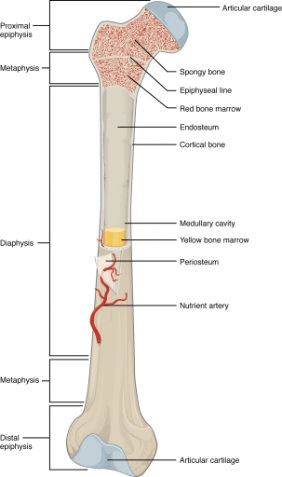
What is the location and function of red bone marrow?
Red bone marrow - found in the epiphyses of long bones and within flat bones - performs hematopoeisis
What compounds combine to form acetylcholine?
What enzyme degrades acetylcholine?
Acetylcholine is formed from acetate and choline. It is degraded by acetylcholinesterase.
What does mastication mean? What about deglutition?
Mastication - chewing
Deglutition - swallowing
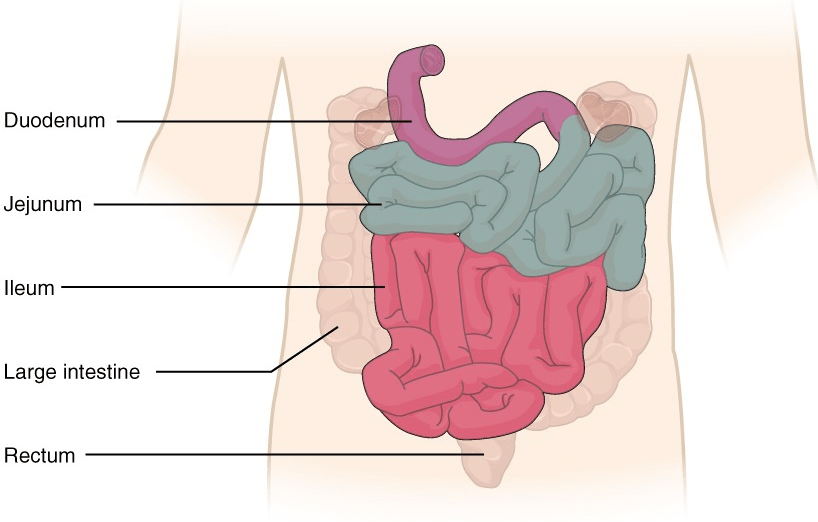
Identify the jejunum.
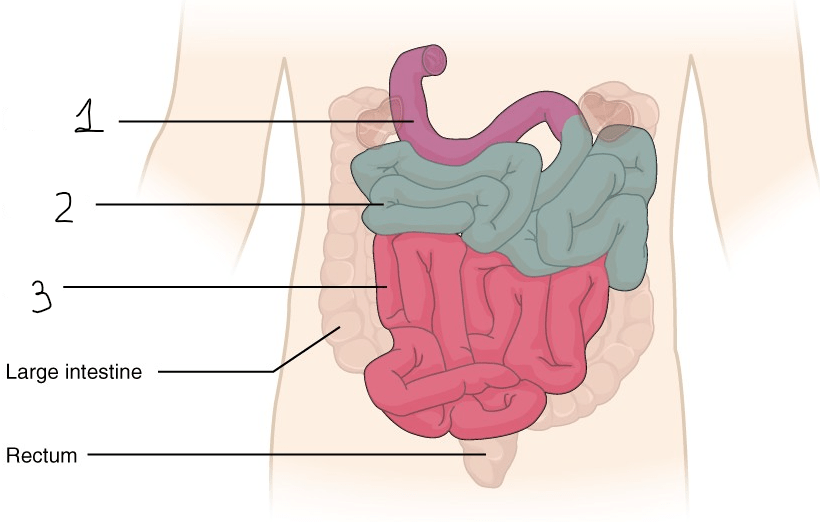
Jejunum - 2
What are the three basic tenets of cell theory?
1) Cells are the basic unit of life
2) Cells only come from other existing cells
3) All organisms are made of cells
What bone cell would be active when blood calcium levels are low? Why?
Osteoclasts - they break down bone and free up calcium when blood calcium levels are low
What is the function of the premotor cortex? What is the function of the hypothalamus?
The premotor cortex plans movements.
The hypothalamus is ultimately responsible for maintaining homeostasis. It plays a part in hunger, thirst, circadian rhythm, body temperature, and heart rate, among other things.
Identify the missing structures.
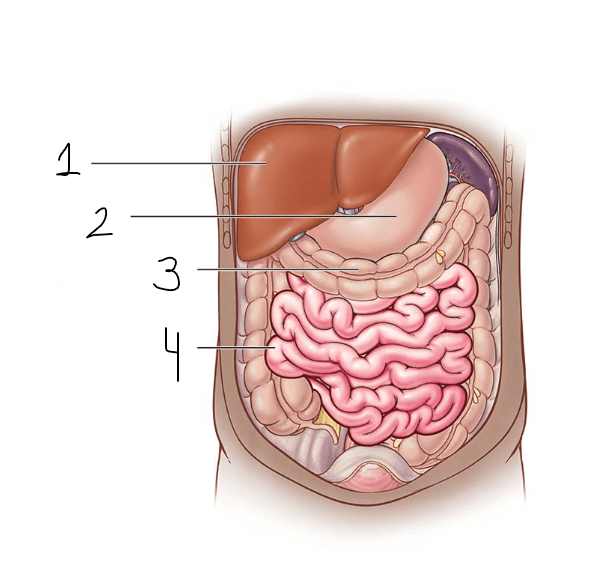
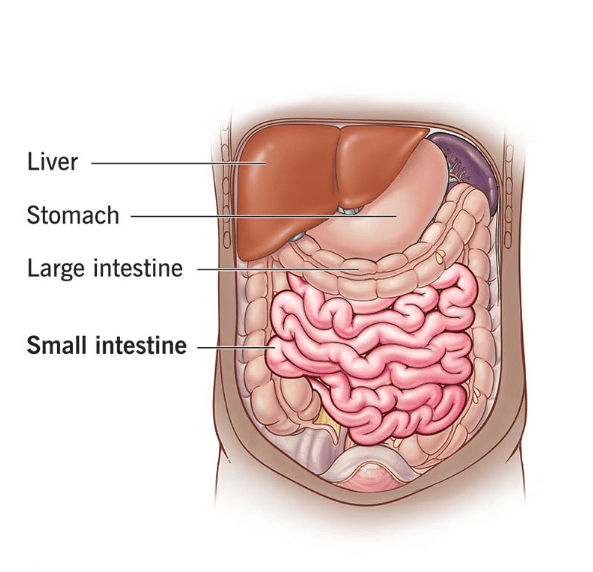
1) Liver
2) Stomach
3) Large intestine
4) Small intestine
Identify this structure.
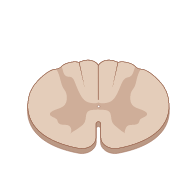
Spinal cord
Where is the coronary sinus? What is its function?
The coronary sinus is found on the posterior aspect of the heart, between the left atrium and left ventricle. It collects the deoxygenated blood from the coronary arteries and returns it to the right atrium.
Are the pelvic and shoulder girdles part of the axial or appendicular skeleton?
Appendicular skeleton
What is the preganglionic neurotransmitter of the PSNS? The SNS?
What is the postganglionic neurotransmitter of the PSNS? The SNS?
Preganglionic: Acetylcholine (both)
Postganglionic: Acetylcholine (PSNS), norepinephrine (SNS)
What is mechanical digestion? What is chemical digestion?
Mechanical digestion - breaking food into small pieces - via chewing, churning of the stomach
Chemical digestion - breakdown of food into molecules and ions via digestive enzymes, acids
What is the term for the smallest projection from this organ wall? What is its function?
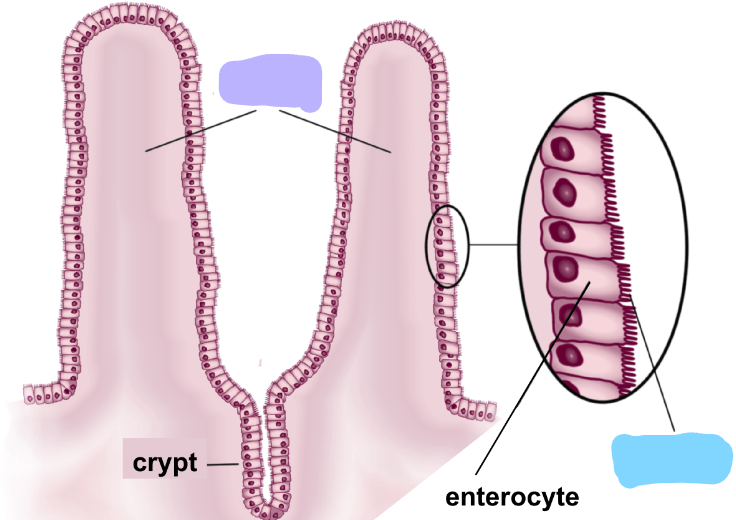
Microvilli - increase surface area to increase absorption
What is mean arterial pressure? How is it calculated?
Mean arterial pressure is the average pressure on the arteries through the course of one full cardiac cycle.
MAP = DP + 1/3(SP – DP), or
MAP = [SBP + (2 × DBP)]/3
How do bones grow?
Osteoblasts lay down new tissue around the exterior of the bone, while osteoclasts expand the marrow cavity on the interior
What is the effect of activation of Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1, and Beta 2 receptors?
Alpha 1 - vasoconstriction
Alpha 2 - inhibition of insulin release
Beta 1 - increase heart rate, force of contractility
Beta 2 - bronchodilation
What are the functions of the digestive system?
Dismantle food
Absorb nutrients
Synthesize vitamins (vitamin K)
Collect and eliminate waste
Produce enzymes
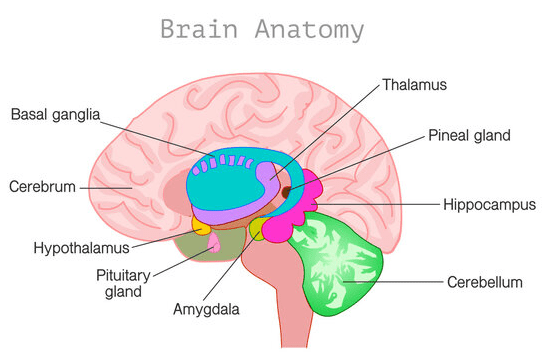
Identify the brain structure in green (6).
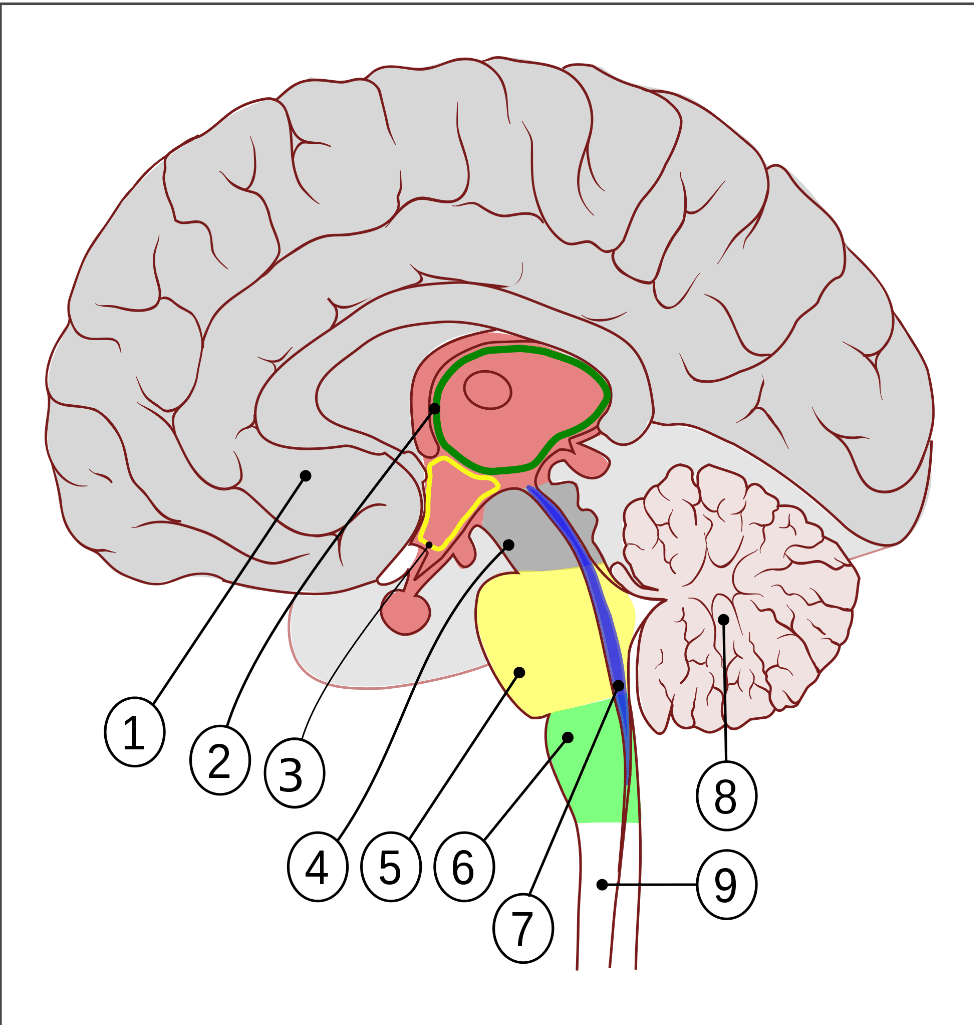
Medulla oblongata
What does a chemoreceptor do? Where are they found?
A chemoreceptor senses the levels of different things in the blood (CO2, O2, pH). They're found in the aortic arch and carotid bodies (peripheral) and near the medulla oblongata (central).
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
1) Support
2) Protection
3) Movement
4) Mineral storage
5) Hematopoeisis
What condition(s) cause demyelination? What is the effect?
Multiple sclerosis, an autoimmune disorder; demyelination is associated with poor conduction, leading to muscle weakness, loss of coordination, and movement problems
What part does the liver play in digestion?
The liver produces digestive enzymes for chemical digestion and produces hormones for glucose regulation
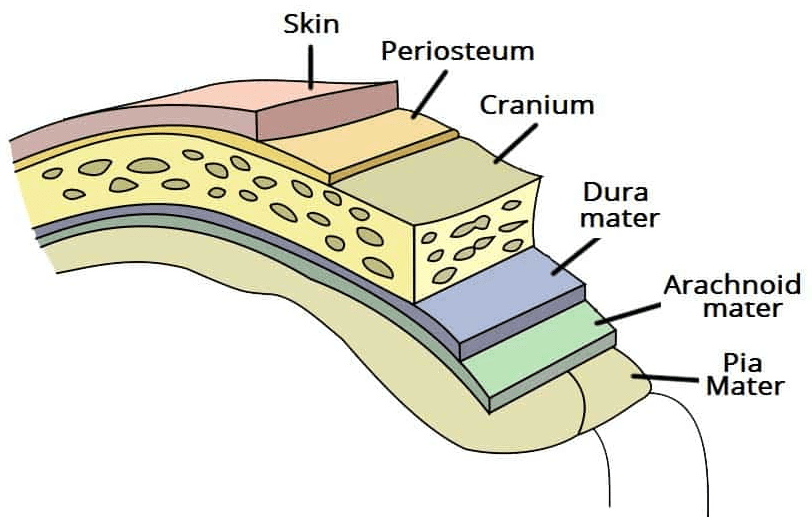
What is this structure? What is its function? Identify the layers.
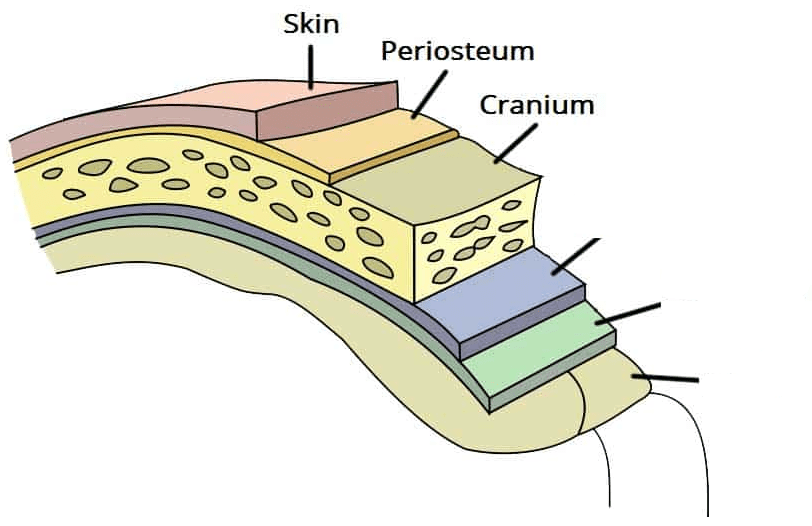
Meninges - cover and protect the brain and spinal cord
What are the steps of wound healing?
1) Hemostatic phase
2) Inflammatory phase
3) Proliferative phase
4) Remodelling phase
What are the five structural categories of bones? What is an example of each?
1) Long bones - e.g., femur, humerus, tibia & fibula, radius & ulna
2) Short bones - e.g., carpals in the hand, tarsals in the foot
3) Irregular bones - e.g., vertebra
4) Flat bones - e.g., ribs, sternum, skull
5) Sesamoid bones - e.g., patella
The sensory neurons pass impulses along the ____ pathway toward the CNS, while the motor neurons pass impulses along the ____ pathway away from the CNS.
Afferent; efferent
What are the functions of the mucosal layer of the intestines?
Production of mucus - provides a barrier for pathogens, acidic substances
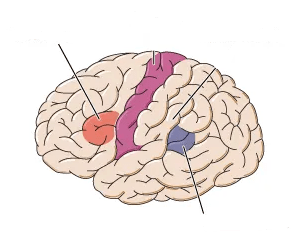
Which colour represents Wernicke's area? What is the function of Wernicke's area?
Wernicke's area is responsible for speech comprehension.
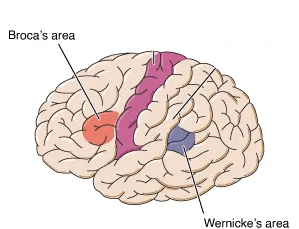
Name 2 factors that will decrease hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen. Does reducing hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen represent a left or a right shift?
Increased temperature; increased [H+] (decreased pH); increased 2,3-DPG; increased CO2
Reduced affinity = right shift (Rs go together!)
How would our bone cells work together to heal a fracture?
Osteoclasts clean up bone chips and fracture edges
Osteoblasts lay down new bone tissue and mature into osteocytes to bridge the fracture
Where is the spinal cord found anatomically? Is the inside of the spinal cord composed of white or grey matter?
The spinal cord is found in the superior two-thirds of the spinal column in the vertebral column of the adult. The interior of the spinal cord is formed by grey matter.
What is the function of bile?
Bile is released into the duodenum as a bolus of food enters the small intestine. Bile is highly alkalotic and will neutralize the acidity of the stomach acid to prevent damage to the subsequent organs.
Identify the structure responsible for thermoregulation.
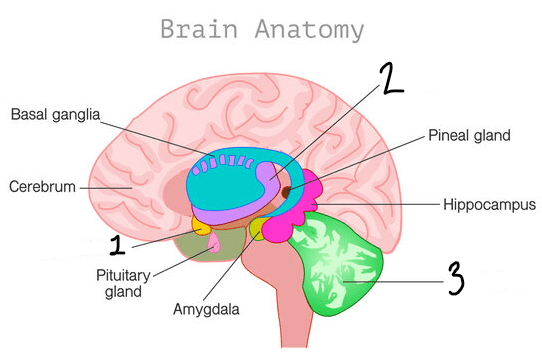
The hypothalamus (1) is responsible for thermoregulation.