This mathematical relationship
What is constant or no relationshiop?
To move at one steady speed
What is constant velocity motion?
To move with a changing speed; speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction
What is accelerated motion?
The force of a surface holding an object up
What is the normal force?
What is conduction?
This mathematical relationship
What is linear?
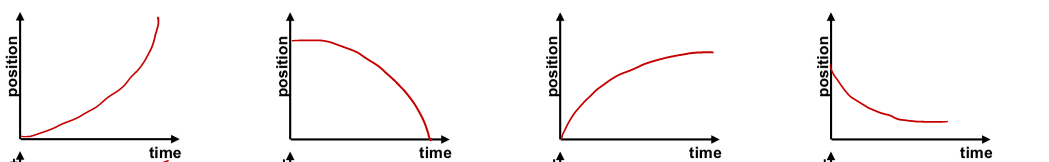
Position versus time graph representing constant velocity motion
What are any of the following

Position versus time graph representing accelerated motion
What are any of the following
A free body diagram of an object at rest on a table
What is

A temporary attraction of a neutral object to a charged object; positive and negative charges temporarily redistribute in neutral object
What is polarization?
This mathematical relationship
What is quadratic?
Velocity vs time graph representing constant velocity motion
What are any of the following
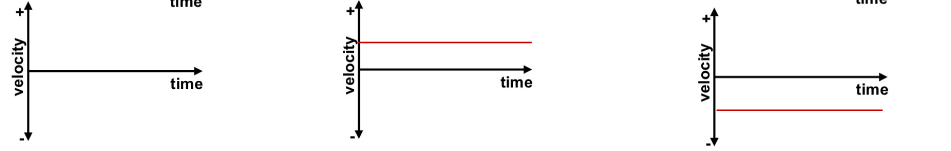
Velocity versus time graphs representing accelerated motion
What are any of the following
Free body diagram for an object moving with a constant velocity to the left
What is

Note: Fpush is the same as Fapply
The difference between the electric field lines between two like charges and two unlike charges
What is

This type of mathematical relationship
What is inverse?
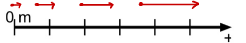
Motion map representing constant velocity motion
What is any motion map with equally sized and equally spaced arrows, like below
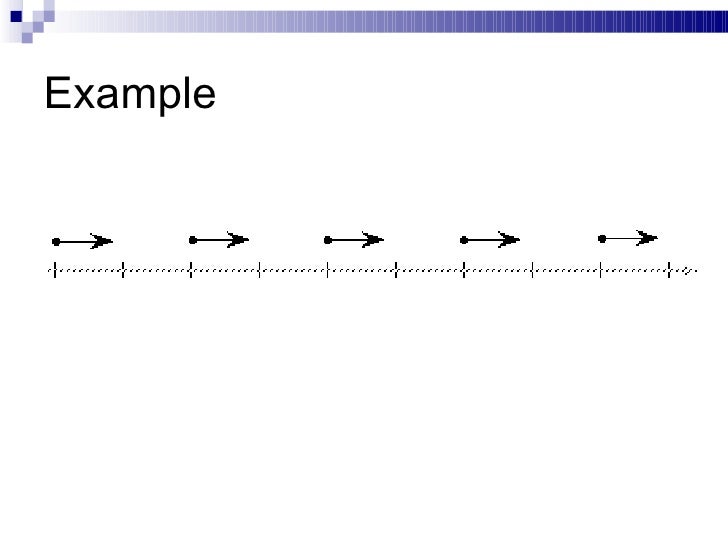
Motion map representing accelerated motion
Any motion map with arrows of increasing or decreasing sizes like
Free body diagram for a falling object
What is
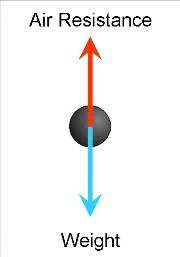
Note: air resistance is friction; weight is Fg
Light bulbs are brighter when wired together in this type of circuit; This type of circuit allows for one single charge to give all its electric potential to one circuit element instead of dividing it up among all circuit elements
What is parallel circuit?
The slope of this line
What is 4 m/s?
The velocity of a car that travels 100 meters in 25 seconds.
What is 4 m/s?
Acceleration of an object beginning at rest that reaches a top speed of 48 m/s in 6 seconds
What is 8 m/s2?
The acceleration of a 10 kilogram object being pushed with a net force of 50 newtons
What is 5 m/s2?
How the energy of a single charge changes as it flows through an electric circuit
What is the charge gains energy in the battery and loses energy in the circuit elements (ex. a light bulb)?
Explanation: In a circuit with a 12 V battery and 2 light bulbs, millions of charges move faster than the eye can see every second. We can understand how this circuit works by thinking of just one of these charges moving through the circuit. As one charge moves through the battery, it gains 12 V of electric potential (energy). As it moves through the first light bulb, it loses 6 V of electric potential to generate light and heat in the bulb. In the second bulb, it loses the other 6 V of its electric potential to generate light and heat. Now it has 0 V of energy. It goes back through the battery and the cycle of gaining and losing energy continues. Please note that charges do NOT get used up. They continue to gain and lose energy and cycle back through the circuit.