A disease caused by antibody stimulation of the thyroid gland causing excessive thyroid hormone secretion.
Grave's disease.
Immune mediated destruction of the endocrine pancreas that results in insulin deficiency.
Type I DM
A disease caused by insulin resistance and insufficient insulin production by the endocrine pancreas.
Diabetes Mellitus II. Amyloidosis of the Islets of Langerhans is seen on imaging.
The dark zone surrounding a germinal center.
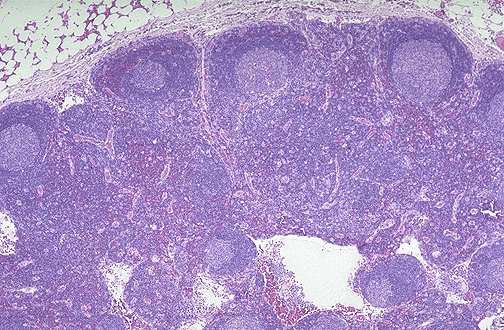
Mantle (or marginal zone)
Researchers attempt to develop a vaccine against viral meningitis. In doing so, they infect pigs with viral meningitis and then extract a single virus-specific plasma cell from a pig. The researchers induce the cell to proliferate and produce large amounts of virus-specific IgG. However, they find that antibodies produced by the plasma cell are less effective in treating viral meningitis compared to IgG containing plasma from people recovering from viral meningitis. What is the most likely reason for the difference in efficacy between single plasma cell derived antibody and IgG containing plasma?
IgG containing plasma is a mix of antibodies that recognize various antigen epitopes from the virus rather than a single epitope recognized by the single IgG molecule produced by a single cell.
A disorder characterized by the destruction of exocrine glands, including salivary and lacrimal glands.
Sjogren's Syndrome. Diagnostic with SSA/Ro and SSB/La antigens in the blood and associated symptoms.
A disease caused by mutation in BTK gene.
Agammaglobulinemia (Burton's Disease)
A disease that commonly presents as shifting abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and bloating.
Appendicitis. Pain is first caused by stimulation of cecal nerve endings and then caused by irritation of the peritoneum which results in shifting abdominal pain.
The circular portion of DNA created as a by-product of VDJ recombination that may also be used as a screening tool for immunodeficiency.
KRECs (BRECs) and TRECs
A disorder caused by mutations in adhesion proteins, such as selectin or integrin, that results in leukocyte recruitment dysfunction.
Leukocyte adhesion deficiencies (LADs).
A disease that results in noncaseating granulomas on histopathology. The disease commonly affects the lungs and skin.
Sarcoidosis. Treatment is corticosteroids or other immune modulators.
A disease that may result in fatigue, weakness, weight loss, bronze skin, and hypotension.
Primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease), most often caused by immune destruction of the adrenal gland.
IgE mediated degranulation of these leukocytes is responsible for allergic reactions (must name both).
mast cells and basophils.
A disease caused by mutation in NADPH oxidase that results in dysfunction of phagocytic activity.
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). Treatment is bone marrow transplant.
A disease characterized by loss of synovial space, osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis, and subchondral cysts.
Osteoarthritis (OA), the treatment for which is physical therapy and anti-inflammatory medication.
MSH2,MLH1,PMS2,MSH6 (all part of the mismatch repair pathway). Mutations also may cause hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer.
Cells that express the receptor for CD80/86.
T cells. The receptor is CD28. CD80/86 is known as B7-1 and B7-2.
A disease caused by mutation in phosphatidylinositol glycan A (PIGA) that results in the destruction of red blood cells by complement activation.
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). The cure for which is eculizumab or marrow transplant. Deficiency in PIGA causes RBC Decay accelerating factor (complement inhibitor) dysfunction.
A disease that may manifest as anemia, bone destruction, renal dysfunction, and hypercalcemia.
Multiple myeloma (CRAB). The treatment for which includes traditional chemotherapies like methotrexate, corticosteroids, CAR-T cell therapy targeting plasma cells, biologic therapy targeting CD138 cells, or bone marrow transplant.
Five congenital heart defects that cause a right to left shunt resulting in cyanosis of the newborn.
Patent truncus arteriosus, transposition of the great arteries, tricuspid atresia, tetralogy of Fallot, total anomalous pulmonary venous return.
The type of T helper cell most likely to activate in response to candida albicans infection.
Th17 cells, via release of IL-17.