to compare the means of more than two groups on a single independent variable (IV).
What is the purpose of doing a one-way ANOVA?
The number of independent variables in a study that has a design statement:
2 x 2 x 4
What is 3?
The number of variables needed to run a correlation?
What is two (X, Y)?
To attempt to predict one person's score on one variable from their score on a closely related variable.
What is the purpose of doing a regression.
We have finished running an ANOVA and it indicates that there is a significant main effect of Factor A, which has 3 groups. It is the correct time to do this:
What is, the correct time to do a post hoc test?
K
What is the number of levels/groups in the independent variable?
The number of cells (i.e., groups, or k) you would have if you did a factorial design that had the following design statement
5 x 5
What is 25?
A correlation coefficient of +1.82
What is a correlation coefficient that theoretically couldn't exist (someone made a mistake)?
X
What is the predictor variable?
A Pairwise comparison
What are comparisons made between two groups (or two means)?
Between-groups variation.
What is variation that we can attribute to the independent variable/treatment/manipulation?
The effects we examine in a Factorial ANOVA that use the marginal means.
What are the main effects?
Looking at GPA and video games you find the following relationship.
What is a negative correlation?
Y
What is the criterion (outcome) variable?
We use this statistic to determine the critical values for comparing the means of two groups when doing Tukey's post-hoc test.
What is the studentized range statistic (q)?
We assume that the variance in each population being tested or represented within our sample(s) has approximately the same level of variation in their scores.
What is the assumption of homogeneity of variance?
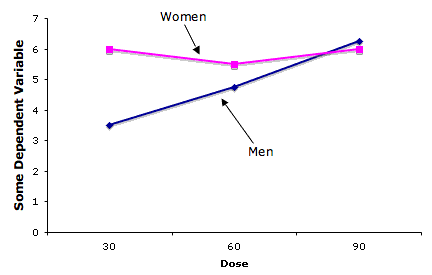 For the AXB term in the ANOVA, with the above table you would expect to see this.
For the AXB term in the ANOVA, with the above table you would expect to see this.
What is a significant interaction?
H0: ρ = 0
What is the null hypothesis for a correlation?
The sum of squares of the cross-products divided by the sum of squares of the predictor variable (X).
What is the formula for calculating the slope (b).
We need this MS (mean square) term from our ANOVA to calculate Tukey's test.
What is the MSerror?
This term represents the overall variation in our scores that cannot be attributed to any of our manipulations (i.e., treatment).
What is the mean square error?
MSa / MSerror
An assumption that must be met to run a correlation. Assumes that the datapoints are best "described" by a straight line and not a curved one.
What is the assumption of linearity?
The number of intercepts and slopes we would have if doing a multiple regression that had 3 predictor variables (X's) predicting 1 criterion variable (Y).
What is 1 intercept and 3 slopes?
After doing a correlation between two variables, if you had an r = .56. This score would be the amount of variability accounted for by the relationship between the two variables (hint: you have to provide the numerical answer)
What is 31.36%