Which of the following evolutionary mechanisms increases the amount of genetic variation in a population?
a. Founder's Effect
b. Bottleneck Effect
c. Sexual Selection
d. Mutations
d. Mutations
Mutations are the original source of genetic variation
Which of the following best describes evolution on the smallest scale?
a. Descent with modification
b. Survival of the fittest
c. broad patterns of evolutionary change above species level
d. changes in allele frequencies over time
d. changes in allele frequencies over time

The biological species concept emphasizes
a. location of species
b. different structures
c. absence of gene flow
d. smallest group on phylogenetic tree
c. absence of gene flow
Biological species concept: States that a species is a group of populations whose members have the potential to interbreed in nature and produce viable, fertile offspring.
Morphological Species concept defines by structure
Ecological Species concept is based on location
Phylogenetic Species concept is based on smallest group on phylogenetic tree.
Which of the following characteristics were most likely present in the first animals that colonized land?
a. Presence of toxic producing glands.
b. Tetrapods (4 limbs)
c. Ability to resist dehydration
d. Digestive system to consume other organisms
c. Ability to resist dehydration

The relatively brief time in geologic history when many present-day phyla of animals first appeared in the fossil record. This burst of evolutionary change is known as the
a. Proterozoic explosion
b. Paleozoic explosion
c. Mesozoic explosion
d. Cambrian explosion
d. Cambrian explosion
Natural selection effects a population by
a. Increasing genetic variation
b. Increasing the frequency of the most common trait
c. Increasing the match between a population and their environment
d. Decreasing genetic variation
c. Increasing the match between a population and their environment
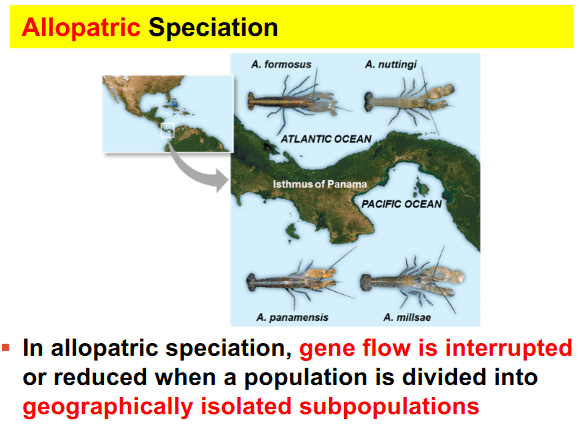
When Arizona's Grand Canyon formed, a population of squirrels were separated and no longer able to make contact. Over time, the two new populations diverged giving rise to two new species of squirrels. This is an example of
a. Sympatric Speciation
b. Allopatric Speciation
c. Post-zygotic barrier
d. Mechanical Isolation
b. Allopatric Speciation
Mechanical Isolation: Morphological differences
can prevent successful completion of mating (Pre-zygotic barrier)
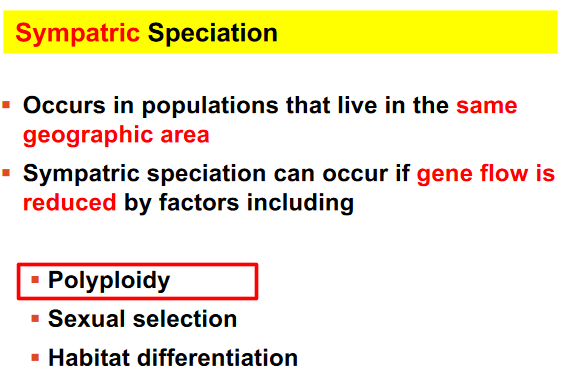
In a single generation, which can produce a reproductive barrier?
a. Decreased sexual selection
b. Habitat sharing
c. Increased gene flow
d. Polyploidy
d. Polyploidy

The first living organisms were
a. Multicellular eukaryotes
b. Single-celled eukaryotes
c. Multicellular prokaryotes
d. Single-celled prokaryotes
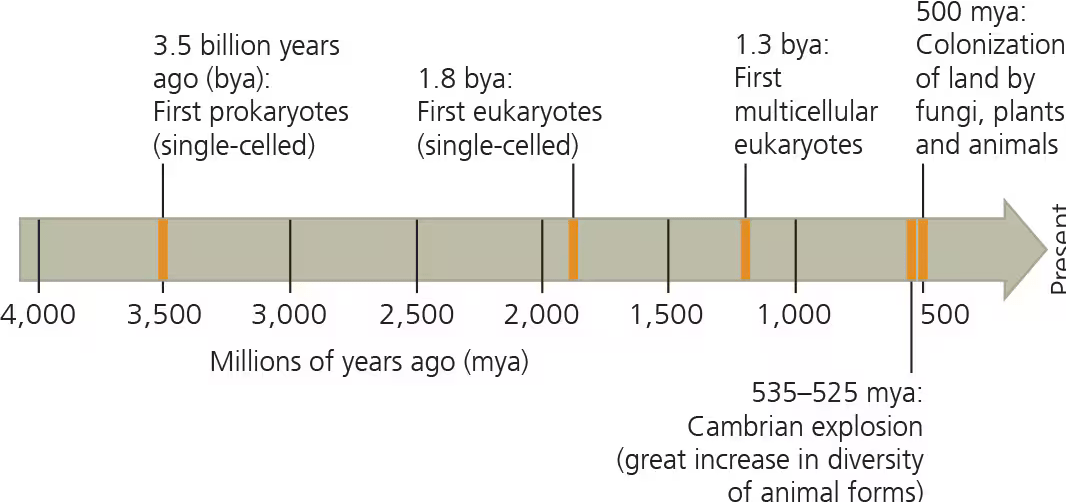
Which of the following best characterizes the atmosphere of early Earth compared to the current atmosphere?
a. Atmosphere was less oxidizing
b. Experienced less radiation from the sun
c. Richer in gases released from volcanoes
d. Greater quantities of ozone
c. Richer in gases released from volcanoes
Comparisons of Galapagos Finch DNA and South American bird DNA shows high base similarity. Which process of population genetic could generate these results?
a. Adaptive Radiation
b. Genetic Drift
c. Gene Flow
d. Natural Selection
C. Gene Flow
Gene flow is the movement of alleles among populations.
Alleles can be transferred through the movement of fertile individuals or gametes (for example pollen).
Two different species of lemurs mate and successfully produce a zygote. However, the embryo dies shortly after fertilization occurs. Which reproductive barrier keeps the species separated?
a. Reduced hybrid viability
b. Reduced hybrid fertility
c. Hybrid breakdown
d. Gametic Isolation
a. Reduced hybrid viability
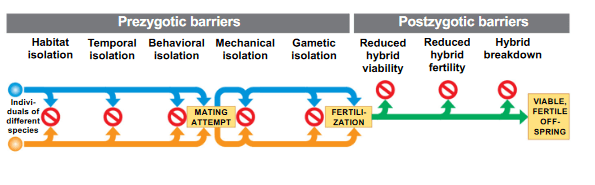
Reduced hybrid viability: (Post-zygotic)
Genes of the different parent species may interact and impair the hybrid’s development or survival in its environment
Reduced hybrid fertility: (Post-zygotic)
Even if hybrids are vigorous, they may be sterile.
Hybrid breakdown: (Post-zygotic)
Some first-generation hybrids are fertile, but when they mate with each other or with either parent species, offspring of the next generation are sterile.
Gametic Isolation (Pre-zygotic)
Sperm of one species may not be able to fertilize eggs of another species
Four populations of birds look very similar, but the males from each population sing different songs to attract females. The different songs are an example of
a. Postzygotic barrier
b. Temporal isolating barrier
c. Behavioral isolating barrier
d. Habitat isolating barrier
c. Behavioral isolating barrier
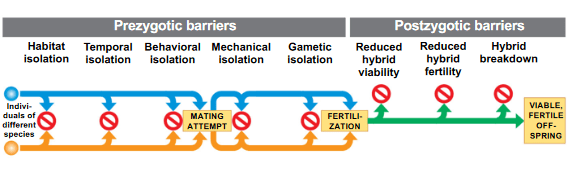
Habitat Isolation: Two species encounter each other rarely, or not at all, because they occupy different habitats, even though not isolated by physical barriers.
Temporal Isolation: Species that breed at different times of the day, or different seasons.
Behavioral isolation: Courtship rituals and other behaviors unique to a species are effective barriers to mating
Which of the following statements provides the best evidence that the fossil record is an incomplete record of evolution?
a. The fossil record shows changes in kinds of organisms that lived on earth.
b. The fossil record shows that many animals are extinct.
c. The fossil record is biased for organisms that had hard shells and skeletons.
d. Fossils document how new organisms come from preexisting organisms.
c. The fossil record is biased for organisms that had hard shells and skeletons.
Which of the following lists most likely represents the correct sequence, from earliest to most recent, in the origin of cell organelles and cellular organization?
a. photosynthetic prokaryotes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, multicellular eukaryotes
b. photosynthetic prokaryotes, chloroplasts, multicellular eukaryotes, mitochondria
c. mitochondria, multicellular eukaryotes, chloroplasts, photosynthetic prokaryotes
d. chloroplasts, mitochondria, photosynthetic prokaryotes, multicellular eukaryotes
a. photosynthetic prokaryotes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, multicellular eukaryotes
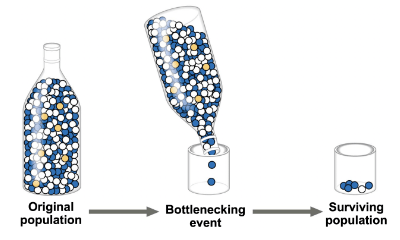
A volcano erupts on island killing 95% of the snail population. The surviving snails, by chance, have a higher frequency of bright colored shells than the original population. The volcano erupting is an example of
a. Natural Selection
b. Gene Flow
c. Founder's Effect
d. Bottleneck effect
d. Bottleneck effect
Genetic drift
- Describes how allele frequencies fluctuate unpredictably from one generation to the next.
- Includes Founder’s effect and Bottleneck effect.
Founder’s Effect
- Occurs when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population.
- Allele frequencies in the small founder population can be different from those in the larger parent population.
Bottleneck Effect
- Drastic reduction in population size due to a sudden change in the environment
- The resulting gene pool may no longer be reflective of the original population’s gene pool
The offspring of a male donkey and a female horse is a mule, which is robust but sterile. The reproductive isolating barrier present is
Reduced hybrid fertility
Hybrids may be able to live, but are sterile (unable to reproduce).
Strains of cultivated rice have accumulated different mutant recessive alleles at two loci in the course of their divergence from a common ancestor. Hybrids between them are vigorous and fertile, but plants in the next generation that carry too many of these recessive alleles are small and sterile. This is an example of
Hybrid breakdown
Some first-generation hybrids are viable and fertile, but when they mate with one another or with either parent species, offspring of the next generation are feeble or sterile.
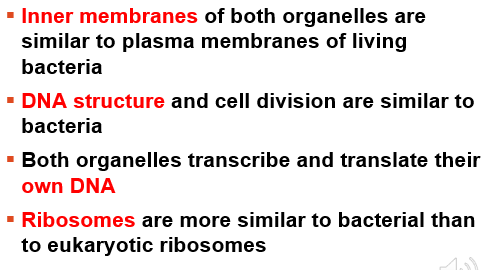
All of the following support the endosymbiotic origin of mitochondria and plastids EXCEPT:
a. Inner membranes of both organelles are similar to plasma membranes of bacteria
b. Both organelles transcribe and translate their own DNA
c. Both of their genetic material consists of multiple linear chromosomes
d. Ribosomes are more similar to bacteria than eukaryotes
c. Both of their genetic material consists of multiple linear chromosomes
a. Occurred during extreme episode of volcanism
b. CO2 drastically increased in the atmosphere
c. The global temperature cooled significantly
d. Ocean acidifcation
a. Occurred during extreme episode of volcanism
b. CO2 drastically increased in the atmosphere
d. Ocean acidifcation


In a population of lemurs, 12% have a rare autosomal recessive disease. What percentage of the population is heterozygous at this locus?
q2= .12
q= .35
p+q=1
p= .65
2pq= .46
Sea urchins release their sperm and eggs into the surrounding water, where they fuse and form zygotes. It is difficult for gametes of different species to fuse because of proteins on the surfaces of the eggs and sperm bind poorly to each other. This is an example of which reproductive barrier?
Gametic Isolation: Sperm of one species may not be able to fertilize the eggs of another species.
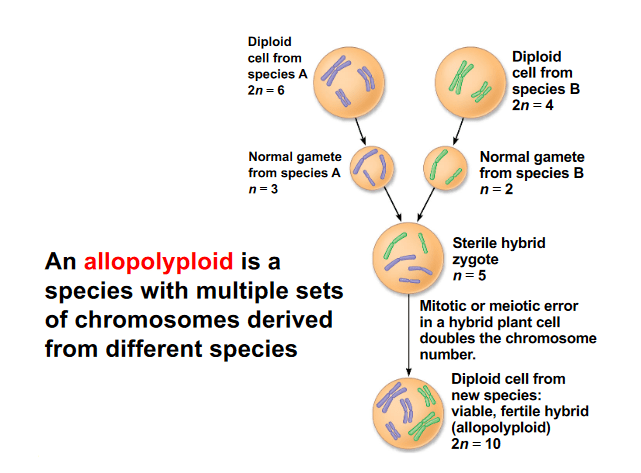
Plant species A has a diploid count of 6. Plant species B has a 2n=4. A and B plant to give rise to a new species, C, via an allopolyploid event. The diploid number for species C would be?
10
Prior to the extinction of dinosaurs, what most likely prevented adaptive radiation by mammals?
Competition for food with the dinosaurs

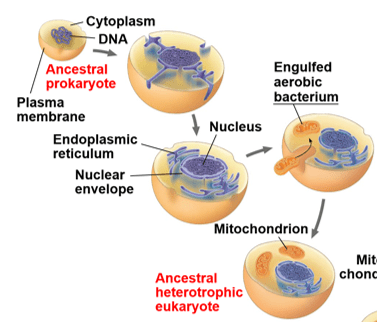
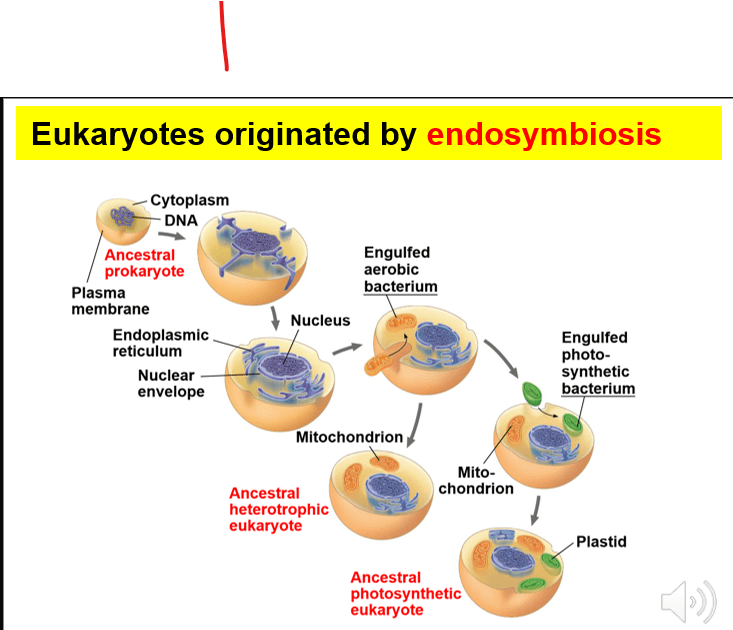
Explain the origin of the mitochondria
1. Ancestral prokaryote's plasma membrane began to fold inwards producing a nucleus and ER region.
2. This prokaryote then engulfed an aerobic bacteria (able to use O2 for metabolism)
3. Over time, a mutually beneficial relationship developed between the two cells (endosymbiosis)
4. The endosymbiote bacteria has evolved to become the mitochondria.