100 Points
What type of motor neuron damage is associated with Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
Damage to the peripheral nervous system caused by demyelination.
What is the main difference between MS and GBS in terms of the nervous system affected?
MS affects the central nervous system, while GBS affects the peripheral nervous system.
What is the primary neurotransmitter deficit in Parkinson’s Disease?
Dopamine.
Which motor neurons are affected in ALS?
Both upper and lower motor neurons.
Which condition is primarily associated with motor symptoms and does not typically involve sensory impairments: PD or ALS?
ALS
What is the typical progression pattern of weakness in GBS?
Ascending weakness, starting in the lower extremities and moving upward.
Which condition is more likely to present with sensory changes like paresthesia: MS or GBS?
Both conditions can present with paresthesia, but it is more common and persistent in MS.
What is the hallmark motor symptom often described as a "shuffling gait"?
Bradykinesia, leading to short, shuffling steps.
What is a common early symptom of ALS?
Progressive weakness, often starting in the hands or feet.
What is the primary difference in the progression of ALS compared to PD?
ALS progresses rapidly and is ultimately fatal, while PD progresses more slowly and is primarily degenerative.
During the acute phase of GBS, what should occupational therapy interventions focus on?
Positioning, pain management, and preventing secondary complications.
Why is aerobic exercise recommended for clients with MS but cautiously introduced for clients recovering from GBS?
Aerobic exercise can improve overall function in MS, but in GBS, overexertion can worsen symptoms.
What intervention can help reduce freezing of gait in Parkinson’s Disease?
Visual or auditory cues, such as stepping over lines or listening to rhythmic beats.
What is the focus of occupational therapy during the mid-to-late stages of ALS?
Maximizing function, preserving independence with adaptive equipment, and ensuring caregiver support.
How do speech impairments differ between PD and ALS?
In PD, speech is often soft and monotone due to bradykinesia, while in ALS, speech becomes slurred and weak due to muscle weakness.
What is a primary goal of occupational therapy during the recovery phase of GBS?
Gradually increasing activity tolerance and restoring functional independence.
In MS, which cognitive function is most often affected, and how might an OT address it?
Executive function; OTs can implement memory aids, task sequencing, and environmental modifications.
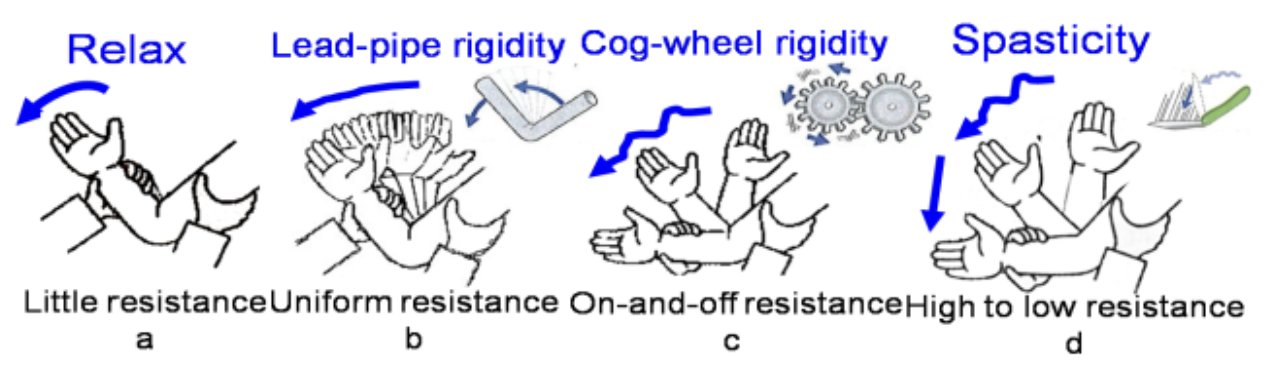
How does rigidity in Parkinson’s Disease present, and what are two types?
Rigidity presents as resistance to passive movement and includes "lead-pipe" and "cogwheel" rigidity.
What is the primary cause of death in most individuals with ALS?
Respiratory failure.
Why is early intervention critical in both PD and ALS?
Early intervention maximizes independence, addresses emerging symptoms, and supports long-term planning for progressive impairments.
Why is overexertion during therapy contraindicated in clients recovering from GBS?
Overexertion can delay nerve recovery and exacerbate muscle weakness.
hat is a common long-term adaptation strategy for both MS and GBS to address fatigue?
Teaching energy conservation techniques, such as prioritizing tasks, delegating, and scheduling rest periods.
hat type of exercise has been shown to improve motor and non-motor symptoms in early-stage Parkinson’s Disease?
Intense aerobic exercise.
What is the difference between spasticity and flaccidity in ALS, and how does it reflect the progression of the disease?
Spasticity is caused by upper motor neuron damage, while flaccidity results from lower motor neuron damage; both can coexist as the disease progresses.
What adaptive equipment might be used for a client with advanced PD versus advanced ALS?
In advanced PD: Weighted utensils to reduce tremors. In advanced ALS: Power wheelchairs for mobility and communication devices for speech loss.