(300 pts for best answer)
(300 pts each; include units)
(100 pts each)
Voltage is measured in ________ and is the force that pushes current through a circuit.
volts
Define electricity.
Electricity is the flow of electric charge, typically carried by electrons, through a conductor like a wire. It is a form of energy resulting from the presence and motion of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, and can be used to power devices, transmit information, and generate heat or light. Electricity is a fundamental force of nature and is essential for many modern technologies and systems.
What is the voltage if a resistance of 25 Ω produces a current of 250 amperes?
V = I x R
V = (250) (25)
V=6250 Volts
Which American company consumes the highest percentage of the world’s energy?
- General Motors
- ExxonMobil
- Dow
3. Google
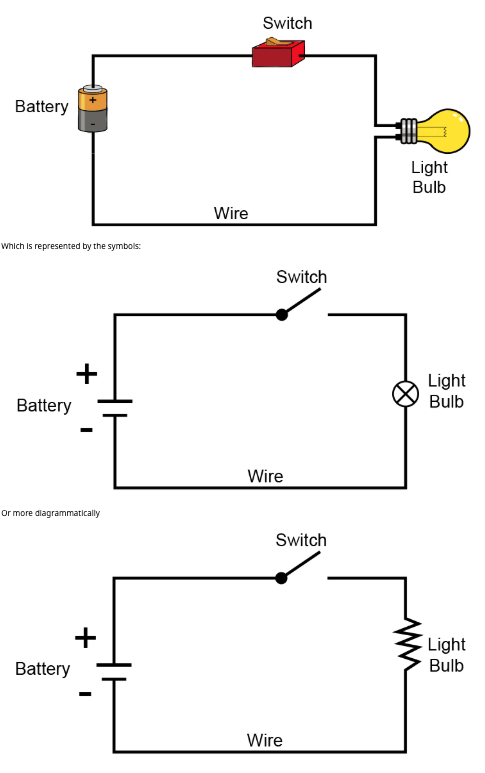
Draw a diagram of a series circuit.
A ________ allows electrical current to flow freely, while an ________ prevents the flow of current.
conductor, insulator
Define voltage.
Voltage (measured in volts, VVV) is the difference in electric potential energy between two points in a circuit. It tells us how much energy is available to move charges (like electrons) between those points.
What is the current produced by a voltage of 240 V through a resistance of 0.2 Ω?
I=V÷ R
I = (240) ÷ (0.2)
I = 1200 Amps
Which home appliance consumes the most electricity?
- Water heater
- Refrigerator
- Television
- Personal Computers
2. Refrigerator
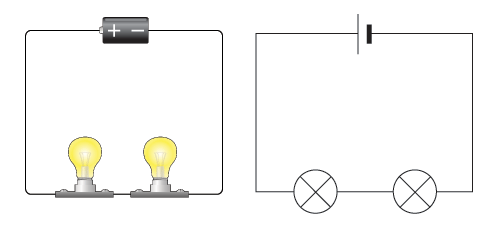
Draw a diagram of a parallel circuit.


Direct current (DC) flows in ________ direction(s), whereas alternating current (AC) flows in ________ direction(s).
one, two
Define current.
Current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor over time, measured in amperes (A). It represents how many charges pass a specific point in a circuit each second. Current is analogous to the flow rate of water in a pipe.
What resistance would produce a current of 120 amps from a 6-V battery?
R=V÷ I
R = (6) ÷ (120)
R = 0.05 Ohms (Ω)
A lead acid battery stores what kind of electricity?
1. direct current
2. alternating current
3. virtual
4. static
1. direct current
What is this a diagram of?

Traffic light
Quantum physics studies the behavior of matter and energy on a ________ scale.
microscopic
Define resistance.
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current in a material, measured in ohms (Ω). It determines how much the material reduces the current, with higher resistance leading to lower current for the same voltage. Resistance can be thought of as the "friction" that slows the flow of electricity.
A lamp needs 250 W of power from a generator. How much energy does the lamp convert in 5 seconds?
E=250W×5s=1250J
Who invented the battery?
1. Alessandro Volta
2. Thomas Edison
3. Albert Einstein
4. Pierre Curie
1. Alessandro Volta
What does this circuit control and power?

Electromagnet
Voltage is like the ________ pushing water through a pipe, current is the ________ of water, and resistance is like the ________ of the pipe.
pressure, flow, width
Define quantum physics.
Quantum physics, also known as quantum mechanics, is the branch of physics that studies the behavior of matter and energy on the smallest scales, such as atoms and subatomic particles. It reveals that particles can exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties, exist in multiple states simultaneously (superposition), and interact in ways that defy classical physics, such as through quantum entanglement. Quantum physics provides the foundation for modern technologies like semiconductors, lasers, and quantum computers, and it challenges our understanding of reality at its most fundamental level.
A motor converts 100 W of power into 500 J of electrical energy. How long does it take the motor?
t = 500J / 100W = 5 seconds
Which of the following is not an electrical conductor?
1. copper
2. glass
3. aluminum
4. steel
2. glass