Sign of dehydration:
THIRST
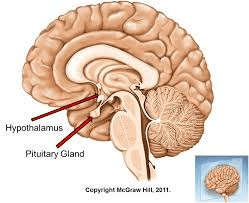
The osmoreceptors within and around the hypothalamus.
Blood volume rises - osmoreceptors swell up - signifies fluid volume excess
Blood volume falls - osmoreceptors signal fluid volume deficit
I range from 275-295 mOsm/kg
What am I ?
Serum osmolality
Serum osmolality is a measure of the concentration of dissolved particles (solutes) in the blood. It reflects the body's fluid balance and electrolyte composition.
I am a must know
I am a hormone released from the atrium when there is fluid excess
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
ANP promotes the excretion of sodium (natriuresis) and water (diuresis), which helps lower fluid volume and blood pressure, ultimately reducing edema.

I am the most common clinical problems associated with fluid imbalances
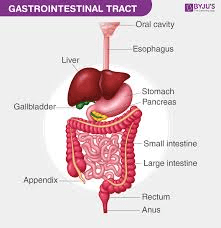
GI
Vomiting and diarrhea
GI Suctioning
Increased salt intake
Intestinal obstruction
Perforated Ulcer
Excessive hypotonic fluids: oral and intravenous
Major cation in the bloodstream (extracellular)
NA+
Regulated by kidneys and adrenal glands
135-145
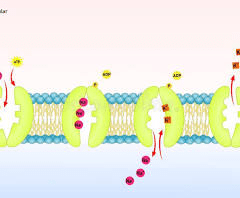
Sodium-Potassium pump
Initiates action potential from neurons to neuromuscular excitability
Hormone produced in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland
ADH - Antidiuretic hormone
Causes water reabsorption in the kidney
Then:
the osmoreceptors stop signaling thirst and stop the release of ADH
If I am above 295mOsm/kg what am I?
High serum osmolality
Dehydration
Your blood osmolality increases when the amount of water in your blood decreases or the number of substances such as sodium, chloride, and glucose increases. When your blood osmolality goes up it causes your kidney to hold onto water. This makes your urine more concentrated.
I am a hormone released from the ventricle when there is fluid excess
b-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
BNP is a hormone released by the heart in response to stress or strain, such as when the heart is not pumping efficiently. Heart stretching increase levels.
Indicates severity and stage for Heart Failure (HF)
Normal - Less than 100
BNP levels are a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring HF. Elevated BNP levels can indicate the presence of HF, and higher levels may suggest more severe disease.
Renal common clinical problems
Renal failure
Renal disease
Major cation inside the cell (intracellular fluid)
K+
3.5-5.3
Neuromuscular excitability
Acid-base balance
Huge for cardiac function - look at this one first
Regulated by the kidneys
Na + ion retained - K+ ion is excreted
*Think Na+ K+ pump
PNS - Parasympathetic nervous system secretes what neurotransmitter with volume changes:
Acetylcholine
Baroreceptors- located in the carotid arteries, large lung vessels, and aortic arch. Blood volume increases - Blood pressure increases
Acetylcholine causes the "rest and digest"- vasodilation, decrease in BP, and decrease in heart rate.
If I am below 275 mOsm/kg what am I?
Over hydrated
Low serum osmolality indicates a low concentration of dissolved substances (solutes) in the blood.
Ex: Heart failure - we see edema
Excessive water intake
Kidney disease
I am present or absent with fluid deficit or fluid excess.
What am I?
Edema
Affects fluid equilibrium between the blood vessels(capillaries) and the tissues (interstitium)
Increased arterial pressure causes increased hydrostatic pressure causes fluid being pushed out into the tissue
Cardiac
Heart Failure
Responsible ion (mineral) for bone formation
Ca+
8.5-10.5
Clotting
Strengthens cardiac contractions
Stabilizing neuromuscular cell resting potentials
Ca+ and PO4 - are inversely related
Phosphorus - 2.5-4.5 mg/dl
SNS - sympathetic nervous system "fight or flight"
Adrenal Medulla
SNS activated with drop in BP - baroreceptors activate the Adrenal medulla
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Increase vasoconstriction, Heart rate, and force of contraction, raising BP
Increases the amount of urine produced and ADH to secrete so fluid is retained
I am a peptide hormone secreted by the kidneys:
Juxtaglomerular cells (JG)
Renin
Kidneys want to block the SNS (vasoconstriction)
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6EUSEa6Lw8g
I am a large amount of generalized body edema
What am I?
Anasarca
Miscellaneous

Fever
Profuse diaphoresis
SAIDH
Burns
Ascites
Massive trauma
Drugs
Cortisone group
The second most abundant intracellular cation
"Great Stabilizer"
Mg++
1.8-2.6mg/dl
Stabilize both cardiac and neuromuscular cell membranes
Hypothalamus - Where am I located?
Measure the concentration of blood and activates with decreased fluid changes:
Loss of blood volume
Third spacing : ascites
Hemorrhaging
Dehydration

Key take away
What is secreted by adrenal cortex during RAAS?
Aldosterone is a steroid hormone released by the adrenal cortex when the RAAS system is activated
Where sodium goes, water follows
When sodium is retained, water is retained
Both: angiotension2 and aldosterone cause sodium and water retention
Critical Thinking Like A Nurse
How can you assess or cues you will look at that will prevent, identify, decrease or increase in fluid?
Knowing the high risk diagnosis
Trend BP, pulse, and O2 sats.
Monitor intake of fluids: PO, IV, IVP, IVPB, free water
Monitor output: Urine, Stools, Vomit, NG, Drains
Sweat, breathing
Daily Wts:
Assessments: Lung sounds, heart sounds, Abd., peripheral, CNS
Know Medications!
JASON
Brain tumors
Brain injury
Older adults
Children

Essential electrolyte - combines with NA+
CL-
96-106
Works with Na+, K+, & Bicarb
Assists with Acid-base balance
Crucial maintain proper Ph balances
When Na+ retained so is CL- (causes water retention)
Combines with H+ to form HCL acid