Patients with ESRD and uncontrolled diabetes are at risk for this acid-base imbalance.
ST segment depression on an EKG could be a sign of this electrolyte imbalance.
What is hypokalemia?
Furosemide can be used to treat elevations in this electrolyte?
What is potassium?
This measurement is the most reliable indicator of fluid loss of fluid loss for infants and small children.
What is body weight?
A clean-catch urine specimen should be collected at this time.
What is midstream?
Pickled beets are rich in this electrolyte

What is sodium?
You notice your patient eating these like candy, and they state "I could eat the whole bottle! They taste so good!" You explain to them they better not do that, because they will be at risk for ____________ .
What is metabolic alkalosis?
A patient with severe hypernatremia should be placed on __________ precautions.
Hypokalemia places patients at high risk for toxicity of this antiarrhythmic drug.
What is digitalis (Digoxin)?
This fluid shares the same osmolality or concentration as the body's plasma, therefore result in no shift in fluid compartments.
What are isotonic fluids?
This waste product results from protein breakdown, changes in amount in blood are highly dependent on renal function.
What is creatinine?
These are full of this electrolyte.

What is potassium?

What is metabolic acidosis?
IV Insulin helps to correct this electrolyte imbalance forcing the cation back into the intracellular space.
What is hyperkalemia?
Metabolic acidosis usually leads to this potassium imbalance.
What is hyperkalemia?
The osmolality of these fluids are lower than that of the body's plasma, resulting in a fluid shift from the extracellular space to the intracellular space.
What are hypotonic fluids?
This is a medical term for bedwetting.
What is enuresis?
If Jason has the munchies and hits up all the local restaurants in his neighborhood, consuming these foods, he is likely to end up with this electrolyte imbalance.

What is hypernatremia?

What is respiratory acidosis?
A positive Chvostek's sign is indicative of ___________.
What is hypocalcemia?
_____magnesemia results in increased nerve excitation resulting in paresthesia and hyperreflexia.
What is hypo
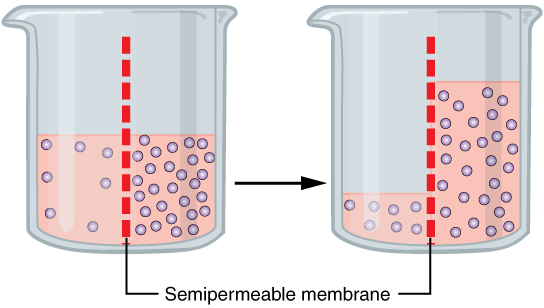
This is a shift in fluids from an area of low concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
What is osmosis?
All of these patients/conditions will place the patient at risk for this kidney infection.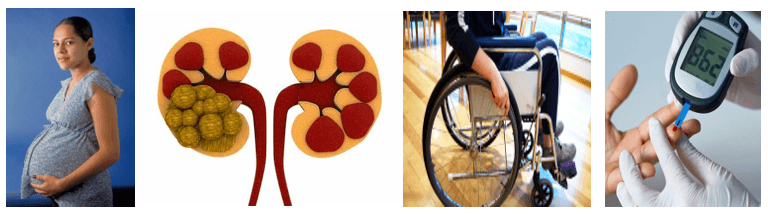
What is pyelonephritis?
This melon is rich in this electrolyte.

What is potassium?

What is respiratory alkalosis?

Alcoholism places patients at risk for this magnesium imbalance.
What is hypomagnesemia?
Spironolactone use places patients at risk for this electrolyte imbalance.
What is hyperkalemia.
Aside from body weight and vital signs, monitoring/measurement of this can give a good indication of fluid balance.
Hint: It does not require nursing skills.
What is intake and output?
BPH can lead to what type of acute renal failure?
What is postrenal?
Persons with this electrolyte imbalance should avoid these.
What is hypernatremia?

What is metabolic alkalosis?
Tapping the cheek lightly to assess for muscle twitching in the mouth is known as ___________ sign.
What is Chvostek's sign?
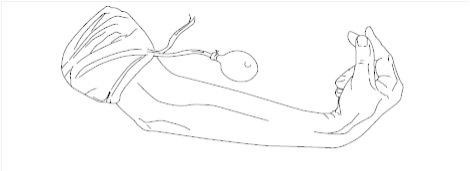
What is Trousseau's sign?
D5W is ordered for your patient with 3 days history of vomiting and diarrhea. This is considered (a)n_________ solution.
What is isotonic?
This simple lab test should be performed on an infant with decreased PO intake and irritability or an elderly patient with new onset confusion.
What is a urinalysis?
Your patient's most recent labs indicate a serum potassium level of 5.5mEq/L. She wants to know if she can eat this for lunch. Your answer is this.
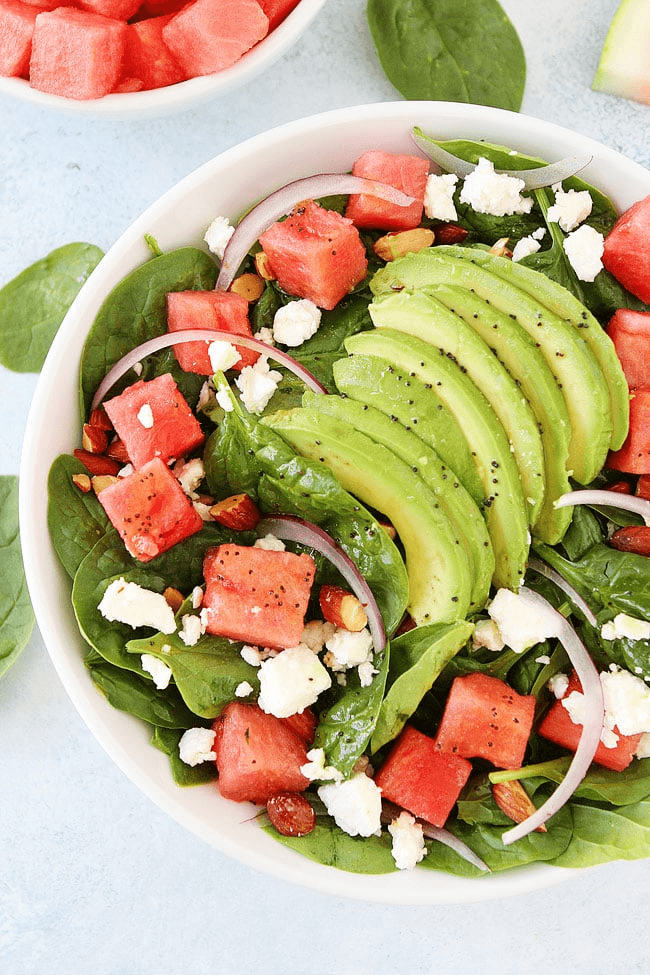
Your patient's most recent labs indicate a serum potassium level of 5.5mEq/L. She wants to know if she can eat this for lunch. Your answer is this.

What is respiratory acidosis?
Deep tendon reflexes will be _________ with patients with hypomagnesemia.
What is increased (hyperreflexia)?
Calcium has an ________ relationship with phosphorus, meaning with calcium goes ____ , phosphorus goes _____ .
What are inverse, up and down (or down and up)?
An infant with a prolonged fever is going to be at risk for fluid volume excess due to this type of fluid loss.
What is insensible?
SLE, pyelonephritis, and poisoning all can lead to this type of kidney failure.
What is intrinsic or intrarenal?
If my feet look like this, I probably need to maintain this type of diet.
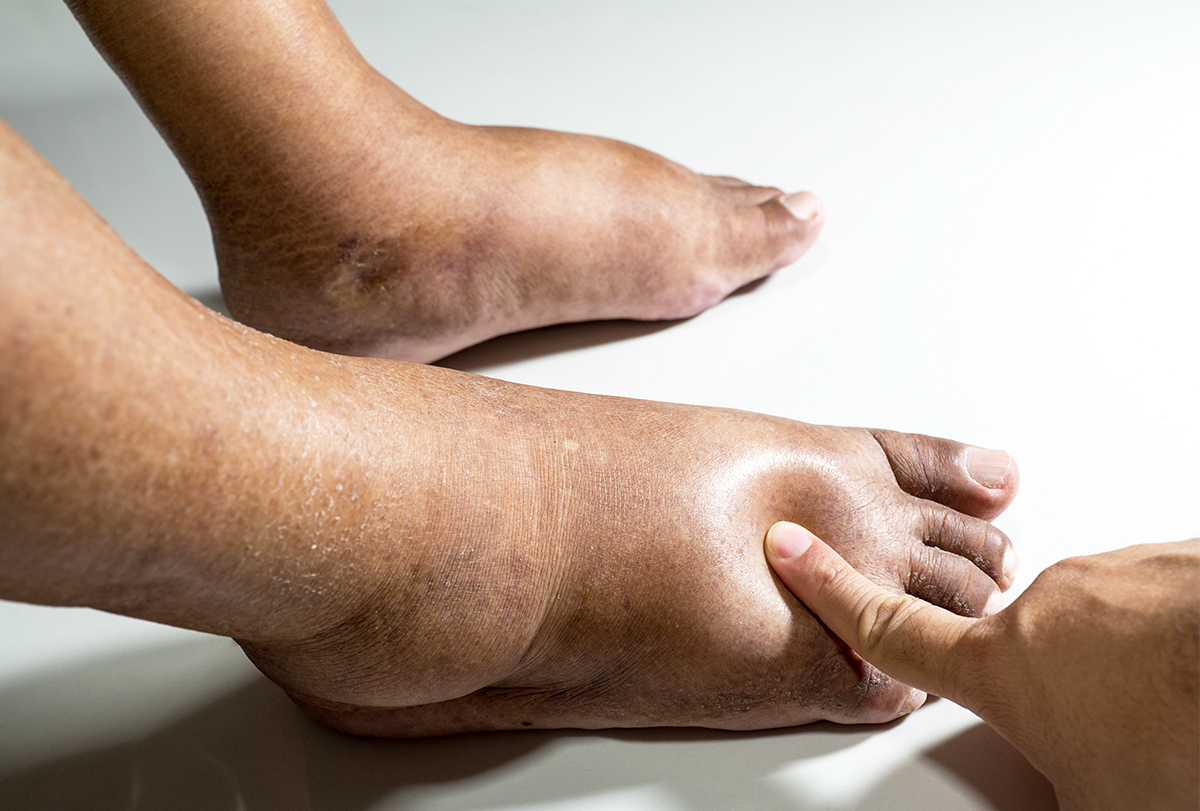
What is a low sodium diet?

What is respiratory acidosis?
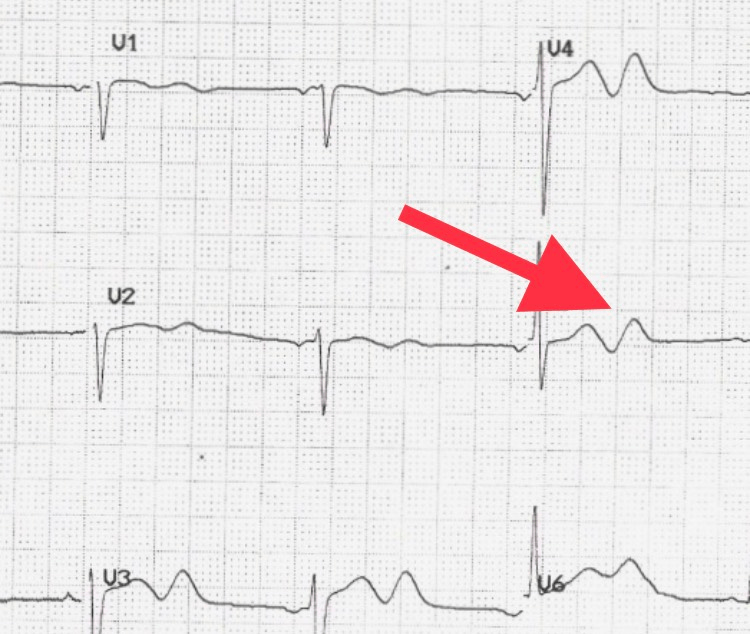 Your patient is admitted due to intractable vomiting, this EKG finding is found in patients with low potassium or hypokalemia.
Your patient is admitted due to intractable vomiting, this EKG finding is found in patients with low potassium or hypokalemia.
What is a u-wave?
Corticosteroid use can lead to this imbalance in potassium.
What is hypokalemia?
This solution would likely be used to treat a patient with a sodium of 158 mEq/L.
What is hypotonic?
A child presents with facial edema, decreased urine output, and hematuria following a recent strep throat infection. These 2 things are being restricted in the patient's diet to reduce edema and prevent further complications.
What is sodium and fluids?
My patient is on a renal diet and is trying to select the best side choice for his next meal. This selection is the only appropriate choice. ( Dried apricots, rice, mashed potatoes, or sweet potatoes with raisins)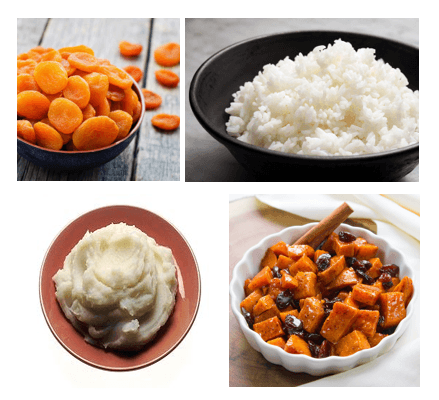
What is rice?
Mr. Jefferson was admitted to the hospital 3 days ago with partial SBO. He was placed on an NPO diet with NG tube inserted in ER and IV fluids infusing with hopes of the obstruction correcting itself. He complains of numbness and tingling around his mouth and in his extremities. Which labs below would you expect when the MD orders ABGs to be drawn:
A. pH 7.49, pO2 80, pCO2 33, HCO3 26
B. pH 7.51, pO2 62, pCO2 49, HCO3 20
C. pH 7.47, pO2 91, pCO2 35, HCO3 29
D. pH 7.33, pO2 73, pCO2 50, HCO3 33
What is C ? pH and Bicarb are high
Use of lithium for bipolar disorder can place the patient at risk for this sodium imbalance.
What is hyponatremia?
Vitamin D deficiency places patients at risk for this electrolyte imbalance.
What is hypocalcemia?
These fluids should be administered cautiously, as they place the patient at risk for cerebral edema.
What are hypotonic fluids?
A client with ESRD is being treated with peritoneal dialysis. He is notices dialysate that is clear in color and less than instilled, experiencing abdominal pain and nausea and noted a 2lb weight loss since last week.
The patient's wife knows she must report this symptom above to the physician immediately.
What is nausea and abdominal pain?
(signs of peritonitis)
A person with this condition should avoid these items below.
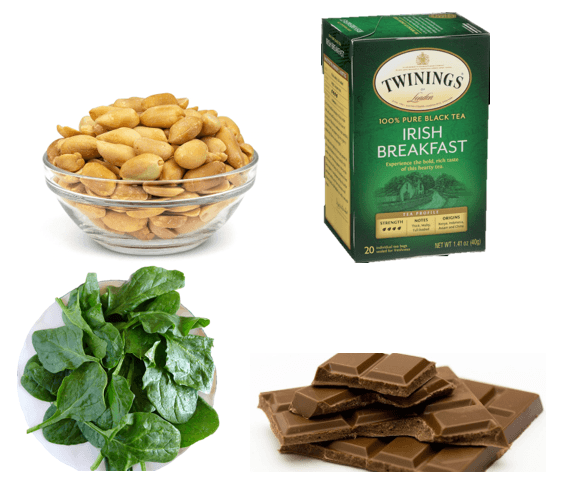

What is urolithiasis?
(Items to avoid on a low calcium oxalate diet)
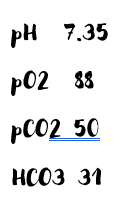
This medication is the antidote for magnesium toxicity.
What is calcium gluconate?
SIADH is associated with this abnormality in sodium.
What is hyponatremia?

Christmas was 2 days ago and Mr Rodriguez, your current dialysis patient presents with anasarca (generalized edema) and shortness of breath after eating a high sodium, high fat diet for the past few days. You weigh him and note he has had a 3.5kg weight gain! How many milliliters (mL) of fluid has he gained?
3500mL is the answer
1L = 1kg
3.5L = 3500mL
A nurse is caring for a 3-year-old child who has had 160 mL of urine output over the past 8 hr period. The child weighs 33 lb. The nurse should do this.
What is continue to monitor the patient?
(urine output for children should be at least 1mL/kg/hr, therefore this patient has normal output for his weight)
Grandma Myrtis has just prepared lunch for herself. Besides sodium, what cation are these foods rich in? (Canned salmon and dark green leafy collard greens)

What is calcium?