Hypertonic solutions
What is 3% NS, D5 1/2 NS, D10W
Shrinks cells
Bunches of bananas. AKA range
Possible S/S
What is bounding pulse and cough, s3 heart sounds, acute weight gain, HTN, increased RR and urine output, pulmonary congestion- crackles/sob/edema/ascites, JVD, SOB while laying down.
In these severe cases IV mag is given.
What is seizures due to preeclampsia or eclampsia, torsade’s de pointes, asthma, HTN, parenteral nutrition. Always verify pump settings- possible OD.
The amount of teeth crack head Bobby has. (range)
What is 2.7-4.5.
Calcium is known for creating this.
What is bones. S/S are opposite of prefix.
Lithium is given to these patients.
What is SIADH.
Magnesium
What is 1.8-2.6. CNS stimulant/depressant.
Digs water into cells- HIPPO
What is hypotonic solutions?
the 6 L's stands for
What is lethargy, leg cramps, limp muscles, low shallow RR, lethal cardiac dysrhythmias, lots of urine.
Interventions
What is fluid restriction.
What is diuretics: thiazide and loop.
This is a CNS stimulant.
What is true. Does the opposite of the prefix.
Prevention is KEY!! These are foods and supplements that can be taken.
What is dairy products, meats, beans, nuts, fish, poultry, whole grains, phosphate supplements, Vit D.
Pts who can't tolerate large amount of sodium are given this IM injection.
What is Calcitonin.
Normal range is 126-150
What is false. range is 135-145. ** remember you have 1.35-1.45 for your soda.
"Perfect teeth"
What is crackhead Bobby, phosphorus, 2.7-4.5.
0.9% NS, LR
What is Isotonic solutions
Does the same as the prefix except for.
What is HR and urine output
IV fluids.
What is hypertonic solutions.
What is 3% NS, D5 1/2 NS, or D10W.
Levels need to be checked every 2-3 days with what patients.
What is patients withdrawaling from alcohol.
Patient might need surgery or treatment for this.
What is removal of parathyroid tumor and treatment for cancer.
Most complained about S/S
What is bone pain and fractures- causes brittle bones. Kidney stones.
IV fluid solutions.
What is isotonic or hypertonic solutions. Hypertonic used for severe cases or pts with TBI.
What is potassium.
Hypotonic solutions
What is 1/2 NS or 0.45%
Some cardiac issues seen
What is ST segment depression, flat or inverted T waves (or both), elevated U wave, prolonged QRS intervals, heart block, ventricular dysrhythmias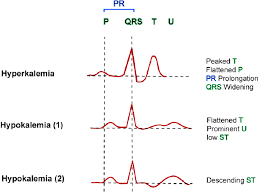
Third spacing.
What is ascites.
This test should always be done due to cardiac dysrhythmias.
What is ECG/EKG. Increases HR- v fib, svt, pvcs. PUT ON TELE!!
Med that activates calcium receptors.
Diet changes.
What is low calcium, adequate fiber and fluid intake.
Neurological changes.
What is AMS, seizure, coma. sodium think brain= brain changes.
Levels lower than 115 can show signs of increased intracranial pressure.
Normal levels 8.8-10.4. Think creating bones.
What is Calcium.
Both isotonic and hypotonic solutions
What is D5W?
This happens if you replace potassium TOO quickly
What is death. No more than 10 mEq/hr.
Imaging that will show pulmonary congestion. Labs that will be low.
What is chest X-ray and all labs will be low.
These happen due to hypocalcemia and/or hypokalemia.
What is increases neuromuscular contractility and irritability: trousseau and Chvostek sign, and muscle cramps, tremors, and seizures.
These patients are high risk for what issue.
What is fractures. Phosphorus think teeth- perfect teeth.
Teeter-totters with what other electrolyte.
What is calcium.
O in hypOnatremia stands for.
What is fluid Overload.
This affects changes in the brain.
What is Sodium, normal levels 135-145.