What is the most common cause of diastolic heart failure/ heart failure with preserved ejection fraction?
Hypertension
Diastolic HF as impaired ventricular relaxation due to chronic high blood pressures which causes heart muscle to thicken and become stiff
What is the drug of choice for diabetes management in pregnancy?
Insulin
Can use oral agents if patient not amenable to insulin, but they through the placenta as well and do not control as well-- Metformin, sulfonylureas
What are 2-3 distinguishing features between acute tension headaches and acute migraines?
Tension-type headaches typically present as bilateral, pressing or tightening pain of mild to moderate intensity, without nausea or vomiting.
Migraines often present as unilateral, pulsating pain of moderate to severe intensity, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, photophobia, or phonophobia.
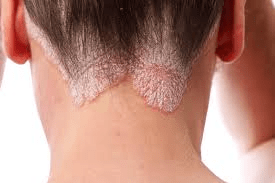
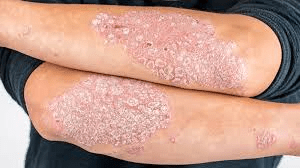
Plaque psoriasis of the scalp and arms
Flaky patches of skin which form scales. Can look pink of red and scales can be white or silvery.
On darker pigmented skin tones, can look purple or dark brown and scales may look grey.
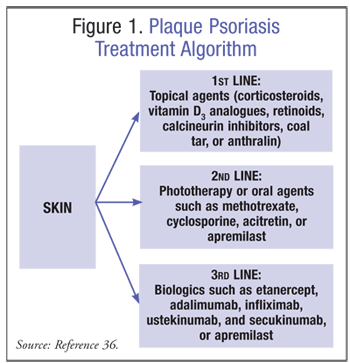
Treatments?
A 48-year-old woman reports fatigue and weight gain. PE shows dry skin and delayed relaxation of reflexes. What is the next step?
A. Free T4
B. TSH
C. ACTH
D. CBC
E. Cortisol
B. TSH
Hypothyroid symptoms:

10-20% of patients get a chronic cough using which anti-HTN medication?
Ace-inhibitor
What is 1 of 4 ways to diagnose type 2 diabetes mellitus?
What is FBG >/= 126
A1C >/= 6.5
OGTT 75 gram >200 over 2 hours
Random BG >200 with symptoms
Who to screen??
Screen all adults ≥35 or with risk factors (like obesity) using A1c.
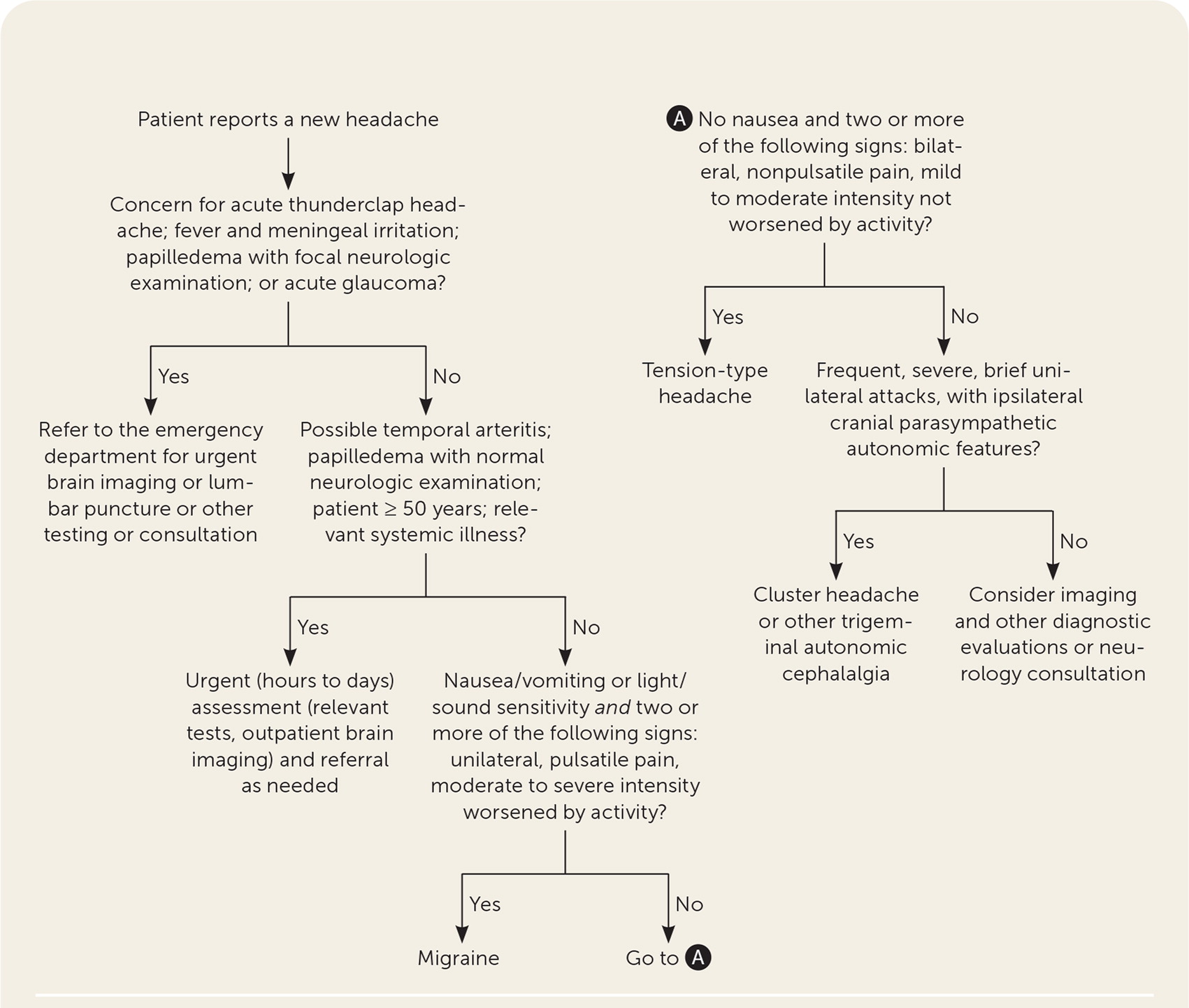
Name 3 "RED FLAG"s (SNNOOPPPP) to differentiate between benign and more concerning secondary headaches?
IE- what questions would you ask or look for in an exam to evaluate for red flags?
"THUNDERCLAP" Headache definition: Abrupt sudden severe headache that reaches MAX intensity within 1 minute of starting.

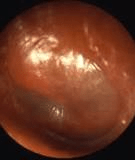
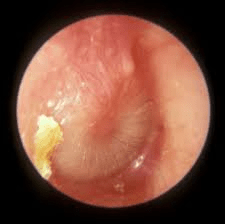
Otitis Media
Bulging erythematous ear drum, can see the purulence in the middle ear, loss of ear landmarks
Normal compared to OM:
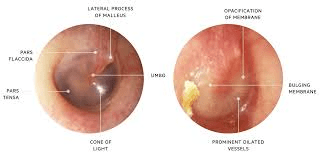
Treatment??
First line treatment for uncomplicated AOM in most children is oral amoxicillin.
A 1-year-old uncircumcised boy has fever, vomiting, and suprapubic tenderness. Urine culture is positive. What is the next step?
A. Oral antibiotics only
B. IV antibiotics and discharge
C. Renal ultrasound
D. VCUG immediately
E. Circumcision
First febrile UTI in a child under 5 → renal ultrasound to rule out anatomical anomalies.
Which three categories of anti-hypertension medications are recommended as first line treatment for hypertension according to JNC8?
CCB, Thiazide diuretic, and ACE-i

What are four preventative health maintenance care needs for diabetic patients?
Secondary prevention-related
Annual eye exam
annual foot exam
annual urine microalbumin
ACE-i/nephro protection
PCV20 (pneumococcal vaccine)
statin
What are common triggers and associated features of migraine headaches?
Common migraine triggers include stress, certain foods, hormonal changes, and lack of sleep. Associated features often encompass nausea, vomiting, photophobia, phonophobia, and sometimes an aura preceding the headache.
Double Jeopardy--How would you describe "aura" to a patient?
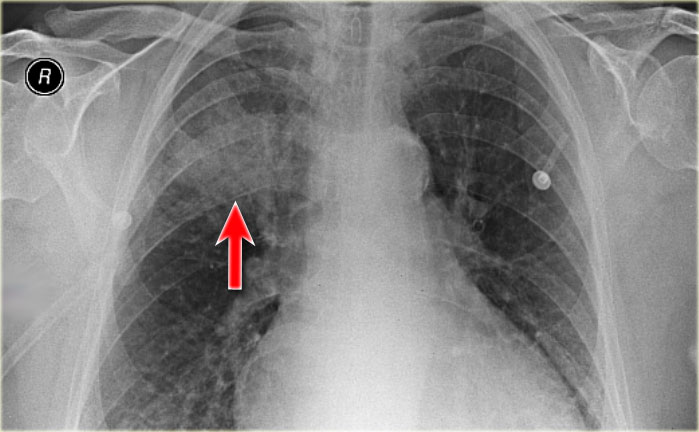
Lobar pneumonia
Arrow is pointing to an air-bronchogram which is harder to see but its the bronchi being more visible as the alveoli around the bronchi become more dense.
Other findings-
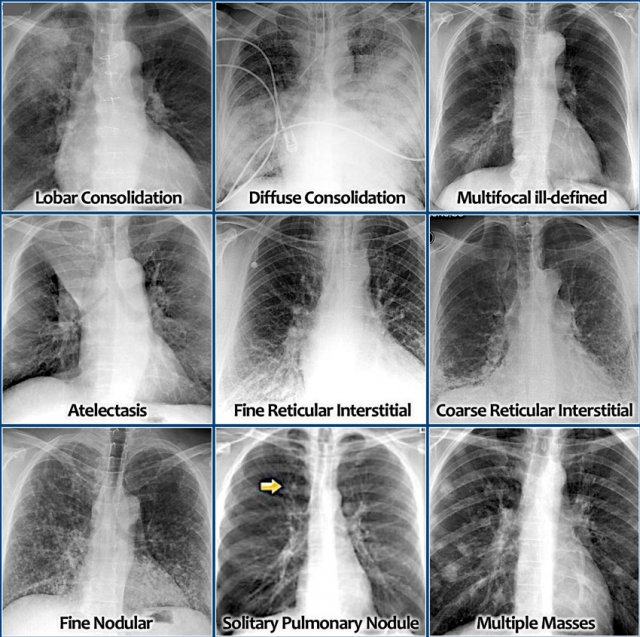
Great resource- https://radiologyassistant.nl/chest/chest-x-ray/lung-disease
Name 2 of the most common causes of bacterial meningitis in neonates (0-4 weeks)
Group B strep
E.coli
Listeria
What are 3 lab abnormalities associated with thiazide use?
HCTZ, Chlorthalidone use--
hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, hypercalcemia, hyperlipidemia, hyponatremia, hypokalemia
Which class of medication for DM2 can cause fluid retention, bladder cancer, heart failure, and increased fracture risk?
thiazolidinediones (TZD/ -glitazones)
Ex. Actos- Pioglitazone
A 27-year-old woman with migraines reports 4 disabling headaches per month. What is the next best step?
A. Start sumatriptan as needed
B. Prescribe opioids
C. Initiate beta-blocker prophylaxis
D. Recommend acetaminophen
E. Refer for neuroimaging
C. Initiate beta-blocker prophylaxis
More than 4 severe migraines/month OR 8+ headache days/month = prophylaxis indicated.

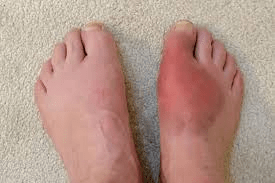
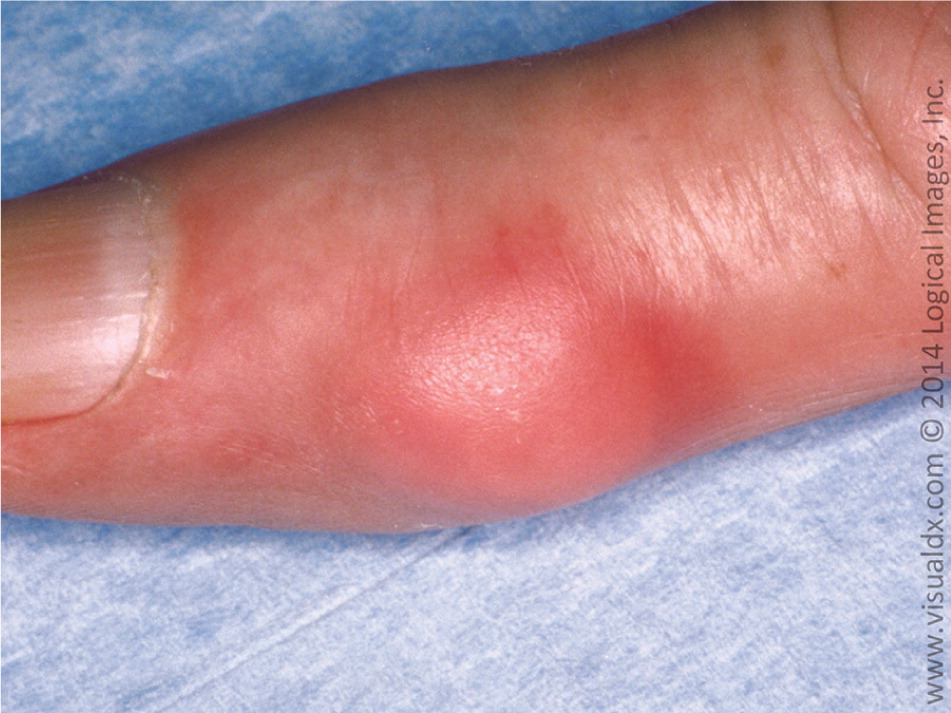
Gout - inflammatory arthritis
First line treatment?
Prevention meds?
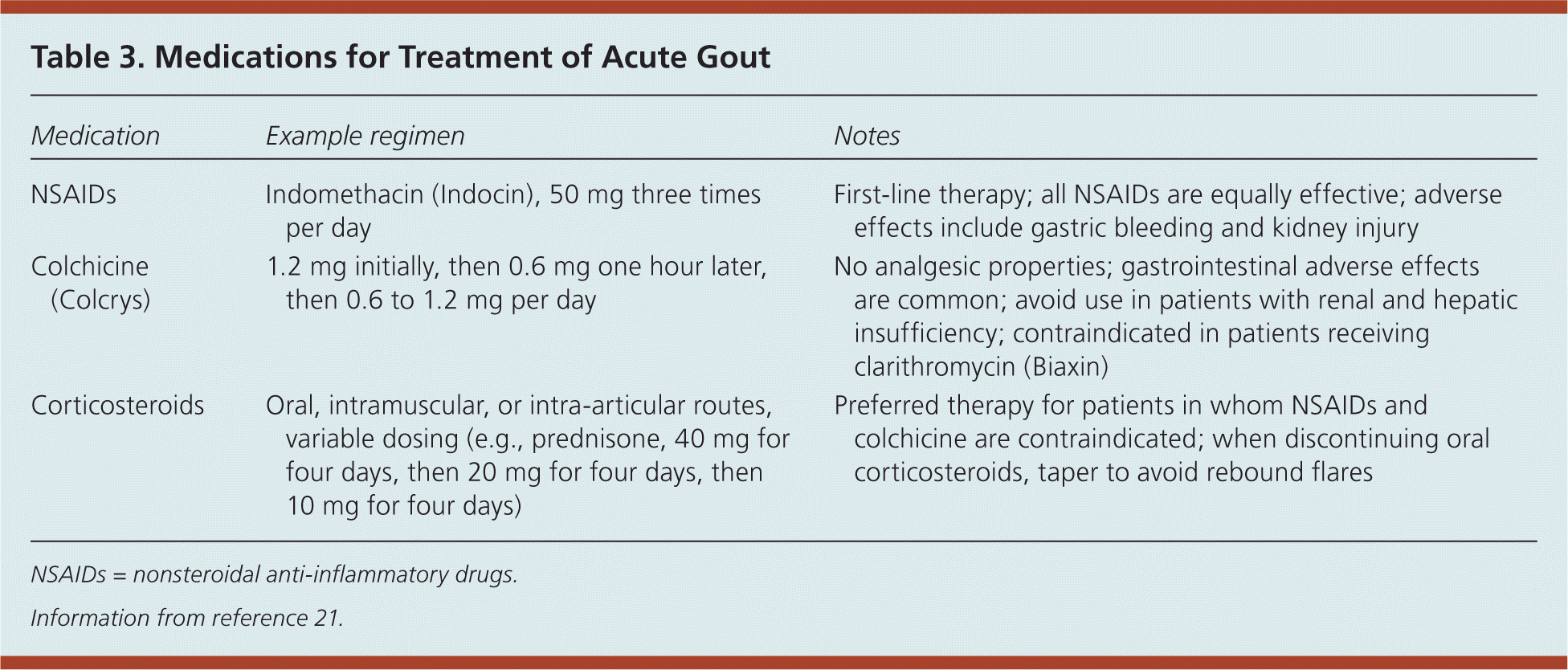
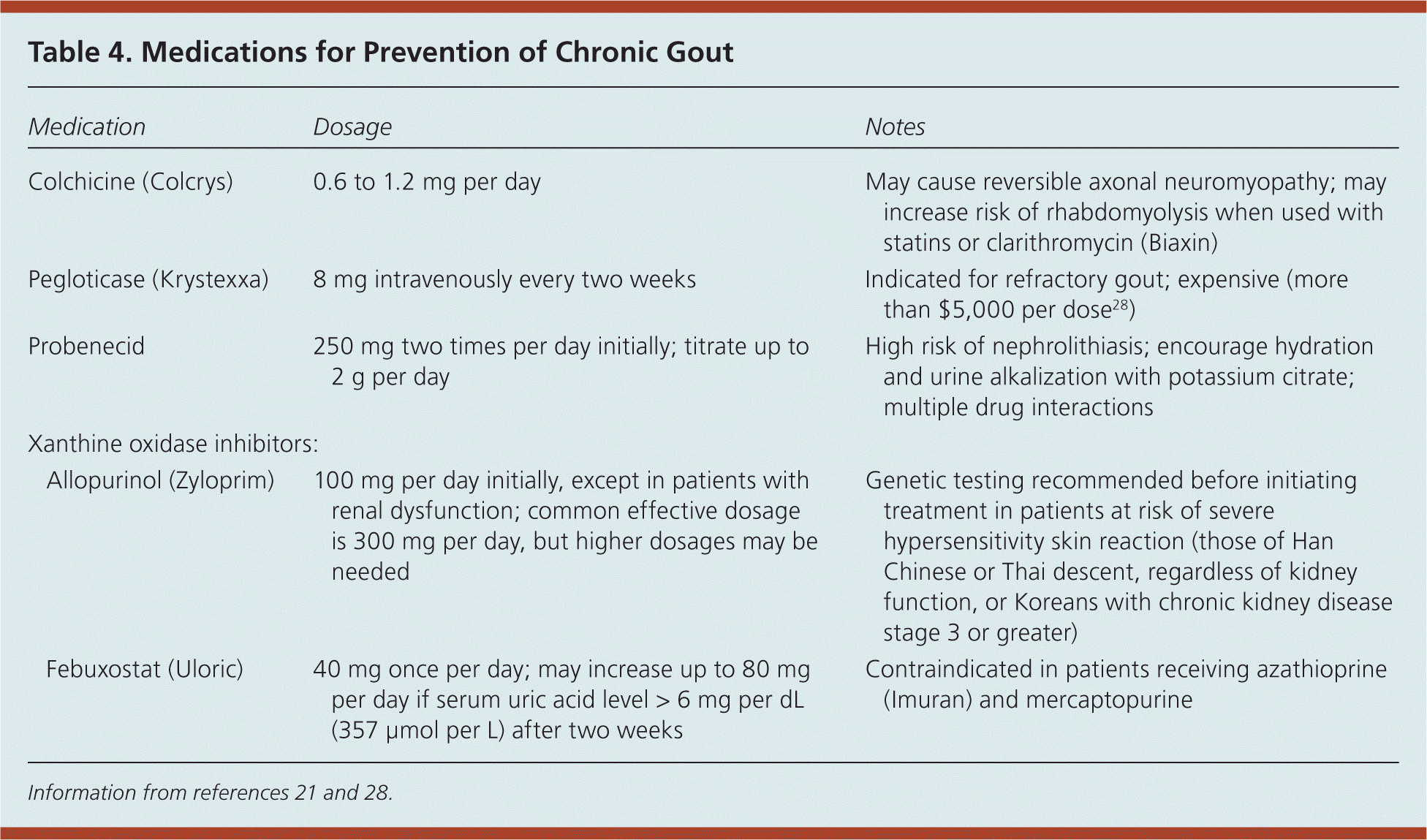
Need to answer both!-
At what CD4 count do you start prophylaxis for PCP/PJPneumonia? Which medicine can you use?
CD4<200
TMP-SMX (Bactrim), dapsone, or atovaquone
What does PJP look like clinically?

What other CD4 counts do you start prophylactic meds?

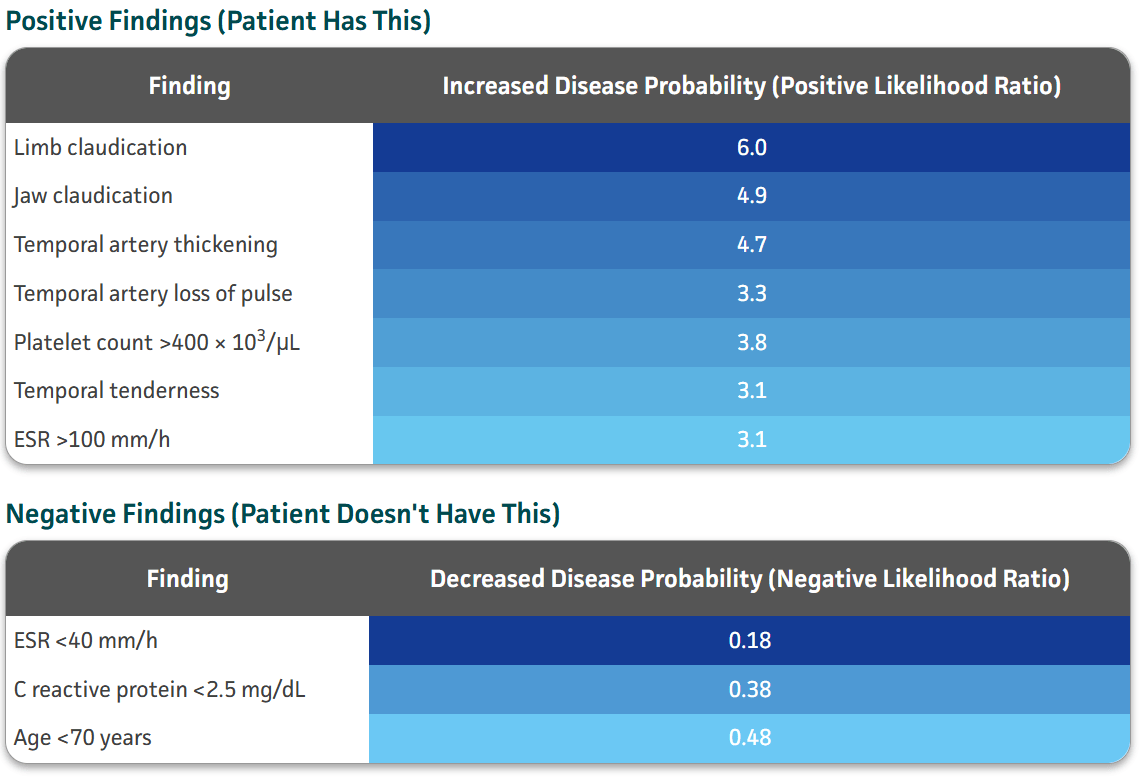
Name at least 3 features of giant cell arteritis (GCA).
In patients older than 50 years, giant cell arteritis must be considered for new or worsening HEADACHE.
The presence of FEVER, SCALP TENDERNESS overlying the temple, jaw claudication (i.e., pain or facial fatigue with CHEWING), or symptoms of polymyalgia rheumatica (i.e., pain, stiffness, decreased range of motion in shoulder muscles). VISION CHANGES.
These patients need an urgent laboratory evaluation because of the potential for ophthalmic and neurologic complications.
Labs include--> CRP, ESR, CBC, CMP
Can also refer to ED to help expedite workup and management. UCI has an ultrasound protocol to help diagnose it too, doesn't always need a temporal artery biopsy.