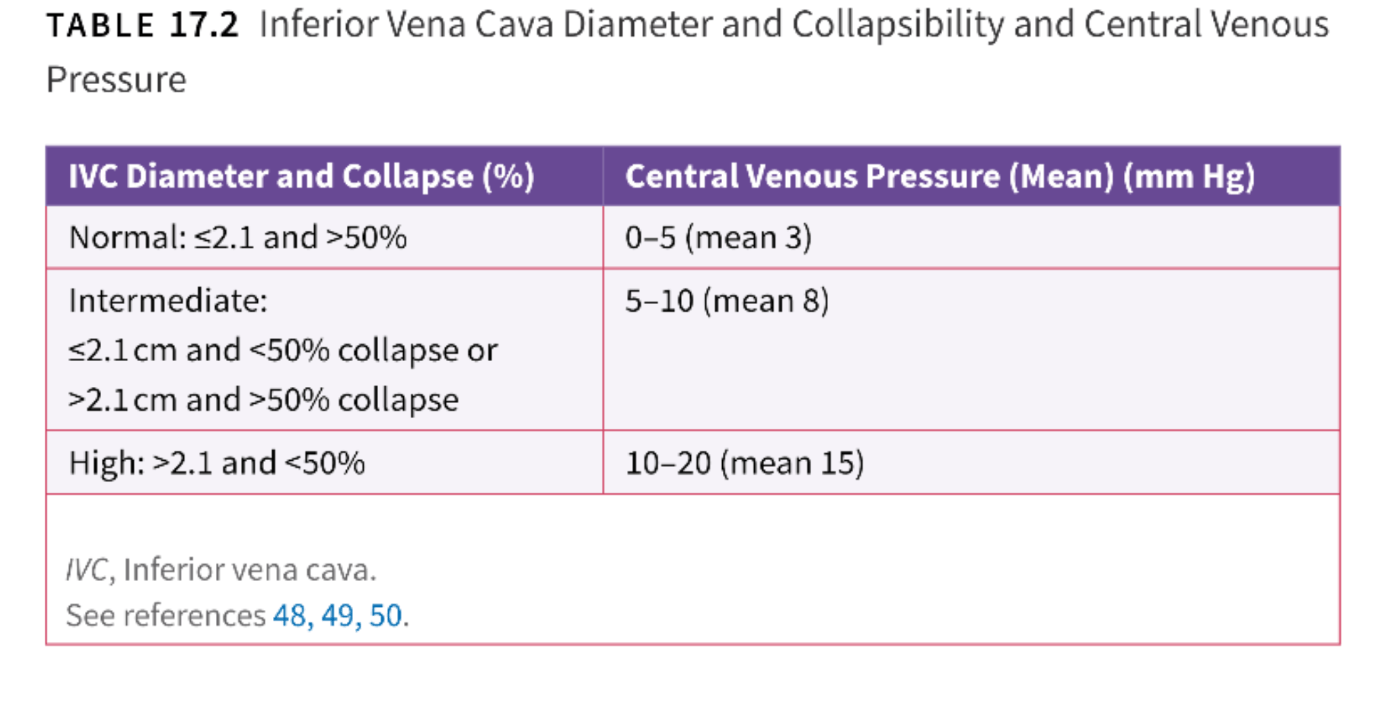
Above this diameter of the IVC on bedside cardiac exam correlates with CVP of 10-20
The following finding requires prompt recognition and action.

What is Large Right Sided Pneumothorax?
Microcytic anemia with high ferritin, normal transferrin, low iron.
What is anemia of chronic disease?

Elderly women with history of CAD and DM stabilized with IVFs after initially presenting in septic shock, 12 hours later now reporting acute onset abdominal pain and hematochezia.
What is ischemic colitis?
Suspected SAH in a patient with a negative NCTH, this procedure is gold standard for diagnosis
What is lumber puncture? (Bonus: Xanthochromia)
Highest diagnostic accuracy for Nephrolithiasis with this radiology protocol.
What is CT A/P without contrast?
A 28-year old Greek man with microcytic anemia and codocytes (ie target cells) on peripheral blood smear.
An anginal equivalent includes these reported symptoms.
What is exertional dyspnea, nausea, vomiting , diaphoresis, epigastric abdominal pain, or fatigue.
Carotid sinus massage is indicated for this use.
Indicated for the diagnostic evaluation of syncope and the diagnosis/acute treatment of stable SVTs (PSVT).
1) Auscultate for any ipsilateral carotid bruit and review history for recent TIA/CVA w/i 3mo
2) Apply firm and steady circular pressure (5 secs) to the right or left carotid sinus, but do not occlude the artery and do not apply pressure to both sinuses at the same time.
3) Restoration of sinus rhythm indicates that the procedure has been successful.


Reference: https://www-nejm-org.ucsf.idm.oclc.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMvcm1313338
Presenting with fever, cough, dyspnea, found to have a (Location) Pneumonia.
What is RLL PNA. (Bonus 200 if states Lingular).
In the setting anemia, an increase in the reticulocyte count (%) above this threshold can be considered a normal bone marrow response.
What is >2%.
1) Reticulocytes are immature RBCs produced in bone marrow that mature within 24-36hrs.
2) Normal Retic count is 1-2%
3) Dx for Reticulocytosis
- Repletion of B12/Iron/Folate
- Recovery from an episode of bleeding
- Administration of Epo
- Recovery from bone marrow insult
- Mild Thalassemia
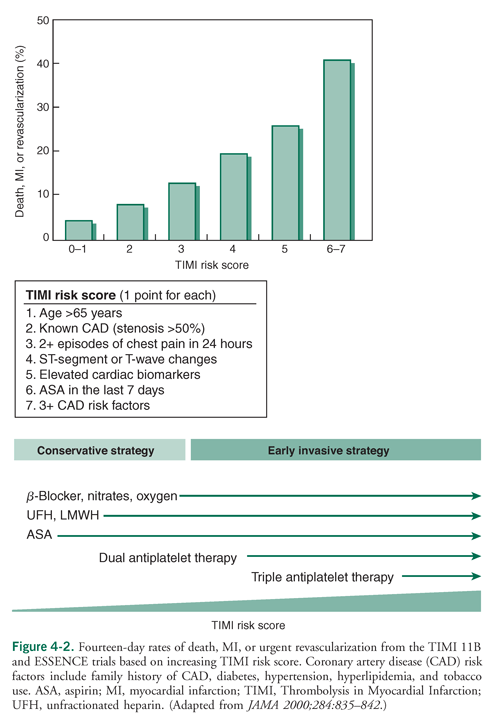
Risk scoring system used to prognosticate the patient's 14-day risk of death or non-fatal MI.
What is TIMI score?
Relative contraindication to do an LP below this threshold of platelets.
What is 50K Platelets?
The following finding requires prompt recognition.

What is pneumoperitoneum?
Large amount of free intraperitoneal gas beneath both hemidiaphragms (pneumoperitoneum).
Outside of Inflammatory conditions, this condition/disease can also lead to increased baseline ferritin.
What is CKD or liver disease.
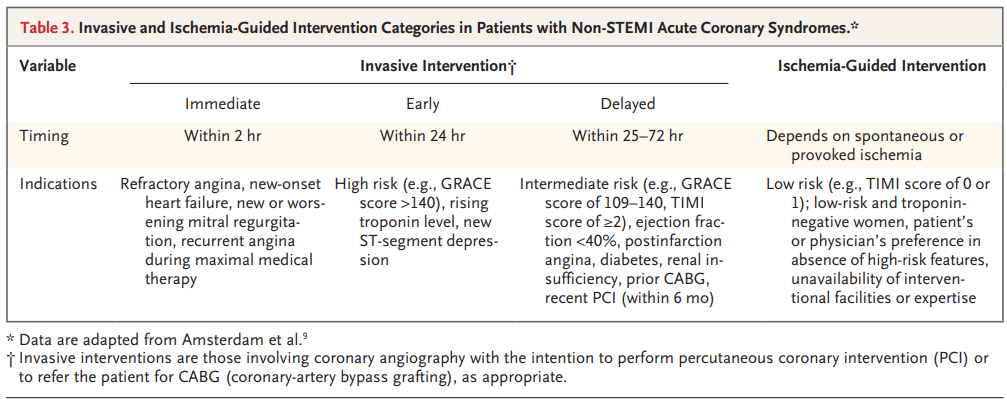
Indication(s) for immediate cardiac catheterization (within 2 hrs) for Non-STEMI ACS.
What is refractory angina, new-onset heart failure, new or worse MR, recurrent angina on maximal medical therapy.
 Resource: N Engl J Med 2017;376:2053-64. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1606915
Resource: N Engl J Med 2017;376:2053-64. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1606915
Daily Double: 30F smoker, admitted for subacute progressive dyspnea and orthopnea, found to have a large R pleural effusion. Thoracentesis was performed. Two hours after the procedure, she acutely dyspneic and hypoxic requiring significant oxygen support found to have a CXR concerning for this rare complication.

What is Rexpansion Pulmonary Edema

1) Reexpansion pulmonary edema occurs within 24 hours of the drainage procedure and is characterized by hypoxemia and alveolar infiltrates in the reexpanded lung and even rarely in the contralateral lung. Highest risk
source:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5461997/

What is Foreign Body?
A 23 year old woman admits to regularly tampering with whipped cream canisters to get high, presenting with this type class of anemia.
What is microcytic anemia (Megaloblastic Anemia)?
ACC/AHA recommends avoiding and/or discontinuing this medication during hospitalization for unstable angina or NSTEMI due to an increased risk of mortality and complications.
What is NSAIDs (except ASA)?