What organism is most frequently implicated in health care-associated infective endocarditis?
What is staph aureus
A 67-year-old woman presents to the clinic following a fainting episode. She was sitting in bed
reading when she suddenly felt dizzy and then lost consciousness. Her spouse reported that she
awoke after half a minute and appeared to be mentally alert but dizzy. This is the first time she has
ever experienced these symptoms. Vital signs
BP of 121/84 mm Hg and RR of 13/minute. Physical examination including EKG are unremarkable.
What finding on EKG is consistent with normal sinus rhythm
What is upright in
leads I, II, and usually aVF; inverted in aVR; upright, biphasic, or inverted in III and aVL; upright or
biphasic in V1 and V2; and upright in V3 through V6.
A 42-year-old man presents to the clinic with 6 months of intermittent chest pain. He feels the pain
tightening his chest, and it is most noticeable with moderate activity like mowing the lawn or going
for long walks. He has not had a heart attack before but is worried he may have one in the future. Vitals are within normal limits including EKG
What is the most approprite test to determine patients cardiac risk
W
Exercise stress EKG
A 54-year-old man presents to the clinic with dizziness. It is not associated with standing or lying
down, but he notices the dizziness is occasionally associated with chest pain and palpitations. He
has a history of myocardial infarction a few years prior. The patient’s neck veins are distended.
What is the medical term drop in systolic blood pressure during inhalation
What is pulsus paradoxus
What drug class is the first-line therapy in the ongoing management of patients
who are diagnosed with angina caused by exercise-induced ischemia?
What are beta blockers
What is the best test to evaluate for valvular endocarditis in a patient with bacteremia
What is a trans-esophageal echocardiogram
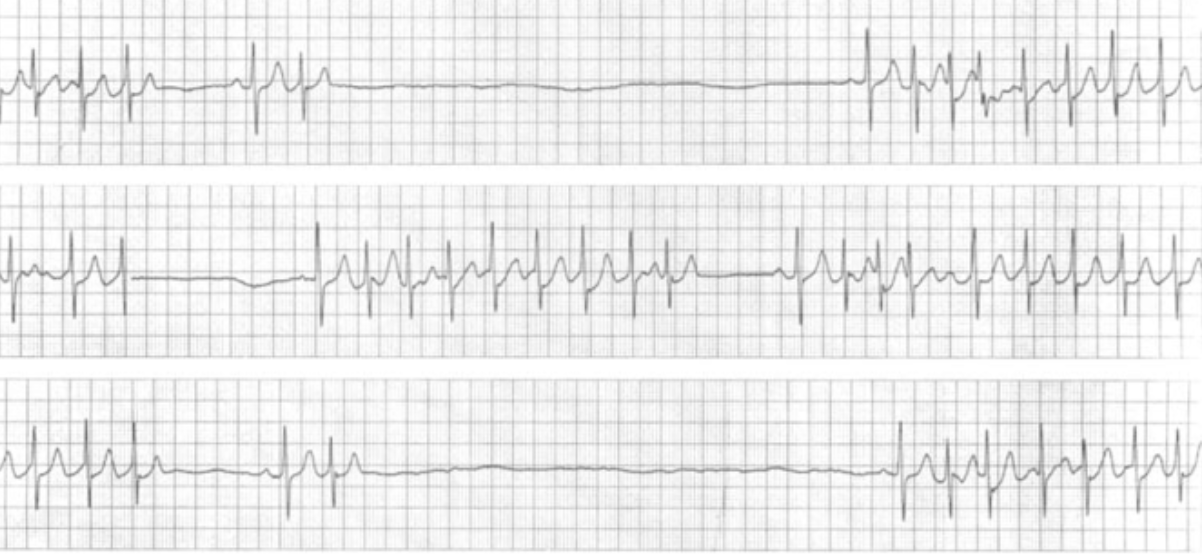
What is the name of this rhythm
Sick sinus syndrome what is sinus pause
A 34-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a chief complaint of pleuritic chest
pain. She has no shortness of breath. A chest X-ray reveals cardiomegaly but is otherwise normal.
An electrocardiogram reveals electrical alternans
What test is the best next step in diagnosing the patient
A 2-week-old female infant born at 39 weeks of gestation presents to the clinic for a well-infant visit.
She is feeding and growing well. Physical examination reveals a harsh, holosystolic murmur heard
best at the lower left sternal border.
What is the most likely diagnosis
VSD
What other valvular defects can produce the same murmur?
A 76-year-old man is evaluated in follow-up for a 4-month history of intermittent claudication, for which he completed an exercise rehabilitation program. He continues to experience left lower extremity discomfort with exertion, which has limited his walking ability.
What drug will likely help in improving the patients activity tolerance
What is Cilastazole
What is the mechanism of action of the drug given to patients with mechanical heart valves
what is inhibition of vitamin K epoxide reductase
 What is the name of the first line medication for treatment and dose
What is the name of the first line medication for treatment and dose
What is adenosine
What is 6mg
A 74-year-old man is evaluated for a 6-month history of progressive bilateral calf pain. The discomfort is worse with walking and improves quickly with rest. Medical history is significant for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He has a 50-pack-year history of smoking but quit 5 years ago. Medications are rosuvastatin, quinapril, and metoprolol.
What is the next best test in diagnosis of this patient
What is ABI or exercise ankle brachial index testing
A 60-year-old woman comes to the office for follow-up evaluation 1 year after having a drug-eluting stent placed in the mid left anterior descending coronary artery to treat non–ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome. She has been adherent to dual antiplatelet therapy for the past year without any bleeding events. The patient's only other medical problem is diabetes mellitus. Medications are metformin, liraglutide, atorvastatin, clopidogrel, and aspirin.
What is the most reasonable management of this patients anti-platelet therapy
what is continue ASA and clopidogrel
patient has DM and is high risk
A 43-year-old man is evaluated during a follow-up visit for heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction (ejection fraction, 45%) and type 2 diabetes mellitus. He is currently asymptomatic. Medications are metformin, valsartan-sacubitril, metoprolol, spironolactone, and atorvastatin.
HGBa1c 6.9
What medication should be added to the patients regimen
Empagliflozin (Jardiance)
A 74-year-old woman presents to the clinic with a two-month history of exertional dyspnea, chest
pressure, and presyncope. Physical examination reveals a paradoxically split S2 heart sound and a
late-peaking, harsh, systolic ejection murmur heard best over the right second intercostal space and
transmitted equally to the carotid arteries. Echocardiography reveals aortic stenosis.
What is the best treatment for this patient?
Aortic Valve replacement
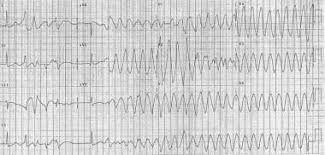
What is the rhythm featured in the EKG and the treatment
what is Torsades de pointes
what is magnesium sulfate
A 41-year-old man is evaluated for a 2-week history of daily palpitations that last minutes at a time and resolve spontaneously. The palpitations are not associated with any specific activity. He is otherwise healthy and takes no medications.
What is the best initial test for the patient
What is 12 lead EKG testing
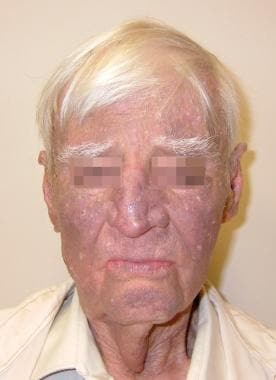
What additional test should be done to evaluate additional side effects of the drug that caused this side effect
What is PFT, TSH,
What are the drug classes that are the cornerstone of guideline directed medical therapy for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
What is renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, evidence-based β-blockers, mineralocorticoid inhibitors and sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2)
A 28-year-old woman is seen for pregnancy planning. She underwent mitral valve replacement with a mechanical prosthesis 4 years ago for congenital mitral valve stenosis. She is asymptomatic. Medications are warfarin, 4 mg/d, and low-dose aspirin. Her INR measurements have been within the therapeutic range for the past 18 months, including her most recent INR measurement of 3.0.
What is the recommendation for warfarin therapy during this pregnancy
What is continue warfarin
.jpg) What is the re-entrant pathway "accessory pathway" that leads to this EKG finding?
What is the re-entrant pathway "accessory pathway" that leads to this EKG finding?
what is the Bundle of kent
A 49-year-old woman is evaluated during a new patient visit. Physical exam shows a diminished S1, aortic ejection click shortly after the S1. Normal S2. There is a grade 2/6, high-pitched, decrescendo early diastolic murmur heard best at the left sternal border.
What is the best diagnostic test to evaluate the patient
What is a transthoracic echocardiogram
Marked limitation in activity due to symptoms, even during less-than-ordinary activity, e.g. walking short distances (20—100 m). Comfortable only at rest.
What is class III
A 35-year-old woman is evaluated in the emergency department for a 1-week history of fever and chest pain. The pain is sharp and midsternal, worse lying down, and improved leaning forward.
On physical examination, temperature is 38.5 °C (101.3 °F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg with pulsus paradoxus of 10 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 92/min. A three-phase friction rub is heard along the left sternal border and apex.
What is the most appropriate management of this patients condition
What is NSAID and colchicine