This protein-rich ingredient provides the emulsifying power that keeps butter droplets suspended in hollandaise sauce.
What are egg yolks?
These are the building block of proteins
amino acids
Citric acid causes this structural change in fish proteins during Poisson Cru, giving them a firm, opaque appearance.
What is denaturation?
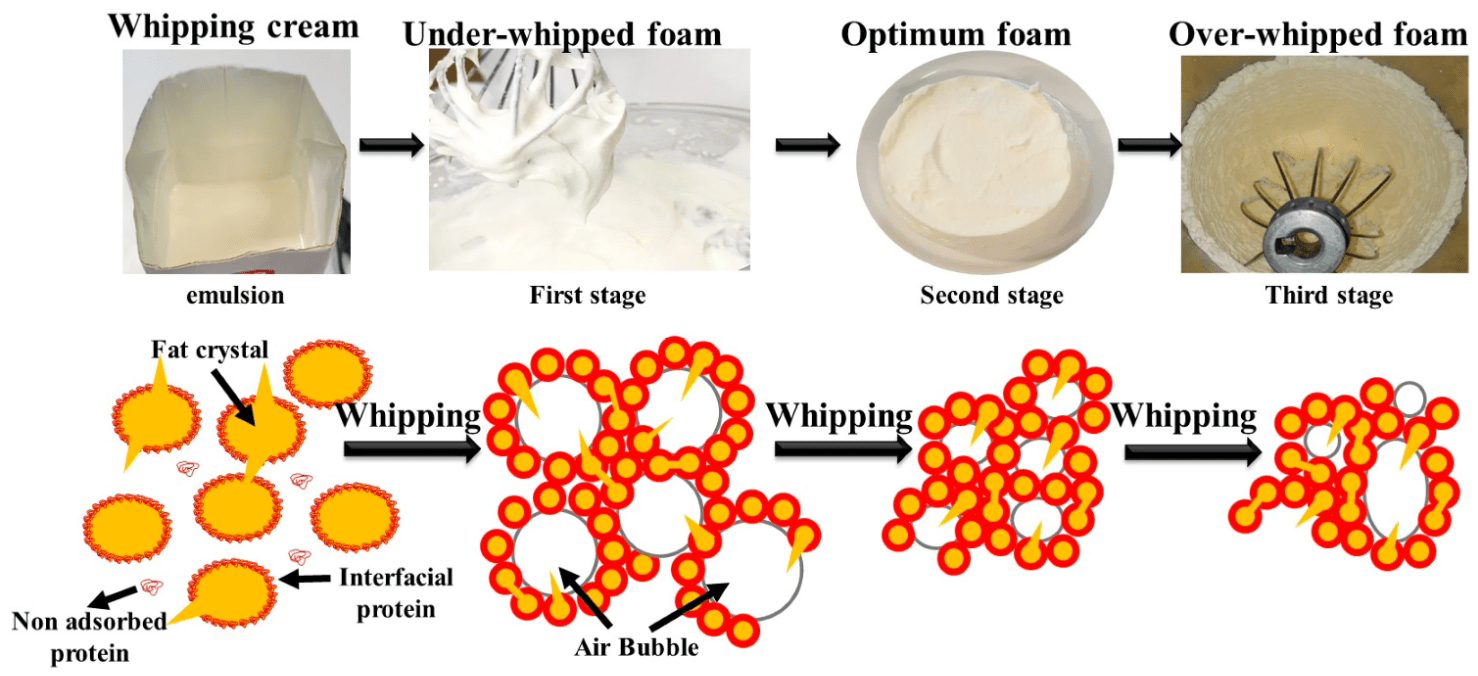
This type of leavening occurs in whipped cream, where air is physically beaten into fat and protein networks.
What is mechanical leavening?
Emulsions take two ____________ liquids and combine them.
Immiscible
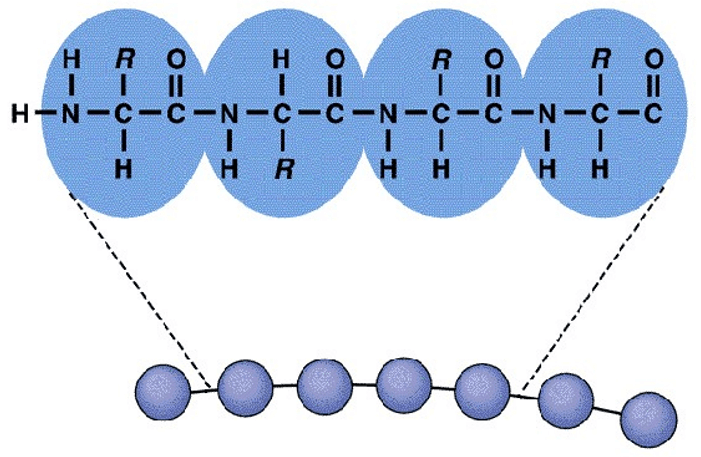 What level of protein structure is this?
What level of protein structure is this?
Primary
This type of mixture, like salt water, has evenly mixed parts you can't see
Solution
Leavening produces an increase in _____________ within the dough matrix.
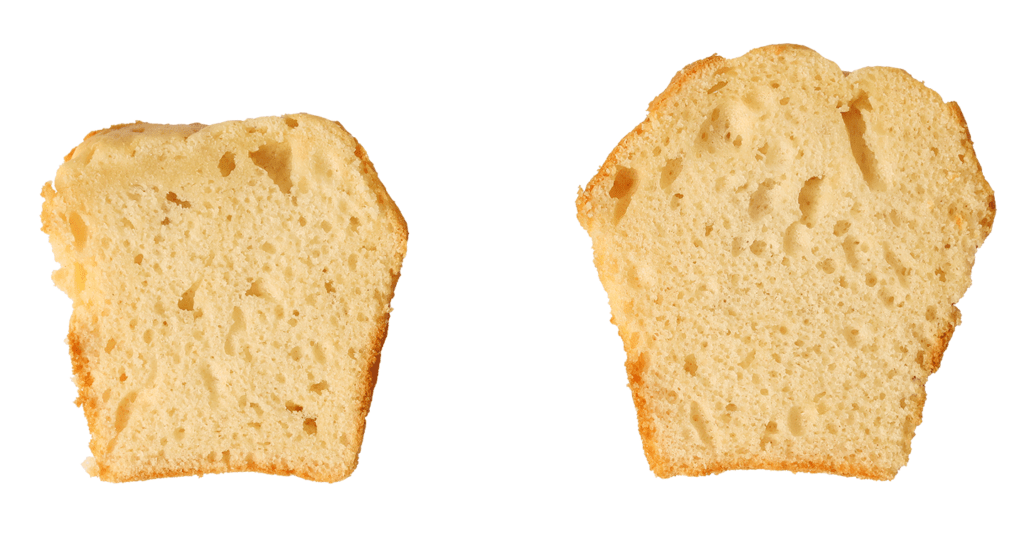
volume
This type of molecule allows for immiscible liquids to combine.
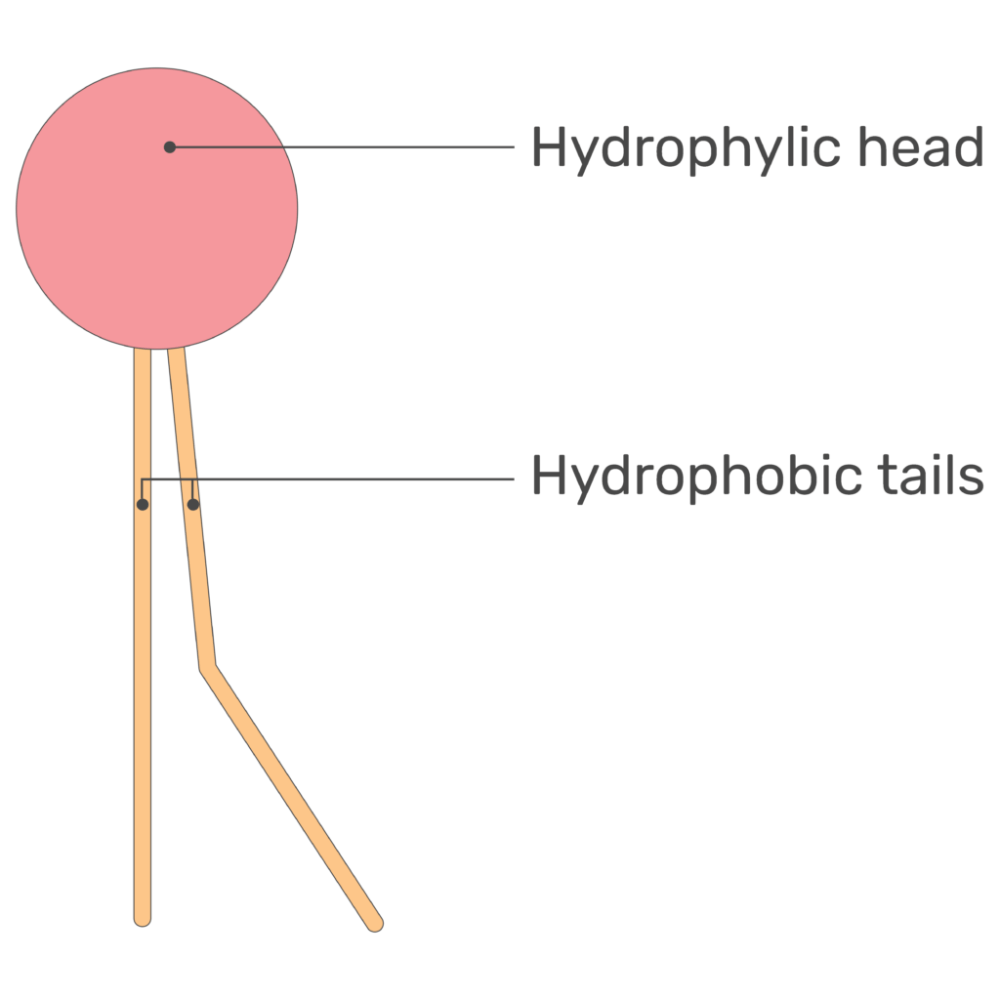
Phospholipid
This amino acid contains a sulfhydryl group that allows the formation of strong covalent crosslinks.
What is cysteine?
In the popping boba lab, these ions replace sodium on alginate chains and create the gel-like skin around the liquid.
What are calcium ions (Ca²⁺)?
Flour tortillas rise mainly through this type of leavening, caused by the expansion of water vapor.
What is steam leavening?
In meringue, this acidic ingredient helps stabilize egg white proteins and prevents them from tightening too much.
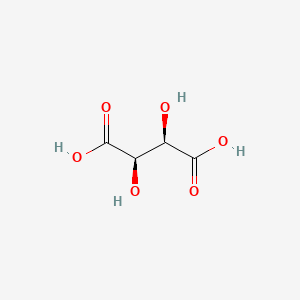
Tartaric Acid
Disulfide bonds act to do this through covalent bonds in the back bone of a protein.
In a solution, this term refers to the substance that gets dissolved.
What is the solute?
When flour and water are mixed, this process begins, allowing the gluten network to form.
What is hydration?
These molecules partially coalesce during whipping, helping stabilize air bubbles in whipped cream.
What is milk fat/lipids
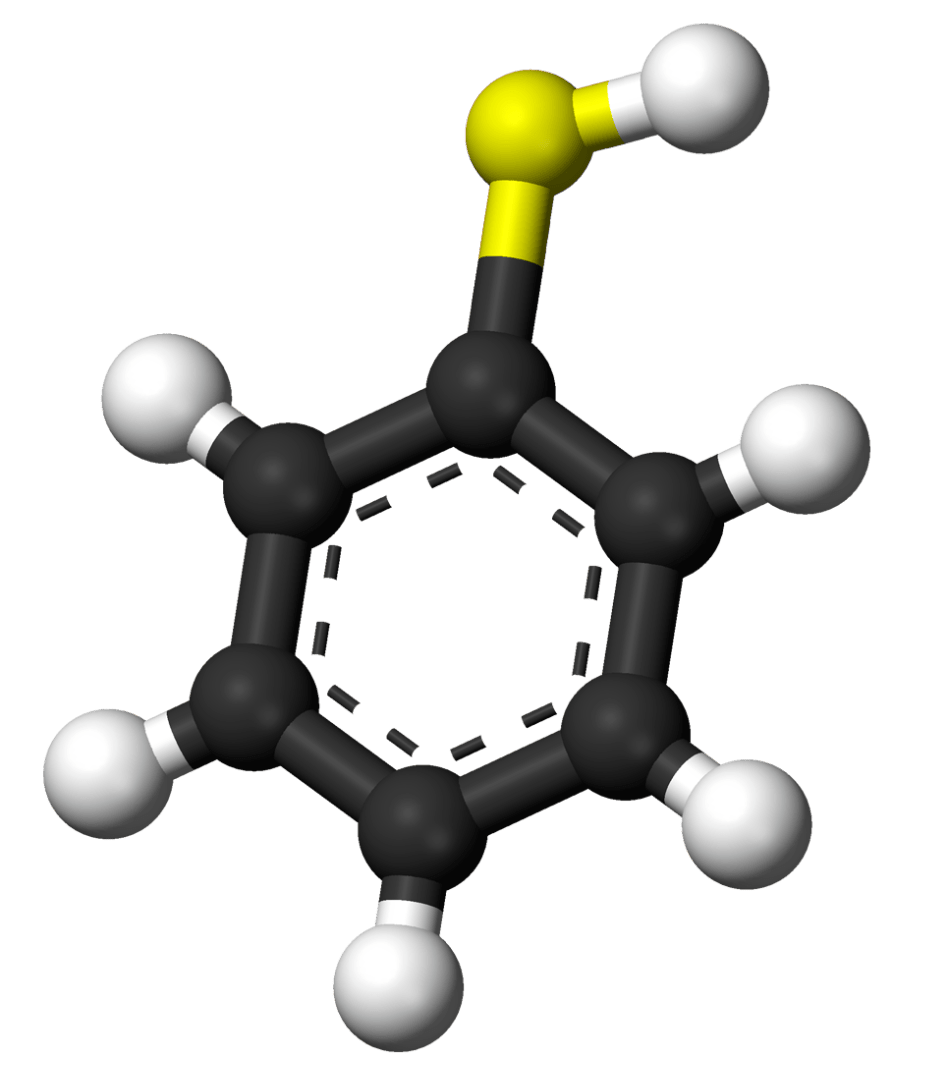
Also called a Thiol, this functional group is shown as the yellow and white section in the image.
What is sulfhydryl
This functional group (–COOH) is abundant in both citric acid and tartaric acid.
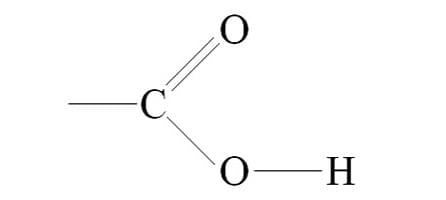
Carboxyl aka Carboxylic acid
When mixed with water, these two proteins form gluten, giving dough its characteristic chewiness.
Gliadin and Glutenin
This molecule from egg yolks works as an emulsifier in things like salad dressings and Hollandaise sauce.
In boiled eggs, this gas produced from sulfur reactions can create the gray-green ring around the yolk.
What is hydrogen sulfide (H₂S)
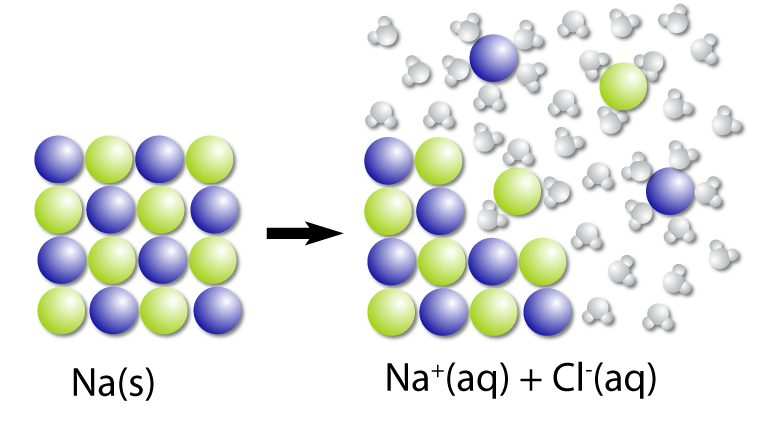 When an acid dissolves in water, this process produces ions and lowers pH.
When an acid dissolves in water, this process produces ions and lowers pH.
What is dissociation?
Two phrase answer!