Organisms that make their own energy and begin the food chain
Producers
Put these organisms in a correct food chain with arrows:
fox, plant, rabbit
Plant -> Rabbit -> Fox
Three different types of ecological pyramids
A simple diagram with arrows showing a single pathway of energy flow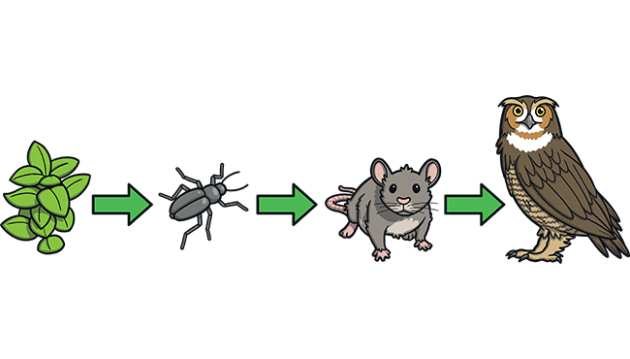
Organisms that gets energy from eating other organisms
Consumers
Put these organisms in a correct food chain with arrows:
coyote, elk, wolf, grass
Grass -> Elk -> Coyote -> Wolf
Only about _____ of the energy available at one tropic level is transferred to the organisms at the next tropic level
10%
A chart showing all the organisms living in the local ecosystem, with arrows drawn between the various organisms showing the direction or pathway of energy flow
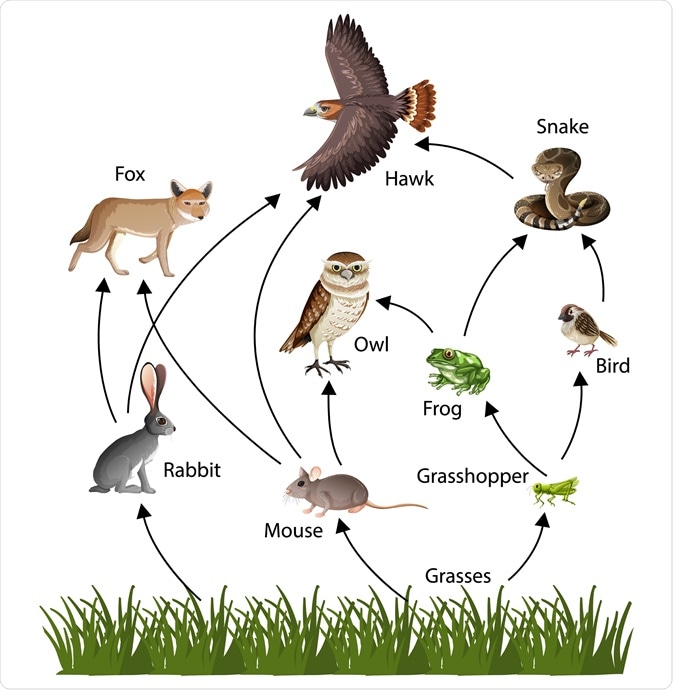
Food Web
Organisms that get their nutrition from dead organic matter
Decomposers
Put these organisms in a correct food chain with arrows:
mouse, grass, cricket, snake, hawk
Grass -> Cricket -> Mouse -> Snake -> Hawk
This is where the greatest amount of biomass is located in the biomass pyramid
The base of the pyramid
A diagram that shows the relative amounts of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web
Ecological pyramid
Animals at the top of the food web that feed off primary or secondary consumers
Tertiary or Top Consumers
After wolves were reintroduced to Yellowstone, explain what happened to the number of elk
Elk decreased because wolves were hunting/killing them
If you started with 2500 calories of leaves, how many calories would make it to the mouse?

25 calories
Any animal that eats organisms from more than one trophic level
Trophic Omnivore
Where producers get their energy from
The sun
After wolves were reintroduced to Yellowstone, explain what happened to the number of beavers
Beavers increased because beavers use willows for food and shelter (there were more willows because of less elk)
Only 10% of the energy available at each trophic level moves on to the next level. What happens to the other 90%?
It is lost as heat
A species that has a disproportionately large impact on its environment
Keystone Species