What is used initially to screen for HIT?
4T score - NPV 98-100% when < 4

Only send Anti-Platelet Factor 4 with or w/o Serotonin Release Assay if 4T is positive.
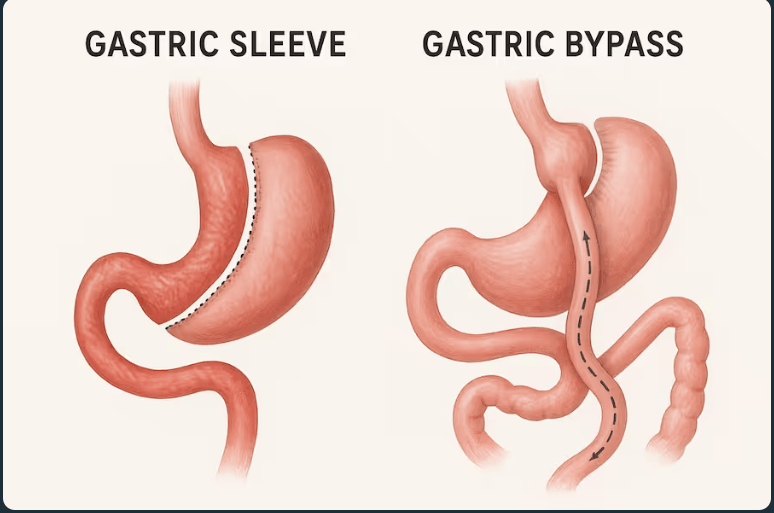
Compare Roux en Y with Sleeve regarding
Weight loss
Nutritional deficiencies
Roux en Y 70% excess weight loss vs. 60%, more sustained at 10 years
Roux en Y more nutritional deficiencies - B12, iron, calcium, vitamin D, B1, B9, trace minerals - MVI for all. Roux mainly concerned for vitamin D + B12
Glucose: 160 mg/dL
Sodium: 132 mmol/L
Potassium: 3.2 mmol/L
Bicarbonate: 15 mmol/L
Anion gap: 20
B-hydroxybutyrate: 4.5 mmol/L
pH: 7.28
Euglycemic DKA
2 Mg of Magnesium
$5.06
Which patient populations does the American Hematologic Society Guidelines suggest should be treated with indefinite anticoagulation after diagnosis of DVT?
Unprovoked DVT
Provoked DVT 2/2 chronic risk factor (Immobility, BMI > 30, HF, Chronic lung disease, GFR<60, Autoimmune disease)
Name 3 complications of Roux en Y that are rarely seen in Sleeve Gastrectomies
Roux en Y anastamotic leak, marginal ulcers, obstruction, internal hernia and dumping syndrome
SG - mainly causes and worsens GERD, overall much less complications
Na: 120
Serum Osm: 260
Urine Osm: 500
Urine Na 45
BUN/Cr: normal
SIADH (after rule out adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism)
Low serum Osm -> hypotonic hyponatremia
Urine Osm > 500 -> innappropriately concentrated urine
Urine Na > 20 -> ADH is on, pt is continuing to naturiese
Normal BUN/Cr -> suggests euvolemia (no hypovolemic AKI)
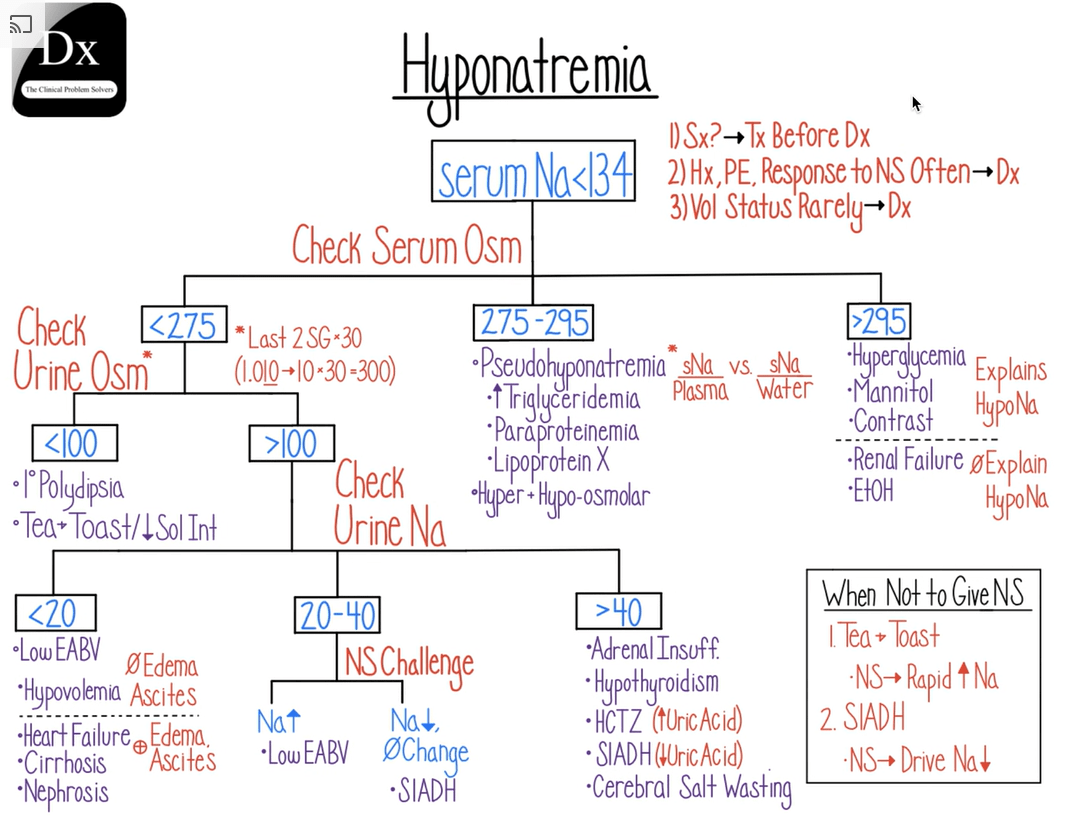
Serotonin Release Assay
$21.13
What does the American Society of Hematology recommend for antiplatelet/anti-coagulant management in patients with stable CVD on chronic aspirin who are diagnosed with a new DVT/PE?
Hold aspirin for the duration of therapeutic anticoagulation.
See AQUATIC trial
For patients with DVT/PE with stable cardiovascular disease, the ASH guidelines suggest suspending aspirin therapy when initiating anticoagulation. The combination of anticoagulation plus aspirin increases the risk of bleeding without clear evidence of benefit for patients with stable cardiovascular disease.
Draw the anatomy of a
Roux and Y
Sleeve
Sodium: 122 mmol/L
Potassium: 6.2 mmol/L
Chloride: 92 mmol/L
Bicarbonate: 16 mEq/L
Glucose: 58 mg/dL
BUN: 32 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.6 mg/dL
Calcium: 11.2 mg/dL
Eosinophils: 8%
TSH: Mildly elevated
Urine sodium: 48 mmol/L
Acute Adrenal Insufficiency (Addisonian Crisis)
Hypo - natremia, glycemia
Hyper - eosinophilia, calcemia, kalemia
NAGMA
Need both glucocorticoid (cortisol, give hydrocort) and mineralocorticoid replacement (aldosterone, give fludrocortisone)
Gastrointestinal Panel PCR
$479.30
What laboratory testing can help differentiate DIC from liver-induced coagulopathy, and what result might be expected?
Factor VIII levels, which are produced by endothelial cells and independent of liver function.
DIC: consumption of all factors - usually low
Liver-induced coagulopathy: endothelial cells increase production to offset coagulopathy - usually high
How did the 2022 guidelines from the metabolic and bariatric surgery change regarding candidates for surgery by BMI alone and by BMI with comorbid conditions?
BMI alone >40 changed to >35
BMI w/ metabolic disease >35 changed to >30
BMI thresholds in Asian population BMI > 27.5 with comorbities and > 30 for BMI alone
pH 7.50
PaCO2 22 mmHg
HCO3 − 10 mEq/L
AG - 20
Primary respiratory alkalosis + concomitant AGMA
pH -> primary alkalosis
Low CO2 -> Respiratory alkalosis
HCO3 - much lower than compensation for either chronic (4-5 lower HCO3 per 10 PCO2) or acute (2 lower HCO3 per 10 PCO2), thus it cannot be compensatory
Classic presentation for aspirin toxicity, though can be seen in any combination of primary resp alk + AGMA
TTE w/ Dopplar Complete
$630.55
Which patient populations do the American Hematologic Society Guidelines suggest should not undergo testing for thrombophilia conditions after a new diagnosis of venous thromboembolism at a usual site (2)?
Patients with venous thromboembolism (VTE) at a usual site (lower extremity DVT or PE) when the event is provoked by major transient risk factors (surgery, trauma, or prolonged immobility).
Unprovoked VTE after completion of primary treatment, as it does not change management or outcomes.
Conditional and based on very low certainty evidence.
Consider testing in select scenarios (e.g. unusual site thrombosis, strong family history, age < 45, pregnancy)
What infection should you consider screening gastric bypass candidates as a part of their evaluation?
H pylori
If positive, should undergo eradication with confirmatory testing prior to surgery.
increases risk of marginal ulcer formation post-operatively.
Calcium 13.5
PTH low
Phosphate high
Vit D - normal
1,25(OH)2 Vit D - Elevated
Granulomatous disease (sarcoidosis, TB etc) or calcitriol-producing lymphoma
Independent of PTH, driven by excess activated vitamin D
MRI Brain With and Without Contrast
$277.98