What happens when you push an object that isn’t moving?
It starts to move
What is the formula AND definition for velocity?
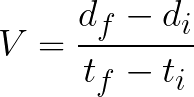
What is friction?
A force that works in the opposite direction of motion
What is required to change an object’s velocity?
A force
A Physical Education (gym) class is playing a game of soccer. During the game, the ball experiences a force of 0 newtons. Which statement explains what is most likely happening with the ball?
It is sitting still.
It is bouncing off someone’s knee.
It has been kicked across the field.
It has been tossed straight up into the air.
1
True or False: Pulling on an object that is already moving can only make it speed up
False, it could also slow it down, stop it, or change direction
A runner is 0 m at 0 seconds and 30 m at 6 seconds. What is the velocity?
5 m/s
Why does a soccer ball eventually stop rolling on grass?
Friction slows it down
If you push a ball backwards while it’s rolling forward, what happens?
Depending on the amount of force it will either stop moving or start moving backwards
Sandra pushed a wooden block and it slid across the floor. The wooden block gradually slowed down and stopped after moving 10 meters.
Why did the block stop moving?
The floor exerted a force that is opposite to the direction of the block’s motion.
The block ran out of force.
The floor absorbs force from the block.
All objects stop moving because their natural state is to be still.
1
Two students push a box in the same direction. What happens to the strength of the force?
It adds up to make a stronger force
A car is 20 m at 2 seconds and 120 m at 12 seconds. What is the velocity?
10 m/s
Which surface has more friction: ice or carpet?
Carpet
Why does a train take longer to stop than a bike?
The train has more mass, so it needs more force to slow it down
The student blows up the balloon, sets the cart on the tabletop, and lets go. Air flows out of the balloon and through the straw, but the cart does not move. Which of these explains why the car does not move?
The force of gravity exceeds the other forces acting on the cart.
The forces pushing the cart forward were greater than the force of mass and gravity.
The force on the cart from the air in the balloon and the friction on the tires is balanced.
The cart experiences an unbalanced force from the air in the balloon and the friction on the tires.
3
Two students push a box with equal force in opposite directions. What happens?
The forces cancel and the box doesn’t move
Explain what happens to velocity if you apply a stronger force.
The object’s velocity changes more quickly – it speeds up or slows down more depending on the direction of the force
How does friction affect velocity?
It decreases velocity – slows an object down
A toy car speeds up when pushed harder. Which learning target does this show?
Stronger force causes greater change in velocity
A rocket sled is 500 m at 10 s and 1400 m at 22 s. What is the velocity?
75 m/s
Give one real-life example of a pull starting motion and one of a push stopping motion.
Examples: pulling a chair to start moving it; pullings someone to prevent them from falling
A skateboarder is 10 m at 3 seconds and 58 m at 11 seconds. What is the velocity?
6 m/s
A hockey puck on ice slides farther than on grass. Why?
Ice has less friction than grass
Explain why a basketball speeds up going downhill without anyone pushing it.
Gravity is applying a force in the direction of motion
A soccer ball is rolling at a constant velocity when a player kicks it harder in the same direction. Explain what happens to the ball’s velocity and why.
The velocity increases because a stronger force is applied in the same direction of motion.