The strength of a force is measured in __________?
Newtons (N)
What is "force"?
A push or a pull on an object.
What is "acceleration"?
The rate of change in an object's velocity in m/s2
True or False: Forces are measured in meters/second (m/s).
False!
Forces are measured in Newtons (N).
Velocity is measured in meters/second.
The area of a magnetic force around a magnet is called the magnetic ____________.
Magnetic field
The type of force that occurs through direct contact between two or more objects.
Contact force
The momentum of an object depends on the object's ____________ and _____________.
Mass & Velocity
Force = ________ x _________
Force = mass x acceleration
True or False: When you kick a soccer ball, the soccer ball is "kicking" you back with equal force in the opposite direction.
True!
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
The reason you don't move and the ball does is due to your heavier mass.
Provide a factor or characteristic that can affect the strength of a magnet's force.
-Size
-Material or type
-Distance
The type of force that is applied without objects touching.
Non-contact forces
How does friction affect an object’s momentum?
Friction is a force that works in the opposite direction of a moving object.
Friction slows objects down by working against their motion.

Which direction would the 0.2 kg object move?
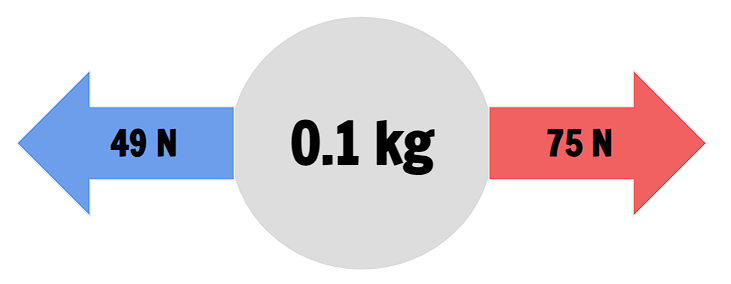
To the right →
True or False: Forces ALWAYS come in pairs.
True!
For every action (1), there is an equal and opposite reaction (2).
Will these two magnets attract or repel each other?

Attracted
Two or more forces that are unequal in strength. These forces don’t cancel out and result in changes in motion.
Unbalanced forces
Analyze the data table. Which object had the MOST momentum according to the data results?
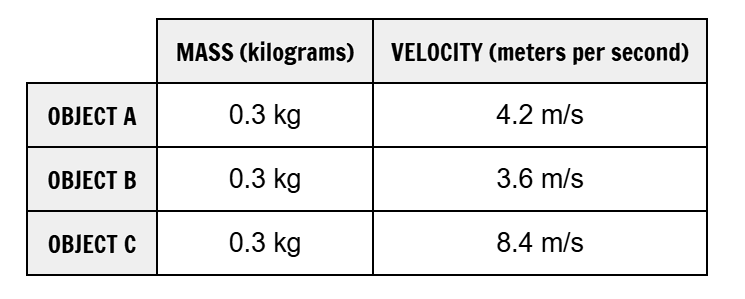
Object C
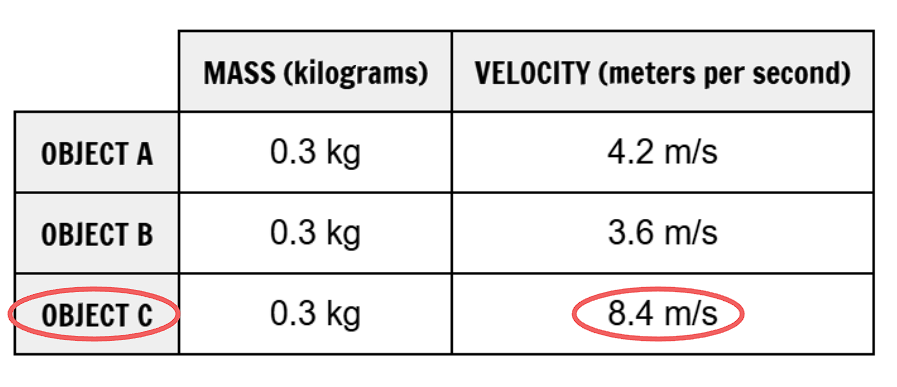
Which direction would the 0.2 kg object move?
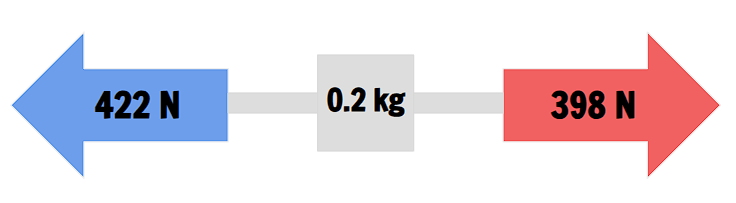
To the left ←
Which of the following is NOT an example of Newton's 3rd Law?
A. a person punches a punching bag, and the punching bag pushes back on their fist with equal force
B. a tree flies off of the top of a car that stopped suddenly
C. a kid jumps off the ground, and the ground pushes back on their feet with equal force
B. a tree flies off of the top of a car that stopped suddenly
This is an example of Newton's 1st Law (inertia)
Will these two magnets attract or repel each other?

Repel
Two or more forces that are equal in strength and opposite in direction. These forces cancel each other out and do not cause a change in motion.
Balanced forces
Which of the following examples describe Newton's 1st Law?
A. a ball gains speed as it rolls down a hill
B. a crash test dummy flies through the windshield when the car hits a wall
C. a rocket pushes on the ground, and the ground pushes back on the rocket
B. a crash test dummy flies through the windshield when the car hits a wall
Analyze the data table. Both objects were pushed with the same amount of force. What do the data results show?
A. Objects with heavier masses require less force to accelerate
B. Objects with heavier masses require more force to accelerate
C. Objects with heavier masses do not accelerate
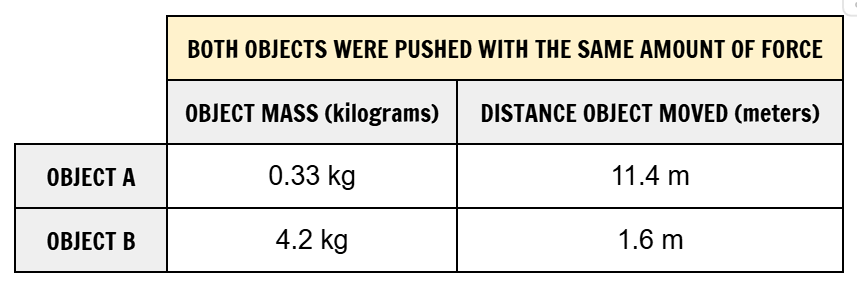
B. Objects with heavier masses require more force to accelerate
Identify the reaction to this action force:
Action: a person punches a punching bag.
What is the equal and opposite reaction?
The punching bag pushes back on the person in the opposite direction with equal force
How do atoms create magnetic force?
Electric charges are caused by the movement of electrons between atoms.
When many electrons move/spin in the same direction, they create a magnetic field.